Lifespan Development
advertisement

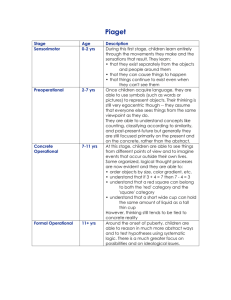
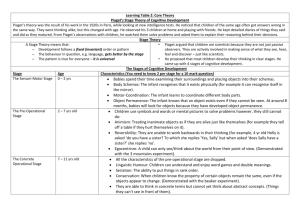
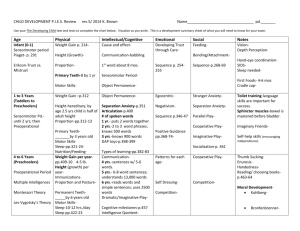
Developmental Psychology I 7-9% Of AP Psychology Exam Development includes the processes and stages of growth from conception across the lifespan. Includes changes in physical, cognitive, moral and social behaviors. Pre-Natal Development • Germinal Stage = 1-2 wks (Zygote) • Embryonic Stage = 2 months (heart, nerv syst, etc.) • Fetal Stage = remainder of pregnancy(organs…) Risks During Pregnancy ILLNESSES -RUBELLA -TERATOGENS -DRUGS -ALCOHOL Video: The Biology of Prenatal Development Take notes as you view the video: Infancy Infacy Physical Development Growth rate declines but is faster than any other post natal period Neo-Natal Reflexes (until about 4 months) such as: Babinski (big toe moves toward the top surface of the foot and the other toes fan out after the sole of the foot has been firmly stroked) Startle Reflex Grasping, Stepping, Rooting, Pursing lips, Withdrawal from pain Infancy - Cognitive Development Preference for facelike patterns 6-12 mo = remember, recognize, & react 12 mo = reasoning & higher level cognitive functions https://www.youtube.com /watch?v=4o-VplYrqBs Development of Knowledge Theory = Piaget Building blocks of human dev = SCHEMAS Generalized mental representation Assimilation = using existing schemas & apply to new info Accommodation = change schema (ex: butterfly flies, but is not a bird) Four Stages 1. Sensorimotor birth – 2 yrs 2. Preoperational 2-7 yrs 3. Concrete Operational 4. Formal Operational 7-11 yrs 11 into adulthood •Infant = learn about the world through senses and body movements 1 to 4 mo = Learn to combine two reflexes 4 to 8 mo = Improve hand- eye coordination 8 to 12 months • Intentional behavior •Learn certain actions lead to certain results •Imitates others •Love playing Peek-A-Boo •Learn Object Permanence 12 to 18 mo = • Trial and error: Push a cracker off a high chair and watch it fall to the floor. Then does it again •Can find hidden objects •Understands that objects exist independently 18 to 24 mo= experiment mentally as well as physically •They think about what they are going to do before they do it • Ages 2 to 7 •Basic Mental operations start replacing sensorimotor activities as the primary way to learn •Make-believe play is used to create and express all kinds of mental images Children learn mostly by language and mental images I “eated” my apple No, it’s ate Then I “ated” my apple Everyone views the world like I do I don’t want to go to sleep! I’m not tired! Use feeling to solve problems rather than logic He hurt my feelings so I hit him! •learning multiple classification– ability to understand that an object may fit into more than one category •learning seriation—the ability top order groups of things •They think the same amount of liquid is more when poured into a tall think glass. •To them taller means more! My birthday is before Christmas and after Halloween •Children may not be aware of what is real and what is make-believe http://www.ted.com/talks/alison_gopnik _what_do_babies_think?language=en#