Grade 10 Chemistry
advertisement

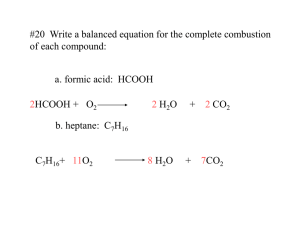
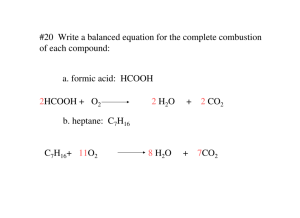
Grade 10 Chemistry 5.9: Polyatomic Ions Polyatomic Ions Ex: These behave exactly like ______________ to produce a ____________ with an overall charge of _________ Polyatomic Ion Formula Ionic Charge Naming Polyatomic Compounds Rules Examples CaCO3 1. Write the name of the _________ 2. Write the name of the _________ › All polyatomic ions are _______ EXCEPT ____________________ Na3PO4 NH4OH Writing Formulas for Polyatomic Compounds Rules Examples 1. Write the SYMBOL/FORMULA for each ion Potassium sulfate › Cation (+ ion) first, then anion (- ion) 2. Put any polyatomic ions in brackets Calcium hydroxide 3. Write the ionic CHARGES above each ion 4. CRISS-CROSS the numbers to make subscripts Aluminum phosphate › DO NOT write the “+” or “-“ or the number 1 › The subscript goes OUTSIDE the brackets. Iron (II) sulfate › You CANNOT change what is inside the brackets!!! Lead (IV) nitrate 5. If necessary, REDUCE the subscripts to the lowest common denominator. 6.1: Describing Chemical Reactions Chemical Reaction A chemical reaction occurs when Examples: Reactants vs. Products Reactants Products Describing Chemical Reactions Chemists use ______________________ to describe chemical reactions. There are 2 different kinds of equations: 1. ___________ Equations: use Example: 2. ____________________Equations: use Example: Symbols Used The _____________ separates reactants and products is read as ____________________________________________________ “____” is used to separate multiple products and/or reactants Letter in brackets after the formula tells the ________ of the substance (s) = (l) = (g) = (aq) = 6.3 The Law of Conservation of Mass The Law of Conservation of Mass Examples: → Reactant A + Reactant B 45 g 25 g 50 g calcium + hydrochloric acid 16 g Product C + Product D → _____ g calcium chloride + hydrogen gas _____ g 28 g 33 g 6.4: Balancing Chemical Equations In chemical reactions, atoms are not “magically” lost or gained, they are just ________________ This means that, in a chemical reaction, the number of atoms reacted ____________________ the number of atoms that are produced In a chemical equation, it’s not always just _________________ of each substance that reacts or is formed. We need to balance chemical equations to ___________________ the NUMBER of ________ on ______________ of a reaction Example: Word Equation Iron + oxygen gas → iron (II) oxide Skeleton Equation (unbalanced) Balanced Chemical Equation How to balance: Step 1: Count the number of each type of element in the reactants and products (REP table) Step 2: Add ____________________ in front of the substances to balance the number of atoms. ** only __________ numbers can be used ** you CANNOT change _______________ Step 3: Check: are all substances balanced? Other Tips and Rules When balanced, simplify the coefficients (___________ them all by a common factor, if possible) Balance any element that occurs _____________________ on one side of the equation_________ (often H and O) Keep polyatomic ions _________________ as a group if it remains unchanged on both sides of the reaction Examples: Balance the following skeleton equations: → 1. N2 + H2 2. Fe + O2 3. Be + Al2O3 4. Mg + HNO3 5. CH4 + O2 → NH3 Fe2O3 → → → CO2 BeO H2 + + + Al Mg(NO3)2 H2O 6.5, 6.6, and 6.9: Types of Chemical Reactions Even though there are millions of possible chemical reactions that take place in nature, in industry, and all over the world, there are only five main types (see next page). Practice – Identify the type of reaction: → 1. H2 + I2 2 HI 2. Mg(NO3)2 + 2 KBr → 3. Mg(NO3)2 4. NaOH + Ca 5. 2 NH3 → → _________________________ → Mg + 2 N2 + 3 H 2 8. PCl5 9. Cu → → _________________________ _________________________ → 2 Li3PO4 + 3 Ca(NO3)2 _____________ 3 C2H4Br2 _________________________ PCl3 + Cl2 + 2 AgNO3 + 2 KNO3 ___________________ NO3- Ca(OH)2 + Na ________________________ 6. Ca3(PO4)2 + 6 LiNO3 7. C2H4 + Br2 MgBr2 → _________________________ Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag ____________________ Type of Reaction Synthesis Decomposition Single Displacement Double Displacement Complete Combustion Description General Pattern Examples What to Look For 6.9: Combustion Reactions In general, combustion is the ________________________________ with _____________ to produce an ________________. Energy is produced in the form of ___________ and _______________ _____________________ (fuel) combustion is a very common combustion reaction. Hydrocarbons are composed of ______________ and _______________. There are thousands of possible combinations. The general formula is CxHy Examples: Propane – ____________ Butane – ______________ Hydrocarbons are used every day: 1. Complete Combustion There is __________________________ in the reaction, so ______ the fuel in the reaction is used up. Only ______________________ and _______________are produced. General formula: Example: Burning of butane in a lighter Characteristics: 2. Incomplete Combustion There is __________________________ in the reaction, so all the fuel _____________used up. ___________________________________ and ______________ are still produced, but so are ________________________ and _________________. General Formula: Example: Burning of butane in a lighter Characteristics Flame is ____________________ CO is a _______________________, and is _________________ and ______________________, so it is difficult to detect and can poison the air without _____________________________ If CO gets into the body, it prevents the transport of _____________ around the body and the person will die by _______________________ from the inside Carbon (C) particles are produced (____________________________) Many _____________________________________ are associated with incomplete combustion! 3. Other Combustion Reactions Other substances – besides hydrocarbons- undergo combustion reactions. These elements react with oxygen to form _______________ Examples: Combustion of Hydrogen Hydrogen reacts with oxygen to form water: Completing Chemical Reactions If you only know the reactant(s) in a reaction, you can predict what products will form! Each type of reaction has a specific pattern. Use this to help you! Steps to follow 1. Identify Reactant(s) 2. Identify Reaction Type 3. Predict the products using the rules for the specific reaction type ◦ If the new products are ionic, you MUST do a new “criss cross” to determine the formula of the new compound(s) 4. Balance the Equation 1. Synthesis Reactions (a) Metal + non-metal Ionic compound ◦ Combine the two elements into a compound ◦ Use criss-cross rule to determine formula of new compound! Ex: Li + Cl2 Ex: Al + O2 (b) non-metal + non-metal molecular compound ◦ Simply combine the two elements into a compound, leaving the subscripts the same. Ex: S + Br2 Ex: C + O2 2. Decomposition Reactions A. Binary compounds o Compound element + element o Break down into their two elements (HOFBrINCl still applies!) Ex: H2O Ex: AlCl3 B. Carbonates o When a compound with CO3 in it decomposes, Carbon dioxide is ALWAYS formed o The other compound is a metal oxide (compound containing the metal and oxygen) Ex: MgCO3 Ex: Na2CO3 3. Single Displacement Reactions o o o The two metals switch places OR the two non-metals switch places MUST do a new criss-cross on the new compound!! DO NOT just carry over the subscripts If a multivalent metal exists, determine its charge from the reactant formula Ex: Mg + CuCl2 Ex: KBr + I2 Ex: SnO2 + Br2 4. Double Displacement Reactions o o o Switch the cations between the two compounds Do new criss-crosses to determine new formulas! If a multivalent metal exists, determine its charge from the reactant formula Ex: NaCl Ex: FeI3 + BeO + Pb(NO3)2 5. Combustion Reactions A. Complete o Two products are always CO2 and H2O Ex: Complete combustion of C6H14 (hexane – used in shoe glue) B. Incomplete o Four products are always CO2, H2O, CO, and C Ex: Incomplete combustion of C8H18 (octane - car fuel) Practice: 1. Ag 2. Na2S 3. SnO 4. HgO 5. CaCO3 6. Al + + → F2 + + Cl2 → KCl → → → FeO →