Mendel’s Second Experiment Inheritance of Two Traits Dihybrid Cross
advertisement

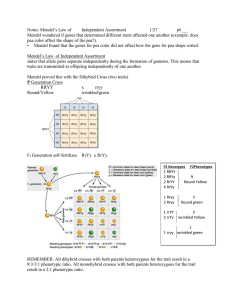
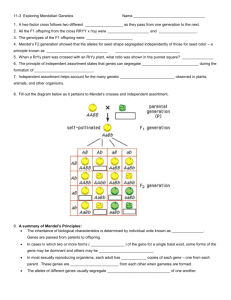
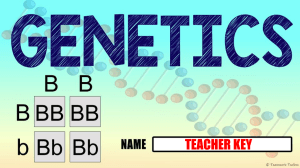
Mendel’s Second Experiment Inheritance of Two Traits Dihybrid Cross Monohybrid Review How many traits were being looked at during the Mendel’s monohybrid cross? – __________________________________ What was being crossed in Mendel’s monohybrid cross? _________________________________ _________________________________ Back Track for a Second What exactly was a purebred species in terms of genotype? – It was a species that had the same alleles in its genetic makeup (either BB or bb) What about a hybrid species in terms of genotype? – It was a species that had different alleles in its genetic makeup (like Bb) PXP When the two parents were crossed, TT X tt, what resulted? The Results were four heterozygous offspring. These are the F1 generation F1 X F1 When the two F1 generation were crossed, TT X tt, what resulted? The Results were three dominant and one recessive in a 3:1 phenotypic ratio but in a 1:2:1 genotypic ratio These are the F2 generation The Law of Segregation What does the Law of Segregation state? – It states that inherited traits are determined by pairs of “factors” – These factors segregate (separate) in the gametes What happened next? Mendel completed the monohybrid cross and started to ask and formulate new questions What do you think he was thinking of next? – He wanted to know if the inheritance of one characteristic influenced the inheritance of a different characteristic What did he try next? He started all over again He produced purebred plants just like last time with the traits he wanted to examine He bread pea plants that were round and yellow pure plants (dominant for both) and then he did the same for wrinkled and green (recessive for both) What did he try next? He then crossed them again The P X P ended up yielding what? – The F1 ended up being all yellow and all round, just like last time – There seems to be some similarity P X P Dihybrid Cross RY RY RY RY ry RrYy RrYy RrYy RrYy ry RrYy RrYy RrYy RrYy ry RrYy RrYy RrYy RrYy ry RrYy RrYy RrYy RrYy Then What? Just like last time he crossed the two F1 Progeny What do you think he got? – He – He – He – He got got got got 9 3 3 1 Yellow and round Green and round Yellow and Wrinkled Green and Wrinkled What’s The Ratio? The ratio that he got was? – 9:3:3:1 How Many? How many plants do you think that Mendel used for this experiment – 551 pea plants – And of that 551 this was the ratio that he got 320 round and yellow 104 round and green 101 wrinkled and yellow 26 wrinkled and green What did this tell him? The ratio of 9:3:3:1 could be explained if the alleles from one trait were inherited independently of the alleles for another trait The Law of Independent Assortment The Law of Independent Assortment The second law of inheritance states:_____________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Different pairs of alleles are passed to the offspring independently of each other The Law of Independent Assortment This means that offspring may have new combinations of alleles that are not present in either parent