10 -1 Solutions & Mixtures 1.
advertisement

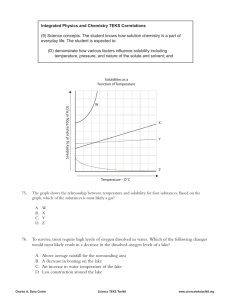
Name ____________________________________ Period ____________ 10 -1 Solutions & Mixtures 1. What is a Solution a. Solutions consist of two basic components: i. Solute- substance that dissolves ii. Solvent- substance that does the dissolving 1. In aqueous solutions water is the solute b. Different solutes have different solubility’s: i. Soluble- able to dissolve ii. Insoluble- unable to dissolve iii. Solubility - The most amount of a substance that will dissolve in a water at a certain temperature 1. More soluble substances have a higher solubility 2. less soluble substances have a lower solubility c. Solutions can have different amounts of solutes dissolved into them i. Saturated- The most solid a solution a solution can hold at a certain temperature. ii. Unsaturated- A solution that holds less solute than it can at a given temperature (you can still dissolve more.) iii. Supersaturated- A solution that holds more solute than it can at a certain temperature. 2. What is concentration a. Consentraion – the amount of solute dissolved in the solvent b. concentration is usually calculated using the following general formula amount of solute (g) % concentration = x 100 % amount of solvent (g) + amount of solute (g) 1. % concentration = ppt = 1/1000 ppm= 1/1000000 ppb= 1/1000000000 2. Example: a 5 % solution = 5 pph = 50/1000 ppt = 5000/1000000 ppm = 50000ppb 5 100 = 1000 = 3. Example: What is the % concentration of salt if 25 g of salt is dissolved in 125 g of water? 4. Example: What is the % concentration of sugar if 10 g of sugar is dissolved in 240 g of water? 1. The most common way to quantify concentration is with moles? 1. Molarity(M) - moles of solute divided by liters of solvent 𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒(𝑛) 𝑀= 𝐿𝑖𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑆𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡(𝐿) 2. What is the molarity of a solution formed by mixing 10.0 g of sulfuric acid with enough water to make 100.0 mL of solution? 3. How many grams of bromine are needed to prepare 0.500 L of a 0.0100 M solution of bromine in water? 4. Describe how would you prepare 100.0 mL of 0.7500 M potassium nitrate? 5. What volume of 0.600 M sodium hydroxide can be prepared from 4.8 g of solute? 10-2 Solubility Curve 1. How can you determine how much solute will dissolve in a solution? a. Solubility curves are a graphical way of determining the concentration of saturated solutions at a given temperatures b. How to read solubility curves: i. The solution is saturated if the amount of solute dissolved lands on the line ii. The solution is unsaturated if the amount of solute dissolved lands below the line iii. The solution is supersaturated if the amount of solute dissolved lands above the line 2. Most solid solutes increase in solubility as temperature increase 3. Gasses tend to decrease in solubility as the temperature of the solution decreases. (this is why warm soda tastes flat) 4. Acids and Bases are the most common solutions a. Acids – acids are substances that dissolve in water to give off hydrogen ions (protons) i. Acids Turn blue litmus paper red, (Red litmus paper stays red) ii. Acids Taste sour iii. They are usually ionic substances (H+ions) iv. Their formulas usually start with H. v. Ex) H2SO4 sulfuric acid b. Bases – bases are substances that dissolve in water to remove hydrogen ions i. Turn red litmus paper blue (Blue litmus paper stays blue) ii. Bases taste bitter. iii. Ex) Ca(OH)2 calcium hidroxide c. Neutralization Reaction- when acids and bases react together they neutralize each other, and form a ionic salt and water Acid + Base → Salt + Water H2SO4 + Ca(OH)2 → CaSO4 + H2 O 1. pH Scale- the pH scale is used to measure how acidic or basic substances are A. How do you get stuff out of water a. Heterogeneous Mixtures can be separated by filtration i. Precipitate – solid Material remaining on the filter is called the ii. Filtrate - The liquid that goes through the filter paper b. Homogeneous Mixtures can be separated by Distillation i. Distillation- a chemical method that separates homogeneous mixtures by boiling them 1. Distillation works because the different substances in the mixture have different boiling points 2. Because these substances have different boiling points you can boil one substance in the mixture without boiling the others 3. This separates the water from whatever is dissolved in it (salt, metals, ions, acids and bases)