C D HILDHOOD EVELOPMENT
advertisement

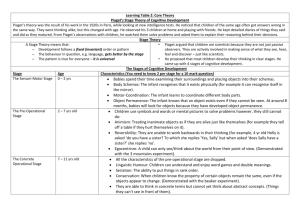
CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT THE BEGINNING! Fetus receives oxygen and nutrients from placenta Placenta acts as screen to keep out harmful substances-not a perfect screen. Teratogens-substances that break through placenta that are harmful. Viruses, toxins, and drugs Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) THE DEVELOPING BRAIN Nervous system immature. Maturation- biological growth process; uninfluenced by experience.. HOWEVER, experience does affect development. Teratogens- harmful effects COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Jean Piaget-believed that the way children think and solved problems depends on stage of cognitive development. Cognition-mental activities Schemas-mental frameworks(your view of the world based on your own experiences) Assimilation- relating new experiences to existing schemas Accommodation-adapting your schemas to reflect your new experiences PIAGET’S STAGES OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Sensorimotor stage (birth-2 yrs old) Object permanence Preoperational stage (2-6/7 yrs old) Conservation Concrete Operational stage (about 7-11 yrs old) Formal Operational stage (12 and up) ( beginning of abstract thinking) SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT Stranger anxiety-commonly displayed by infants Attachment-emotional tie with another person Body contact Familiarity Responsiveness Body contact What’s more important? Being held or fed? Familiarity Critical period-attachment bond forms Imprinting- certain animals form attachments very early in life; humans do not imprint. Responsiveness Affects whether a child is securely or insecurely attached. PARENTING PATTERNS Authoritarian-discipline is strict and often physical. High expectations of maturity. Permissive- rarely discipline. Low expectations of maturity. Authoritative- discipline is moderate with talking and negotiating. Which one is most effective??