Western Europe: Middle Ages & Christian Europe Constructing a Hybrid Civilization
advertisement

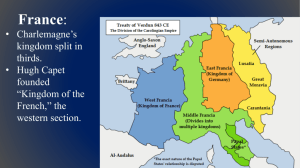
Western Europe: Middle Ages & Christian Europe Constructing a Hybrid Civilization -in place of Stearns, Chapter 10- • Western Europe on margins of world history for most of postclassical period • Early Middle Ages = 500-1000 • High Middle Ages = 1000-1300 Early Middle Ages, 500-1000 Political Life, 500-1000 • Roman collapse brought great change – Combination of Roman heritage & Germanic culture • Clovis – First attempt at order • Viking menace Political Life, 500-1000 • Charlemagne – Most famous Carolingian – Greater central control, but exception to most of period • Feudalism – Established order through decentralized hierarchy of obligations Economic & Social Life, 500-1000 • Manorialism – Relationship b/t serf & lord – Life of the serf • Women w/ considerable freedoms Culture - Catholicism, 500-1000 • Political influence through hierarchy – Pope – Bishops • Political influence through faith – Pressure rulers • Role of monasteries ~QUESTION~ Transitions, 900-1100 • Assimilation of Vikings • Agricultural improvements – Moldboard plow – Horseshoes & collar – Three-field system • Cultural exchange – Crusades High Middle Ages, 1000-1300 Culture, 1000-1300 • Catholicism – Crusades – Scholasticism • Treatment of Jews • Art – Gothic – Vernacular languages Politics, 1000-1300 • Growth of central monarch power – England • Norman conquest • Magna Carta – France & Capetians – Holy Roman Empire • Least successful Economics, 1000-1300 • Mediterranean trade – Venice & Genoa • Northern trade – Hanseatic League Economics, 1000-1300 – cont. • Economic growth led to: – Guilds – City charters – Weakening of 3-estates & rise of merchants Conclusions