Africa and the Spread of Islam
advertisement

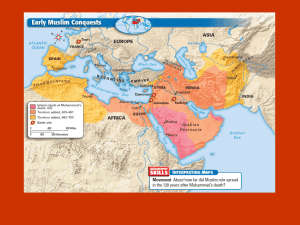
Africa and the Spread of Islam Chapter 8 African Societies Stateless – organized around kinship or other obligations Bantu = base on most African language Religion Animism Veneration of ancestors Economics North Africa = Mediterranean trade Sub-Saharan = varied; mostly agrarian Trade conducted by professional merchants North Africa and Islam 640-700: Invasions Unified under Abbasid Berbers (desert people) formed own states Almoravids and Almohadis – launched jihads to purify Appeal: method of unity and egalitarian Christian Kingdoms Nubia and Egypt Ethiopia (Axum) Copts borrowed from Byzantine Limited outside influence due to geography Spread up Nile to Nubia (Kush) King Lalibela built 11 churches Independent kingdom until 13th century Remained independent The Grasslands and Ghana Sahel: southern edge of Sahara = trading posts Subject to attack and drought Ghana profited from taxing salt and gold trade 10th c. – rulers converted to Islam Mali 13th c. Malinke people broke from Ghana Islam used by kings to justify power Agrarian + trade Juula (merchants) formed partnerships and expanded through west Africa Sundiata, the Lion Prince of Mali Grouped the people by clans 16 military clans 5 religious duty clans 4 specialist clans; ex. blacksmiths and griots (oral historians) Garrisons provided safe travel and trade Successor Mansa Musa traveled to Mecca Outside influence grew Life in the Mali Cosmopolitan court life “Port” cities grew (Timbuktu) off of Niger River Libraries, universities and mosques flourished Book trade was most lucrative Still mostly agrarian Many small farms Geography made it difficult Polygamy helped with labor supply The Songhay Kingdom Middle area of Niger valley “Masters of the soil” Gold trade from west Africa thrived Politics and Society in Sudan Unified states = structure for different groups to coexist One ruling family Islam provided common core of beliefs and law Animism/paganism still important Women enjoyed social freedom; some matrilineal societies as well Extensive slave trade; slavery = one step in conversion to Islam The Swahili Coast – East Africa “Zanj” (Arabic name) Many Bantu-speaking herders and trading ports and fishing villages Refugees from Oman settled Very diverse communities Swahili combined Bantu with Arabic Muslim ruling famlies Extensive trade and wealth A Hybrid Culture 13th c – Growth of Islam in East Africa Mosques built in trading ports Rulers and merchants Muslim; townspeople retained traditional beliefs Swahili became dominant Maternal (property) and paternal lines used for lineage for rulers 1500s: Portuguese influence introduced but minimal Mozambique Fort Jesus, Mombasa Central Nigeria: Yoruba and Benin Yoruba = language Terracotta and bronze art Small city-states Oyo – king controlled “princes” with tribute Edo people in Benin Strong emphasis on image of king and royal lineage Central African Kingdoms Rainforest region Congo River Basin Kinship based societies Katanga: Divine kinship and kingship – ensured crops’ success Kongo Late 15th century Strong agriculture = strong artisan class Traditional division of labor between men and women Family-based villages Hereditary kingship but local chieftains were not Confederation under “manikongo” (king) Iron and art important Great Zimbabwe and Mwene Mutapa Bantu confederation Shona-speaking herders and farmers Between Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers “Zimbabwe”: Stone houses built for rulers The bird of God = link with spirits Mwene Mutapa became king Expanded kingdom Increased trade with coast, Portugal and India Impact of Islam on Africa While Islam spread to large areas of Africa, it was infused with African culture. Many African cultures remained independent. Late 15th century European explorers found welldeveloped kingdoms and empires – especially those that were Muslim. Africa was already a center of trade for salt, ivory, slaves and gold.