Carbon Compounds
advertisement

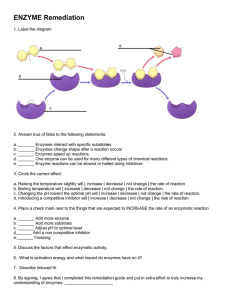
Carbon Compounds Organic Chemistry – The study of all compounds that contain carbon. Draw a carbon atom showing all subatomic particles. What so special about Carbon? • Can form up to four covalent bonds • Can form single, double, or triple bonds • Can bond to other carbons forming long chains and rings Carbon Compounds • Many compounds in cells are so large they are referred to as macromolecules: giant molecules. • Macromolecules are formed by a process known as polymerization. • Monomer: the smaller units that are joined together. • Polymer: the larger unit formed by joining monomers. Carbon Compounds • Dehydration Synthesis: The process where a water molecule is released each time a monomer is joined to a polymer or monomer. • Hydrolysis: The process where a water molecule is use to remove a monomer from a polymer. Carbon Compounds Four Groups of Organic Macromolecules: 1. 2. 3. 4. Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins Carbohydrates Elements: • Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen • 1:2:1 Ratio of C, H, O Function • Main source of energy for cells Monomers: • Called monosaccharides • Examples: Glucose Galactose Fructose Carbohydrates Polymers: • Disaccharides: made • Polysaccharide: made up of several of two monomers. monomers. • Example: – Starch: stores energy in plants. – Glycogen: stores energy in animals. – Cellulose: provides support for plant cells Nucleic Acids Elements: • Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Nitrogen Monomer: Nucleotide • Each nucleotide contains three parts: – Phospahte Group – Sugar – Nitrogenous Base Label the sugar, phosphate, and base as well as the functional groups. Nucleic Acids Polymer: polynucleotide • Polynucleotides are formed when the phosphate group of one nucleotide binds to the sugar of another nucleotide. Function: • Provides instructions to the cell on how to make proteins • Allows genetic information to be passed on from one generation to the next. Lipids Elements • Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen “Monomers” • Glycerol • Fatty Acid Chains • 3 fatty acids attach to a molecule of glycerol to make a triglyceride What functional groups are present in glycerol and fatty acids? Lipids Examples of Lipids: • Wax, Fats, Oil, Steriods/Hormones, Cholesterol Functions • Store energy • Lipids are nonpolar, so they can act as waterproof coverings • Steroids and hormones are lipids that send messages to cells. Lipids Look at the structures of the fatty acids and explain the differences between saturated, unsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Proteins Elements • Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Sulfur (CHNOPS) Monomer: amino acid • What functional groups are in an amino acid? • R group is different for each amino acid • 20 different amino acids found in nature Proteins Polymer: polypeptide • A peptide bond forms between the amine group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of another. Function: – Speeds up chemical reactions – Provides structure and supports – Helps transport material in and out of cells Proteins Protein Structure: Proteins can only function properly if they have the proper shape Levels of Protein Structure: • Primary Structure: the sequence of amino acids. • Secondary Structure: the folding or coiling of the polypeptide chain. • Tertiary Structure: the complete 3D arrangement of polypeptide chain. • Quaternary Structure: the arrangement of the different polypeptide in a protein. 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Metabolism: All living need to carry out chemical reactions in order to stay alive. Energy is released or absorbed whenever chemical bonds are formed or broken in a chemical reaction. • Exergonic Reaction: any chemical reaction that releases energy. – Sometimes occur spontaneously – Sometimes energy is needed to start an exergonic reaction. – Activation Energy: the energy needed to get a chemical reaction started. 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Examples of exergonic reactions 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes • Many of the chemical reactions • Enzymes: proteins that speed up the in cells have activation energy chemical reaction of that is too high and occur to cells. slow in order for the cell to (Enzymes are survive. biological catalysts) • To overcome this problem cells make catalysts: a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy. 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes • Explain how the enzyme affects the chemical reaction. • Does the enzyme have any affect on the product of the reactants? 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes How enzymes work? • The substrate (reactant) binds to a site on the enzyme called the active site. – The substrate and the active site have complimentary shapes. – Each enzyme can only bind to a specific substrate. Animation 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes • After the chemical reaction occurs in the enzyme, the product are released. • The enzyme can then be used over and over again if more substrates are available. 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Regulation of Enzyme Activity • Most enzymes work the best at certain pH and temperature. • Denaturation: a change in the shape of the enzyme. – Cause the enzyme to ineffective because the active site and the substrate no longer fit together. – Changes in pH and increases in temperature can denature enzymes. Animation 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes • Some enzymes can be turned on and off by regulator molecules that bind to the enzyme. Regulation of Enzyme Activity • Enzymes work best at certain pH levels and temperatures. – Most enzymes in humans work best at 37 C • Denaturation – a change in the enzymes shape. – Heat and pH can cause denaturation • Some enzymes can be turned on and off – Lactose intolerance Explain why enzymes cannot work if they change shape. Making a Polymer • The glue contains long strands of molecules like spaghetti. • If the long molecules slide past each other easily, then the substance acts like a liquid because the molecules flow. • If the molecules stick together at a few places along the strand, then the substance behaves like a rubbery. • Borax is the compound that is responsible for hooking the glue’s molecules together to form the putty-like material Making a Polymer 1. Measure 20 ml of solution a into a small beaker 2. Use a graduated cylinder to measure 10 ml of solution B, add it to the beaker. • Add food coloring if you want 3. Stir with a glass rod and knead with fingers 4. Put it into a plastic cup and cap. Label with your name and pick up at the end of the day SUDAN III – Pos. Lipids Honey Egg Oil Lettuce Gelatin Butter Same Same Orange Same Same Orange Carbohydrates Benedicts Iodine - Yellow - Yellow - Yellow - Blue + Yellow - Blue - Yellow - Blue - Yellow - Blue + Yellow - Blue Potato Apple Water Unkno wn Same Same Same Same - Sudan Black Yellow Yellow Yellow + - Green Green Blue Green + - Protiens Biuret Yellow Purple + Blue Blue Purple + Blue - + + + Blue Blue Blue Blue - Y axis B A C D X axis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What letter represents the product? What letter represents the reactant? What letter represents the activation energy? How should the x and y axis be labeled? Is the reaction exergonic or endergonic? Explain Naming Carbon Compounds • Hydrocarbon: any organic compound that contains only the elements, hydrogen and carbon • Organic Prefixes • Indicates the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain Meth- (1) Hex- (6) Eth- (2) Hept- (7) Prop- (3) Oct- (8) But- (4) Non- (9) Pent- (5) Dec- (10) Naming Carbon Compounds Organic Suffixes Series Ending Formula Bonding Alkane -ane CnH2n+2 Single Alkene -ene CnH2n Double Alkyne -yne CnH2n-2 Triple • Indicates the types of covalent bonds that are present in the hydrocarbon chain • Identifies the series to which it belongs Name the following compounds Draw the structure for the following: ethyne hexane Naming Carbon Compounds • Functional Groups: An atom or group of atoms, that replaces hydrogen in an organic compound and that defines the structure of a family of compounds and determines the properties of the family. • Refer to the functional group handout. Organic Molecules Quiz 1. Does the structure represent a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide? 2. What was released when the monomer were bonded together? 3. What functional group is contained in this molecule? 4. Is this molecule saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated? 5. To make a fat, what other type of molecule is necessary? Organic Molecule Quiz 6. What type of organic compound is shown to the right? 7. What is the function of this organic compound? 8. What is the monomer of this organic compound? 9. Identify the structure below: 10. What is the difference between hydrolysis and dehydration synthesis? Organic Molecule Quiz • 2-Butene • pentane • Ethyne • 2-propanol Organic Practice Quiz 2 Name the following hydrocarbons 1.C3H4 5. 2.C8H18 3.C3H6 4. 6.