Air Masses
advertisement
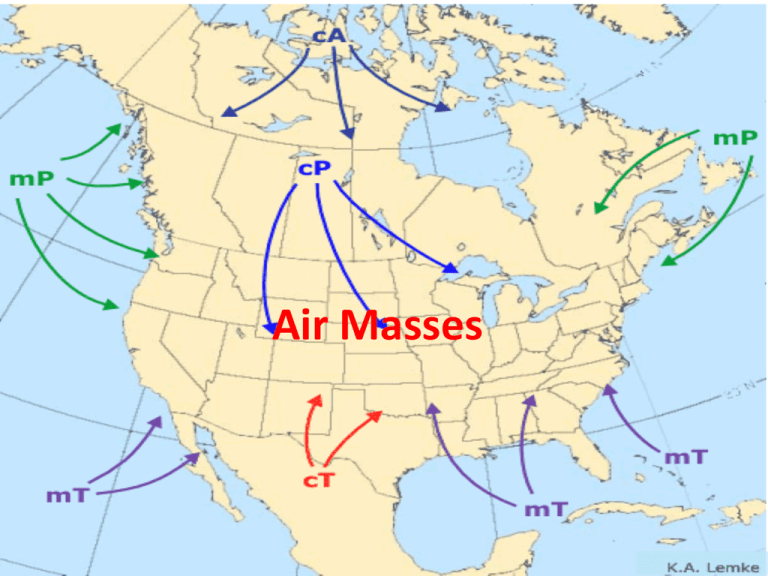
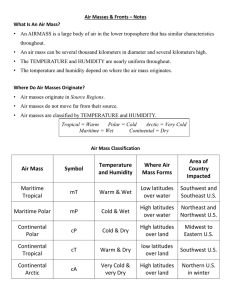
Air Masses • An air mass is a large body of air that has relatively uniform temperature and humidity characteristics. • If air remains over a source region long enough, it will acquire the properties of the surface below • They are grouped into four categories based on their source region – Polar “P”- Cold – Tropical “T”- Warm – Continental “C”- Dry – Maritime “M”- Wet • These letters are combined to indicate the type of air mass: cP: cold, dry air mass mP: cold, moist air mass cT: warm, dry air mass mT: warm, moist air mass Fronts • When 2 air masses meet • Can be 100s of miles long • Named by which mass Overtakes the other mass Cold Front Cold Front • • • • • • • Fast Moving After there are cold temps Vertical boundaries Warm air is pushed up fast Can lead to thunderstorms Video from plane Severe Storm Warm Front Warm Front • • • • Distinct Cloud Pattern Slow Moving Can lead to days of rainy weather Gradual Front Line Occluded Front Occluded Front • Warm air is isolated off of the ground • Heavy Rain • 3 different air masses Stationary Front Stationary Front • Neither air mass overtakes the other • Extended clouds or rain for days