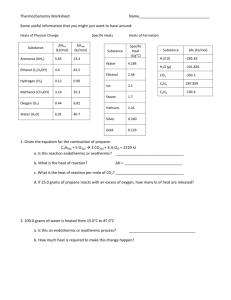
Chemistry 6.0 Name________________________________ Chapter 8 – Chemical Equations
advertisement

Chemistry 6.0 Chapter 8 – Chemical Equations Name________________________________ Chemical Equations Introduction: Write complete equations for the following: 1. Two moles of solid sodium chloride decompose when exposed to an electric current into two moles of sodium metal and 1 mole of chlorine gas. 2. One mole of barium chloride in solution reacts with one mole of sodium sulfate in solution to produce 1 mole of solid barium sulfate and 2 moles of sodium chloride in solution. 3. Two mole of solid potassium chlorate, when heated, decompose into two moles of solid potassium chloride and 3 moles of oxygen gas. 4. One mole of solid calcium carbonate decomposes when heated into one mole of solid calcium oxide and 1 mole of carbon dioxide gas. 5. Two moles of solid aluminum hydroxide decomposes when heated into one mole of solid aluminum oxide and three moles of water vapor. 6. One mole of zinc metal when mixed with two moles of a hydrochloric acid solution react and produce one mole of zinc chloride in solution and one mole of hydrogen gas. 7. Eight moles of fluorine gas are bubbled through a solution containing eight moles of potassium sulfide and react to produce sixteen moles of potassium fluoride in solution and one mole of solid sulfur. 2 Balancing Equations: Balance the following reactions. Place a “B” at the beginning of any that are balanced as written. 8. _____ Zn + _____O2 → _____ZnO 9. _____HI → _____H2 + 10. _____B + _____F2 → _____BF3 11. _____N2 + _____H2 → _____NH3 12. _____Fe + _____H2O → _____Fe3O4 + _____H2 13. _____BaCl2 + 14. _____P4 + 15. _____KClO3 → 16. _____C3H8 17. _____Cu + _____AgNO3 → 18. _____Te + _____H2O → 19. _____La(NO3)3 + 20. _____RhO3 → 21. _____Hf + _____N2 → 22. _____Ga + _____H2SO4 → 23. _____PdCl2 + _____HNO3 → 24. _____RbBr + _____AgCl → 25. _____PaI5 _____I2 _____H2SO4 → _____O2 → + → _____HCl _____P4O10 _____KCl + _____O2 _____BaSO4 + _____O2 → _____CO2 + _____Cu(NO3)2 + _____TeO + _____NaOH → _____RhO + _____Pa + _____H2O _____Ag _____H2 _____La(OH)3 + _____NaNO3 _____O2 _____Hf3N4 _____Ga2(SO4)3 + _____H2 _____Pd(NO3)2 + _____AgBr + _____I2 _____HCl _____RbCl 3 26. Na + O2 → Na2O 27. H2 + O2 → H2 O 28. Na2SO4 + CaCl2 → 29. Al2O3 → Al + 30. C2H6 + O2 → CO2 + 31. SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 32. SiCl4 → 33. C + 34. Br2 + NaI → NaBr + I2 35. Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 36. H2S + O2 → 37. Ba(NO3)2 + 38. C5H12 + O2 → CO2 + 39. HgO → Hg + O2 40. H2SO4 + Pb + 41. C6H12O6 + 42. Ca + 43. C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + 44. HC2H3O2 + NaHCO3 → 45. NaCl + SO2 + 46. Fe2O3 + CO → 47. Ca3(PO4)2 + Si + H2 → CaSO4 + NaCl O2 H2O Cl2 CH4 H2 O + SO2 Na2SO4 → C + PbSO4 + CO2 + H2O H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2O NaNO3 H2O PbO2 → O2 → H2O → BaSO4 + H2 CO2 CO2 + + O2 → CO2 + SiO2 → NaC2H3O2 + Na2SO4 + H2O HCl Fe CaSiO3 + CO + P4 4 48. aluminum + 49. chromium(III) hydroxide + nitric acid 50. chromium + hydrobromic acid 51. krypton difluoride CH3OH + O2 54. Si2H6 + O2 55. CH3NH2 + O2 56. Na2SiO3 + 57. NH3 58. Sb2S3 59. Al 60. C2H5Cl water + hydrochloric acid 53. aluminum chloride + chromium (III) bromide water krypton + 52. chlorine + water + hydrochloric acid + oxygen + hydrogen chromium(III) nitrate + hydrogen + hydrofluoric acid oxygen + H2O SiO2 + H2O CO2 + H2O + N2 HF H2SiF6 + NaF + H2O + O2 NO + H2O + HCl H3SbCl6 + H2S + H2O + H2 NaOH + NaPb CO2 (C2H5)4Pb NaAl(OH)4 + NaCl + Pb 5 Types of Reactions: Balance the following equations and indicate the type of reaction on the line provided. → 61. NaCl Na + 62. Na 63. C2H4 + 64. H2O → 65. H2 66. C8H18 67. NaOH 68. Na 69. K 70. K + AgCl 71. C6H12 + 72. Ca 73. KOH + 74. Al 75. HgO 76. NaOH + 77. Fe + O2 → 78. C6H8 + O2 → 79. Pb(NO3)2 + K2CrO4 → 80. H2 81. C3H5(NO3)3 Cl2 → + O2 + + H2O _____________________ → → → → _____________________ NaCl _____________________ KCl + _____________________ H2O _____________________ _____________________ H2O + KNO3 _____________________ Al2O3 _____________________ O2 _____________________ H2SO4 → → NaCl _____________________ CO2 → Hg + N2 _____________________ CaS HNO3 → H2O + Ag + → O2 + _____________________ KCl → S8 H2O H2O + H2 → + CO2 → O2 + + _____________________ HCl Cl2 + O2 → HCl + _____________________ + O2 + NaCl CO2 → O2 _____________________ → H2 + Cl2 Na2SO4 + H2O _____________________ Fe2O3 CO2 _____________________ + H2O PbCrO4 + _____________________ KNO3 NH3 CO2 + _____________________ _____________________ N2 + H2O + O2 _____________________ 6 Decomposition, Synthesis, and Combustion 82. Pt2O 83. Mg(ClO3)2 84. P2O5 85. SrO + H2O → 86. BaCO3 87. HNO3(aq) 88. C4H10 89. Al 90. Cl2O3 91. Al(OH)3 92. iron(III) chlorate is heated 93. zinc oxide powder is added to water 94. pentane is ignited in air 95. phosphorous acid is heated 96. magnesium phosphide is exposed to an electric current 97. lithium hydroxide is heated 98. hydrogen gas is ignited in air O2 → + + O2 + H2 O → 7 99. magnesium ribbon is heated in the presence of sulfur 100. scandium carbonate is heated 101. dinitrogen pentoxide gas is bubbled through water Single Replacement 102. Zn + CuSO4 → 103. Pb + Mg(NO3)2 → 104. AgC2H3O2 105. Cl2 106. HF(aq) 107. magnesium + nitric acid → 108. sodium chloride + aluminum → 109. barium + calcium sulfate → 110. nickel(II) sulfate + lithium → 111. potassium + water → 112. silver + strontium chloride → 113. sodium fluoride + iodine → 114. rubidium + iron(III) sulfate → 115. sodium + water → + + Li → KBr → + Ca → 8 116. fluorine + aluminum bromide → 117. phosphoric acid + calcium → 118. copper + water → Double Replacement CaSO4 → 119. AgCH3COO 120. Pb(NO3)2 + 121. AgNO3 + FeCl3 → 122. H2SO4 Ba(OH)2 → 123. Al(OH)3 + NH4Cl + + Na2S → → 124. A solution of lead(II) chlorate is mixed with a solution of chromium(III) iodide. 125. A solution of nitric acid is added to a solution of magnesium hydroxide. 126. Solutions of copper(II) chloride and potassium carbonate are mixed. 127. Solid sodium carbonate is sprinkled on a hydrochloric acid spill. 128. Perchloric acid is neutralized by the addition of ammonium hydroxide. Energy and Change of Enthalpy 129. Indicate the following as either exothermic or endothermic. a) CH4 + 74.4 kJ → C + 2H2 a) ___________________ b) 1/8 S8 + O2 → SO2 b) ___________________ C3H8 + 104 kJ c) ___________________ → d) ___________________ c) 3 C + 4 H2 → d) butane + oxygen e) CO2 → CO + ½ O2 carbon dioxide + water ΔH = +238kJ e) ___________________ 9 130. The energy term of an exothermic reaction is added to the (right / left) side of chemical equation because energy is (absorbed / released). 131. The ∆H of an endothermic reaction is indicated as a (+ / −) value because the enthalpy (potential energy) of the reactants is ( > / < ) than the enthalpy of the products. 132. All chemical fuels produce an (endothermic / exothermic) reaction upon ordinary combustion. 133. Baking a potato is an example of an (exothermic / endothermic ) reaction. 134. Copper and oxygen react according to the following: Cu + ½ O2 → CuO ∆H = −155kJ Rewrite this equation for 1 mole of O2 and include energy in the equation. 135. Carbon and sulfur react according to the following equation: 4C + S8 + 3511 kJ → 4CS2 Rewrite the equation for one mole of C, using the ∆H notation. 136. Draw an energy diagram for the equation given in the previous problem. Be sure to label all parts. (progress of the reaction, enthalpy or energy, ∆H, reactants, and products. 137. Using the graph below, determine: a. The activation energy needed for the forward reaction?___________________ b. The activation energy needed for the reverse reaction? ___________________ c. ∆H for the forward reaction? Endothermic or exothermic? ___________________ d. ∆H for the reverse reaction? Endothermic or exothermic? ___________________ e. Label the activated complex on the curve. f. Sketch what the curve might look like if a catalyst was added. 10 138. Draw a potential energy diagram with the following criteria: a. ∆Hrev = −30 kJ b. Ea (forward reaction) = 70 kJ c. Activated Complex = 90 kJ 139. Based on your diagram, determine: a. ∆Hfor _____________________ c. Enthalpy of reactants__________________ b. Ea (reverse) _________________ d. Enthalpy of products_________________ Bond Energy 3 2 140. Given: a. Identify the type and number of bonds broken in this reaction and determine the total amount of energy required to break them. b. Identify the type and number of bonds formed in this reaction and determine the total amount of energy released when they are formed. c. Calculate the enthalpy change for the entire reaction. d. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? e. Write a thermochemical equation for the reaction. f. Draw and label a potential energy diagram for the reaction. 11 141. Using bond energies, calculate the enthalpy change for the following reactions: 2 a. 2 2 b. 2 c. d. 3 2 2 6 12 Determining ∆H Using Hess’s Law: Each manipulated equation must be rewritten. 1) Given: 2P + 3Cl2 → 2PCl3 2P + 5Cl2 → 2PCl5 Calculate ΔH for: PCl3 + Cl2 → PCl5 ΔH = −640. kJ ΔH = −886 kJ 2) Given: 2HF → H2 + F2 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O Calculate ΔH for: 2F2 + 2H2O → 4HF + O2 ΔH = +542.2 kJ ΔH = −571.6 kJ 3) Given: 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O 4NH3 + 3O2 → 2N2 + 6H2O Calculate ΔH for: N2 + O2 → 2NO ΔH = −1170 kJ ΔH = −1530 kJ 4) Given: 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 Calculate ΔH for: 2Al + Fe2O3 → 2Fe + Al2O3 ΔH = −3351.4 kJ ΔH = −1648.4 kJ 5) Given: C + O2 → CO2 H2 + ½ O2 → H2O 2C2H2 + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O Calculate ΔH for: 2C + H2 → C2H2 ΔH = −393.5 kJ ΔH = −286 kJ ΔH = −2598.8 kJ 13 Review (Identify reaction type before writing the equation) 142. calcium metal is added to a solution of nitric acid. 143. solutions of copper(II) nitrate and sodium hydroxide are mixed. 144. scandium carbonate is heated 145. nitrous acid is heated 146. zinc + magnesium carbonate → 147. dichlorine monoxide + water → 148. calcium carbonate + perchloric acid → 149. strontium chlorate is heated 150. lead(IV) sulfide is exposed to an electric current 151. the combustion of octane 152. silver oxide + water → 153. dichromic acid + ammonium hydroxide → 154. barium metal is dropped in water 155. copper(II) hydroxide is heated 156. lithium + sulfur → 157. bromine + iron(III) iodide → 158. solutions of sodium phosphate and calcium bromide are mixed. 159. barium metal is added to a solution of chlorous acid. 14 160. chloric acid is heated 161. aluminum metal is added to a solution of sodium chlorate 162. dinitrogen pentoxide gas is bubbled through water 163. lithium carbonate is heated 164. ammonium carbonate powder is sprinkled on a hydrochloric acid spill 165. iron(III) phosphide is exposed to an electric current 166. hexane is ignited 167. tin(II) oxide is added to water 168. strontium hydroxide is combined with acetic acid 169. tin(IV) hydroxide is heated 170. a piece of silver metal is held in a Bunsen burner flame 171. lead(II) sulfide is heated in a fluorine environment 172. calcium hydroxide powder is added to an ammonium nitrate solution 173. A hydrocarbon compound is found to be 85.71% carbon and 14.29% hydrogen by mass. When vaporized at 35ºC, 0.136 g of the compound occupies a volume of 45.0 mL and exerts a pressure of 691 torr. Write a balanced equation for the combustion of this compound. 15 174. Given: a. Write a balanced molecular equation in ΔH notation. b. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? c. Which has a higher enthalpy, the reactants or the products? d. Would the temperature of the surroundings increase or decrease? 175. Complete the following based on the reactions given below: Reaction 1: 2MnO(s) 2Mn(s) + O2(g) H = +770.4 kJ/mol Reaction 2: 2MnO(s) + O2(g) 2MnO2(s) H = −269.7 kJ/mol a. Apply Hess’s Law to reactions 1 and 2 and determine the enthalpy change for the following reaction: Reaction 3: Mn(s) + O2(g) MnO2(s) b. Does reaction 3 release or absorb heat? __________________ c. Is reaction 3 exothermic or endothermic? __________________ d. Will reaction 3 cause an increase or decrease in temperature? e. Write the thermochemical equation for reaction 3. __________________ f. Write the equation for reaction 3 in H notation. g. Draw and fully label an energy diagram for reaction 3. 16 Cumulative Review Questions 176. For 2607000 give the following: a) Number written in scientific notation _________________________ b) Significant figures _________________________ c) Rounded to 3 significant figures _________________________ 177. Convert 23.6 hectograms to milligrams 178. A copper cube with a mass of 58.60 g is placed into a water-filled graduated cylinder. The water in the cylinder rises from 26.5 mL to 33.1 mL. Determine the density of the copper? 179. List 3 physical properties and 3 chemical properties of water. 180. Complete the following chart Homogeneous or Heterogeneous Element, Compound, Mixture, Solution rubbing alcohol calcium oxide gasoline 181. Write nuclear equations for: a) Alpha emission of radon-222 b) Electron capture by nitrogen-15 c) Neutron bombardment of oxygen-16 17 24 182. What is the mass and charge of 5.26 x 10 electrons? 183. A 2.65 gram sample of cobalt-55, with a half-life of 17.5 hours undergoes decay for 6.56 days. What mass of cobalt-55 remains at this point? 184. An element consists of 1.40% of an isotope with mass 203.973 amu, 24.10% of an isotope with mass 205.9745 amu, 22.10% of an isotope with mass 206.9759 amu, and 52.40% of an isotope with mass 207.9766 amu. Calculate the average atomic mass and identify the element. 185. Where appropriate, write formulas or names for each of the following: a. ammonium sulfate ___________ f) H3AsO4(aq)_________________________ b. dinitrogen monoxide ___________ g) FeSO3 _________________________ c. phosphorous acid ___________ h) CuSO4•5H2O ______________________ d. lead(IV) oxalate ___________ i) BF3 _________________________ e. aluminum nitrite ___________ j) Cr(OH)3 _________________________ 186. Determine the mass, in grams, of 4.22 x 1024 formula units of copper(I) sulfide. 187. What is the total number of electrons in 0.915 moles of nitrogen atoms?