African Societies Life on the Margins of Islam
advertisement

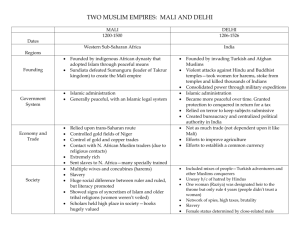
African Societies Life on the Margins of Islam Sahara Sudan / Sahel ~the savanna coastline~ Congo Rainforest Definitions Sudan = region just south of Sahara (literally Arab for land of the blacks) Sahel = an arid climate zone just south of the Sahara Savanna = an ecological zone of grasses just south of the Sahara Africa during Classical Period? Bantu Migrations! Bantu Migration Sedentary tribal group Experience population pressure → Migration …Spreading: Agriculture Language Iron Bantu Ethiopia Resulting Culture Ag & Iron •More efficient, higher pop, specialization Women •Source of lineage, free to contribute & socialize Religion •Animist - except, Christian Ethiopia Africa during Post-Classical Era States Form in 3 Regions Ethiopia Sudan C. African Forests Swahili Coast (E. Africa) …impacted by Islam’s spread Islamic North Africa Ethiopia Sudan (West Africa) C. African Forests Swahili Coast (E. Africa) West Africa Sudan Sudanic West Africa (1) (2) (3) Ghana Mali Songhay Empires Empires: Territorial core w/ subordinate tributaries Sudanic West Africa Strategically located to profit from trade Salt of desert sent south Gold of forests sent north Sudanic West Africa Islamic empires = dawn of new international trade Muslims introduce camel → trans-Saharan trade easier Trade fostered expansion & urbanization North Africans brought salt, horses, cloth to trade for gold W. Africans brought gold to trade for salt Salt Trade Ghana Familiar framework in Ghana King’s power was absolute; acted as a sole judge in all criminal matters Large, powerful army and nobles enforced the king’s decisions Peasants contributed a portion of their harvest so that city dwellers could focus exclusively on their trade Islam comes Indigenous Religions Believed one god created world, & lesser gods ruled over daily life Believed disaster could be avoided by pleasing gods with prayer & ritual Islamic syncretism? Islam W. Africans tolerated Muslims Then, most gov’t officials & merchants converted Why? Gov’t alliances; caliphal leadership of animistic & Islam rituals w/ political rule Merchants brotherhood of trust Social & Political Blending Islam’s Impact Sharia: common laws & expectations for all Muslims does not apply to women Africa tradition of slavery expands under Muslim trade networks Mali Administration Controlled 40-50 million people & approx 400,000 sq miles (2nd largest at time) So… Emphasized justice & crime punishment to maintain peaceful trade Mali Administration Sensitive to empire’s diversity by accepting indigenous rulers & customs Local villages elected leaders County-level officials appointed by governors Governors chosen by regional custom (election, inheritance) but must be approved by Mansa Mali Administration Mansa’s authority through: Loyal generals & standing army of 100,000 Each village obligated to provide a quota of fighting age men Laws enforced by council of judges with representatives from each ethnic group Arabic as language of gov’t Mali Economy 80% of population = farmers Blacksmiths Iron’s Taxed had elevated status role in military 1 gold coin for every load of salt imported & 2 gold coins for every load of salt exported Mali Mansa Hajj Musa & Significance took 8 months & entourage of 60,000 Employed more than 500 slaves (who each carried a 6 pound staff of gold) Had 100 camels carrying 300 pounds of gold each Charity…the 1. 2. 3. 3rd pillar How much gold did Mansa Musa give away? Gold is worth $1300 per ounce. How much was the gold worth? What do you think were the results of this charity? Mali Impact of Mansa Musa Brought attention of Islamic world to Mali Center for scholars, artists, architects Built large libraries, mosques Helped further popularize Islam Mapmakers include Mali Helped lead to European exploration East Africa East Africa Politically fragmented into city-states Examples: Kilwa Mogadishu Zanzibar East Africa Strategically located to profit from trade Monsoons to Arabia provide seasonal route Islamic empires intensify Indian Ocean trade to S Asia From Central Africa: slaves, ivory, gold, for From Middle East, India, SE Asia: tapestries, cotton textiles, silk, porcelain to SE Asia The Swahili Coast? So, East Africa during the Postclassical Period best represented by: Swahili A language that combines Bantu & Arabic Serves to unite an otherwise diverse region Swahili East Coast Cosmopolitan port cities Bantu, Arabs, Indians, Malay Highly urbanized, wealthy, luxurious Ibn Battuta about Kilwa, “One of the most beautiful & well-constructed towns in the world” Dominated rural farmland Central Africa C. African Forests Central Africa Home of: Kongo, Zimbabwe, Benin Source of goods traded in E & W Africa No direct contact with Muslims C. African Forests Central Africa Kongo, Zimbabwe, Benin Bantu migrations & trade revenues act as seeds of state formation Slower development due to relative isolation compared to other African regions Review Explain the patterns seen on the map. Review Explain the significance of Islam on the Middle East and world during the postclassical period. – trade & technology Politically – law & governance Socially – unity, migration, urbanization, language Economically 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Was trade or militaristic incursion more influential in the spread of Islam in Indian society? Why? Was Islamic society or Indian society more influenced by interactions between these two civilizations? Why? How did geography and trade impact affect Africa during this time period? (What areas? Who?, etc) How was the spread of Islam (& its effects) similar and different in S/SE Asia and Africa? To what extent do you agree that trade is more important than government in the postclassical world?