7 Genetics
advertisement

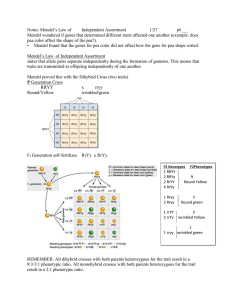
Genetics is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. Heredity is the actual passing of traits from parents to offspring. Gregor Mendel is known as the father of modern genetics. Experimented with pea plants Because of Mendel’s experiments we now know that inherited traits are controlled by different versions of genes known as alleles. Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ◦ Dominant alleles can hide alleles for other traits. Use capital letters to represent them. ◦ Recessive alleles can be hidden by alleles for other traits. Use lower case letters to represent them. The results of most of Mendel’s experiments looked the same. The F1 generation showed all of the dominant traits, while the F2 generation showed the dominant and recessive traits in a ratio of 3:1. Phenotype—an organism’s appearance (word description) Genotype—an organism’s genetic make-up (letter code) ◦ Genotype for purple flowers: PP or Pp ◦ Genotype for white flower: pp Homozygous—both alleles are the same (pure) PP or pp Heterozygous—two alleles are different (hybrid) Pp Monohybrid Crosses —only one characteristic is tracked A tool used to predict the outcome of different types of monohybrid crosses is called a Punnett Square ◦ Example: TT x tt (Pure tall plants x Pure short plants) t t T T Tt Tt Tt Tt Result: 100% Heterozygous tall offspring Genotype = Tt Phenotype = tall Incomplete Dominance occurs when offspring have a phenotype that is in between that of the two parents. RR Rr http://smabiology.blogspot.com/2008_11_01_archive.html rr Punnett Squares for incomplete dominance are completed in the same manner. Except that the heterozygous individuals will have the blended phenotype. Example: Pink Flower x Pink Flower Rr x Rr R r R RR Rr r Rr rr Results: 25% Red flowers 50% Pink flowers 25% White flowers Genotypic Ratio: 1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr Phenotypic Ratio: 1 Red : 2 Pink : 1 White Codominance occurs when both alleles in a pair are expressed but do not actually blend. Human Blood Type is an example of codominance. Three alleles (A,B and O) are involved in determining blood type. However, you still only inherit two (one from mom and one from dad) ◦ A and B are both dominant; O is recessive ◦ Type AB blood has one genotype: AB ◦ Type A blood has two possible genotypes: AA and AO ◦ Type B blood has two possible genotypes: BB and BO ◦ Type O blood has only one possible genotype: OO Dihybrid Cross --shows two traits at the same time. Example: RrYy x RrYy (heterozygous round and yellow seeds) R = round r = wrinkled Y = yellow y = green RY Ry rY ry RY RRYY RRYy RrYY RrYy Ry RRYyRRyy RrYy Rryy rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy ry RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy Results: 9 round/yellow 3 round/green 3 wrinkled/yellow 1 wrinkled/green