2.3: Chemical Bonding & Electronegativity
advertisement

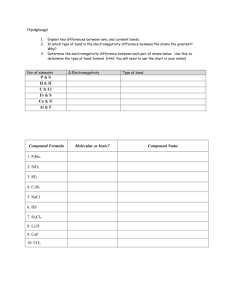
2.3: Chemical Bonding & Electronegativity Bonding & Electronegativity Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond ΔEN means difference in electronegativity This is a number that tells us what type of bond will form Will range from 0 – 3.3 ΔEN: 3.3 Ionic 1.7 0.5 Polar covalent 0 non-polar covalent Bonding & Electronegativity Ex: Calculate ΔEN and determine type of bonding for a) KF b) O2 c) HCl Bonding & Electronegativity Ex: Calculate ΔEN and determine type of bonding for a) KF KF: 4.0 – 0.8 = 3.2 = ionic b) O2 c) HCl Bonding & Electronegativity Ex: Calculate ΔEN and determine type of bonding for a) KF KF: 4.0 – 0.8 = 3.2 = ionic b) O2 O2: 3.5 – 3.5 = 0 = non-polar covalent c) HCl Bonding & Electronegativity Ex: Calculate ΔEN and determine type of bonding for a) KF KF: 4.0 – 0.8 = 3.2 = ionic b) O2 O2: 3.5 – 3.5 = 0 = non-polar covalent c) HCl HCl: 3.0 – 2.1 = 0.9 = polar covalent Bonding & Electronegativity Non-Polar Covalent Bond Electrons are shared equally Usually between atoms of the same element (ie: Cl2) Bonding and Electronegativity Polar Covalent Bond Electrons are NOT shared equally Usually between atoms of the DIFFERENT elements (ie: HCl) Results in a charge separation called a DIPOLE The shared electron pair spends the most time around the more electronegative atom (in this case, Cl – the electron pair spends more time closer to the Cl than the H) The more EN atom has a partial negative charge (δ-) The less EN atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) Polarity and Shape of Molecule Example: H2O, CO2, NH3, CH4 Read pages 70 – 73 and answer #1-8.