Biochemistry BILL Standards
advertisement

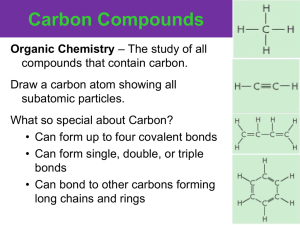
Unit 1 BILL Standards Chemistry of Life The following standards are everything that you should know for the next test. I’m giving this to you now so you can be working on it over the next few weeks. You could probably even answer them in class while we learn about it! So, answer these in your BILL book. Remember, be detailed when answering and include any pictures or drawings if that will help you learn and remember the information. You are basically creating your own study guide. The standards should be highlighted or written in a different color pen. This is due the day of your next test: September 24/25 Chapter 2 Vocab – Define the following terms (Go to http://quizlet.com/46651426/chapter-2-chemistryof-life-flash-cards/) atom nucleus electron element isotope compound ionic bond ion covalent bond molecule van der Waals forces hydrogen bond cohesion adhesion mixture solution solute solvent suspension pH scale acid base buffer monomer polymer carbohydrate monosaccharide lipid nucleic acid nucleotide Biochemistry 1. Draw and label a helium atom (atomic mass 4, atomic number 2) 2. Draw and label a carbon-12 atom 3. What is an isotope? How are they used in science? 4. List and describe the two main types of bonds. 5. How are they similar? How are they different? 6. What are Van der Waals forces? Use this gecko video to help you: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gzm7yD-JuyM Properties of Water 1. Draw and label a water molecule 2. Label the “positive” side and “negative” side from number 1 3. Draw 3 water molecules sticking together with hydrogen bonds. 4. Define Adhesion and give an example of it 5. Define Cohesion and give an example of it 6. Identify the solvent, solute and solution in a mixture of sugar and water. pH 1. Draw and label a pH scale 2. What do buffers do? protein amino acid chemical reaction reactant product activation energy catalyst enzyme substrate Unit 1 BILL Standards Chemistry of Life 3. Group the following terms: alkaline, acid, HCl, extra H+ ions, extra OH- ions, base, soaps, pH 10, pH 3. Biomolecules 1. Compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids 2. Describe the role of each type of biological molecule within a living system 3. Identify a biological molecule based on its formula and structure; draw a glucose, lipid (triglyceride) ,amino acid, and nucleotide. 4. What properties are unique to each biomolecule (How can you tell them apart?) 5. Describe the major role of each biomolecule in biological structure and metabolism 6. Fill in the following chart Biomolecule Monomer Polymer Sketch general structure Function Example Enzymes 1. Label the products and reactants in a chemical reaction 2. Label a general reaction graph (products, reactants, activation energy) 3. Describe the environmental effects (pH, temp) on enzyme activity and explain why these affect enzymes (sketch a graph to show the impact of these on enzyme function) 4. Give specific examples of enzymes and why they are important in the human body 5. Describe the chemical structure of proteins, including amino acids, peptide bonds, and polypeptide formation, 6. Explain the importance of structure and function for enzymes. 7. Explain the lock and key (induced fit) models for enzyme activity. 8. Describe the effects of enzymes on reaction rates, including on activation energy requirements