Heredity/Mendel Guided Notes
advertisement

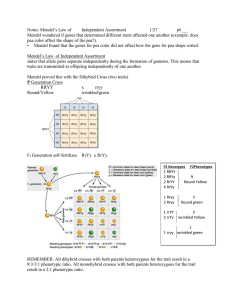
Heredity/Mendel Guided Notes Name_____________________________________ per____ Heredity: The passing of ______________________characteristics onto the offspring ___________________: is the branch of biology that studies heredity Gregor Mendel Considered the ______________________ of genetics Was an Austrian monk that used ________ _____________________ to study heredity Pea plants usually self pollinate so their genetic information can be ____________________ By carefully ___________________________ his data he made some great findings Mendel Crossed Plants with different _____________________ or characteristics Mendel crossed a __________ pea plant with a _________________ pea plant to see what would happen The result was that the offspring (___________________) were all tall However when crossed the second generation, ¼ were _________________ Mendel repeated these crosses for 7 different variations He discovered that in the 2nd generation (______)that the trait that had disappeared in the first generation (________) reappeared again, always. Genetic generation abbreviations P1= _________________________ F1= _________________________ F2=_________________________ Mendels findings 1. Mendel concluded that each organism has 2 factors called ________________ that control each trait _________________ are different gene forms that determine the different form of the trait For example the gene for _____________ has an allele for tall and another for small Typically we use upper and lower case letters to identify these ____=tall allele and _______=short allele Genes can either be homozygous or heterozygous ______________________ has the same 2 alleles ie TT or tt ______________________ has different alleles ie Tt 2. Principle of Dominance = some alleles are dominant and will ____________ a recessive allele So ______ or ____________ will both be tall, whereas tt will be short Dominant genes are represented by upper case letters and recessive (non-dominant) by lower case 3. Noticed that alleles segregate when forming gametes Also noticed alleles segregate independently of each other – ____________________ _________________________ Monohybrid crosses illustrate Mendel’s findings A monohybrid cross is one that looks at only ____________ specific trait and how it segregates Easy to do this using the _____________________ square method Determining Genotype and Phenotype Genotype refers to the allele _____________ of a gene, the actual gene alleles For example the genotype of the punnett square is ¼ TT, ½ Tt, and ¼ tt This gives a genotypic ratio of _______________ Phenotype refers to the trait the is expressed by the organism or what it __________ ________ Since both TT and Tt are tall, the phenotype of the punnett square is ¾ tall and ¼ short The phenotypic ratio is ______________ Dihybrid crosses Dihybrid crosses look at _______ different traits passed on from parents Ex: In peas, seed shape & seed color R = round Y = yellow r = wrinkled y = green Dihybrid Cross Example One Parent is RRYY (__________________________) The other is rryy (___________________________) So RRYY X rryy Step 1: find all possible gamete _____________________by using FOIL (First Outer Inner Last) There will always be ________ different combinations in dihybrid Crosses Possible gametes: RY RY RY RY x ry ry ry Step 2: Set up ___________ punnett square and put possible gametes from parents on top and side, then fill in squares for possible offspring All offspring are heterozygous for both seed shape and seed color - RrYy, what is their phenotype and genotype? Now cross two F1 plants. RrYy x RrYy Possible gametes: ____ ____ ____ ____ x ____ ____ ____ ____ Phenotypic Ratio for a Dihybrid Cross: For this cross, find the number of each - round yellow : round green : wrinkled yellow : wrinkled green ___/16 round yellow (R_Y_) ___/16 round green (R_yy) ___/16 wrinkled yellow (rrY_) ___/16 wrinkled green (rryy) Phenotypic Ratio = ___ : ____ : ____: ____