SCH 4U1 BONDING AND THE OCTET RULE 1)
advertisement

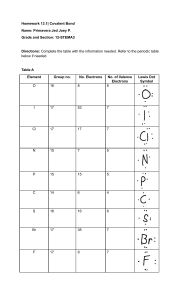
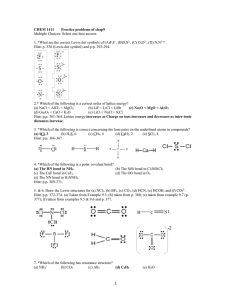
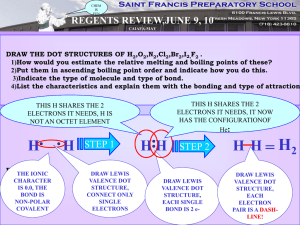
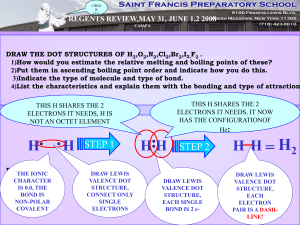
SCH 4U1 BONDING AND THE OCTET RULE 1) Properties of compounds (eg. BP, solubility, hardness, etc.) are greatly influenced by the polarity of the bond. Eg. - Br2 is a covalent bond and is non-polar. (There are no +/- poles.) - O-H is a polar covalent bond and is described as being a polar molecule. There is an unequal distribution of electron density in a neutral water molecule. - Na+ Cl- is an ionic bond and is very polar. (There is a distinct positive pole and a distinct negative pole) 2) Bonding is a continuum so the difference in electronegativity will influence the type of bond that will occur. electronegativity difference 0 1 2 3 |__________|__________|__________|__ non-polar<----- polar ---> <----- ionic -----> covalent 3) Like dissolves like. A non-polar substance will dissolve in a non-polar substance - rubber and graphite from a pencil. A polar substance will dissolve in a polar substance - table salt in water. 4) Bonding will occur because of stability and this is governed by the octet rule. Regardless whether an electron is being transferred (ionic BaCl2) or shared (covalent - NH3) a given atom wants to be surrounded by eight electrons (or have a complete shell). 5) Multiple bonding may occur in order to satisfy this requirement - Eg. CO2 or C2H2 have double and triple bonds respectively.