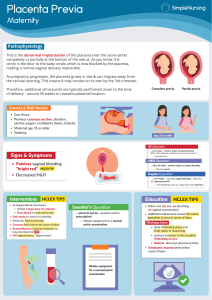
MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. MCN 4 PLACENTA PREVIA - implantation of the placenta in the lower uterine segment CLASSIFICATION LOW- LYING - The placenta encroaches the lower segment of the uterus but does infringe on the cervical os MARGINAL - the placenta touches, but does not cover the top of the cervix PARTIAL - The placenta partially covers the top of the cervix COMPLETE - The placenta completely covers the top of the cervix PREDISPOSING FACTOR Multiparity 80% Advanced maternal age (older than 35 yrs old in 33% cases) Multiple gestation Previous cesarean section Uterine incisions Prior placenta previa (12x greater) ASSESMENT Painless, bright red vaginal bleeding after 7th month of pregnancy Soft, non-tender abdomen; relaxes between contractions FHR stable and within normal limits unless maternal shock is present Signs of infection may be present DIAGNOSIS Transabdominal ultrasound shows location of the placenta and confirms suspicious of placenta previa NURSING INTERVENTIONS No admission vaginal examination; if a vaginal examination is to be performed, double set-ups (vaginal and cesarean) must be provided Take and record VS, assess bleeding, and maintain a perineal pad count. Weigh perineal pads before and after use to estimate blood loss Assess for shock and administer oxygen as indicated Monitor FHR continuously Enforce strict bed rest to minimize risk to fetus (side-lying) Monitor Hgb and Hct; prepare for cesarean if bleeding persists Administer IV therapy and/or blood replacement PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. Prepare client for ambulation and discharge (may be within 48 hours of last bleeding episode) Instruct client to return to hospital if bleeding recurs to avoid intercourse until after birth Proper handwashing and toileting to prevent infection ABRUPTIO PLACENTA - premature separation of a normally implanted placenta after the 20 th week of pregnancy, typically with severe hemorrhage ETIOLOGY - causes is unknown RISK FACTORS INCLUDE: - Uterine anomalies - Multiparity - Preeclampsia - Previous cesarean section - Renal or vascular disease - Trauma to the abdomen - Previous third trimester bleeding - Abnormally large placenta - Short umbilical cord TYPES OF ABRUPTIO PLACENTA CONCEALED (CENTRAL) HEMORRHAGE - Placenta separates centrally - large amount of blood accumulates under the placenta EXTERNAL (MARGINAL) HEMORRHAGE - Placenta separates marginally - blood flows under the membranes and through the cervix ASSESSMENT • Intense localized uterine pain, with or without vaginal bleeding - Concealed if center of the placenta separates and margins are intact; darkred blood may/may not be evident with partially detached placenta at margins • Uterus firm to boardlike, with severe continuous pain • Uterine contractions • Uterine outline possibly enlarged or changing shape FHR present or absent (hyperactivity then cessation of fetal movements ASSOCIATED FINDINGS Severe abruption placenta may produce such complication: Renal failure Disseminated intravascular coagulation PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. Maternal and fetal death Hypofibrogenemia THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTIONS LABORATORY AND DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS -Ultrasound may be able to identify the extent of abruptio. TREATMENT • Replacement of blood loss • WITH MODERATE OR SEVERE SEPARATION OR MATERNAL/FETAL DISTRESS: Emergency cesarean birth • WITH MILD SEPARATION WITHOUT FETAL DISTRESS AND IN THE PRESENCE OF SOME CERVICAL EFFACEMENT AND DILATION: Induction of labor maybe attempted NURSING INTERVENTIONS • continue evaluate maternal and fetal physiologic status, particularly: Vital sign Bleeding Electronic fetal and maternal monitoring tracings Decreasing urine output Never perform vaginal or rectal exam or take any action that would stimulate uterine activity. • If bleeding could not be stopped with bedrest emergency C-section Is indicated • Maintain in bedrest in left lateral recumbent. Assess for shock. Assess abdominal pain, tonicity of abdomen, perineal pads if bleeding evident, Hgb & Hct levels Administer IV therapy and/or blood replacement. Observe for signs of DIC such as seepage of blood from IV site or incisional DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ABRUPTIO PLACENTA AND PLACENTA PREVIA CHARACTERISTICS ABRUPTIO PLACENTA PLACENTA PREVIA rd ONSET 3 trimester 3rd trimester th (common 8 month) BLEEDING May be concealed, external dark Mostly external, small to profuse hemorrhage, or bloody amniotic fluid in amount, bright red PAIN & UTERINE Usually present; irritable uterus, Usually absent; soft uterus TENDERNESS progresses to board-like consistency FHR May be irregular or absent Usually normal PRESENTING PART May or not be engaged Usually engaged SHOCK Moderate to severe depending on the Usually not present unless extent of hemorrhage bleeding is excessive DELIVER Immediate delivery, usually by C Delivery maybe delayed section depending on size of fetus and amount of bleeding PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION (PIH) COMPLICATIONS H- hemolysis E- elevated L- liver enzymes L-low P- platelet Inc. response to normal conc of endogenous vasopressin Vasospasm Shifting of fluid from intravascular to interstitial Kidneys Vascular effect Decrease glomerular filtration 25% vasoconstriction Increase serum conc. Of uric acid Decrease circulation Edema Decrease organ perfusion Decrease urine output Increase BP + protein If mother has PIH Delay production of phosphatidyl GLYCEROL Intermediate component in the metabolism of CHO & lipids Decrease in surfactant production 2 phospholipids Increase in RDS PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 lecithin sphingo MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. PREGNANCY- INDUCED HYPERTENSION -A disorder occurring during pregnancy characterized by a triad of symptoms: edema, hypertension, and proteinuria occurring after the 20th to 24th week of gestation and disappearing 6 weeks after birth. INCIDENCE Occurs primarily in primiparas below 17 years and above 35 years of age Multiparity Chronic hypertension Diabetes mellitus Severe nutritional deficiencies Multiple pregnancy Trophoblastic disease COMMON TYPES OF PIН GESTATIONAL HYPERTENSION • Increased BP during pregnancy that resolves within 6 weeks after birth • No edema or proteinuria is present MILD PREECLAMPSIA ELEVATED BP - A systolic increase of 30 mm Hg and diastolic increase of 15 mm Hg or above baseline X 2 at least 6 hours apart or BP above 140/90 WEIGHT GAIN - More than 1lb/wk in the third trimester EDEMA - Hands and in front of tibia (1+ or 2+) PROTEINURIA - Equal/> 1 gm/24 hr (1+ or 2+ on qualitative testing) SEVERE PREECLAMPSIA All Changes associated with mild preeclampsia, plus ELEVATED BP - Systolic equal/> 160 mm Hg or diastolic equal/> 110 mm Hg X 2 at least 6 hours apart with client restricted to bedrest EDEMA - Generalized edema, puffiness of face (3+ or 4+) PROTEINURIA - Equal/> 5 g/24 hour (3+ or 4+ on qualitative testing) HYPERREFLEXIA - 4+, CLONUS OLIGURIA - Equal/< 400-500 ml OTHER Severe headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, retinal arteriolar spasms, spots before eyes, nausea and vomiting, epigastric pain, irritability, pulmonary edema, elevated liver enzymes, hemolysis ECLAMPSIA All changes associated with preeclampsia, plus tonic and clonic convulsions (grand mal seizure), cerebral hemorrhage, liver rupture, and coma. HELLP SYNDROME (HEMOLYSIS, ELEVATED LIVER ENZYMES, LOW PLATELET COUNT) Occurs with little warning and often with no previous signs of PIH RUQ pain occurs in 90% of women; proteinuria may occur Liver enzymes are elevated; platelets and RBCs are low PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. Blood smear reveals broken cells Schistocytes or burr cells) Occurs after 28 gestation or 48-72 hours after birth SIGNS OF WORSENING PREECLAMPSIA Rapid rise in BP Rapid weight gain Generalized edema Increased proteinuria Epigastric pain, marked hyperreflexia, and severe headache, which usually precede convulsions in eclampsia Visual disturbances Oliguria (<120 ml in 4 hours) Irritability Severe nausea and vomiting SIGNS OF WORSENING PREECLAMPSIA BLOOD CHEMISTRY • Rise in Hct • Elevated uric acid and BUN • Elevated serum creatinine • Decrease in RBCs, platelets QUALITATIVE URINALYSIS • Increase in albumin output (proteinuria) • Decrease in urinary output (oliguria) Question: What is the most common aura associated with Eclamptic clients? Answer: epigastric pain GUIDELINES FOR PREVENTION OF PΙΗ Sound nutrition counseling during pregnancy and lactation. Increase CHON to 60 g daily in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters. 200 Infant aspirin and Motrin may be used daily. Caloric intake increased by 10% during pregnancy. Severe caloric restriction harmful during pregnancy Restriction of Na is harmful during pregnancy, can result in fld.and electrolyte imbalance. (reduced circulatory vol.) Diuretics contraindicated during pregnancy. (Hypovolemia and depletes essential nutrients for mother and child) PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. PIH TREATMENT MILD PREECLAMPSIA Bedrest in the left lateral recumbent position. High-protein diet Ambulatory care: frequent visits to obstetrician. frequent rest periods with feet elevated Sedative to ensure rest and sleep Administer magnesium sulfate. SEVERE PREECLAMPSIA Hospitalization and complete bedrest. Administration of electrolyte replacements, sedative antihypertensives such as diazepam or Phenobarbital or an anticonvulsant such as Phenytoin Magnesium sulfate given IV by infusion pump or IM to prevent or limit seizures. Albumin concentrate to increase renal flow and correct the hypovolemia. Antihypertensives: Hydralazine HCI (Aprésoline) and Diazoxide (Hyperstat) Insert Foley catheter Labor induction or cesarean birth once symptoms are under control ECLAMPSIA Hospitalization and complete bedrest Institute seizures precaution -Minimize all stimuli. -Darken room. - Limit visitors. - Pad bedsides and bedrails. Check V/S and lab. values frequently. Administer medications as ordered such as Magnesium sulfate, Diazepam, Phenobarbital or Phenytoin. Prepare for C-section when seizures stabilized. Continue observations 24-72 hours postpartum. NURSING MANAGEMENT Monitor BP: every 15 minutes during critical phase; every 1-4 hours as condition improves. Insert foley catheter; measure and record output, protein level and specific gravity Maintain high-protein diet with normal salt intake. Assess for edema of face, arms, hands, legs, ankles and feet. Also assess for pulmonary edema. Weigh client daily. Assess deep tendon reflexes every 4 hours, Assess for placental separation, headache and visual disturbance, epigastric pain and altered level of consciousness. Monitor FHR. Observe for signs of labor and bleeding. PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. Be prepared for an induced or emergency cesarean birth. Institute seizure precautions. (Seizures may occur 72 hours after delivery Address emotional and psychosocial needs. MAGNESIUM SULFATE MECHANISM OF ACTION Prevents seizures and blocks neuromuscular transmission. SIDE EFFFECTS: FLUSHING, THIRST, ABSENCE OF DEEP TENDON REFLEXES, RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION, CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS, CARDIAC ARREST. DECREASED URINARY OUTPUT NURSING IMPLICATIONS Assess for magnesium toxicity. Assess for depressed patellar reflex. Assess deep respirations. Signs of paralysis Assess magnesium levels every 6 hours (Therapeutic range: 4-8 mg/dl) Antidote: Calcium gluconate Stop administration if signs of toxicity or if urinary output <30 cc/hr Question: What medication should be at the bedside of a patient of Mg SO4? Answer: calcium gluconate DIAZEPAM (VALIUM) MECHANISM OF ACTION STOPS SEIZURE ACTIVITY SIDE EFFECTS: HYPOTENSION, DROWSINESS, LETHARGY, BLURRED VISION, RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION, NAUSEA, VOMITING, URINARY RETENTION AND CONSTIPATION NURSING IMPLICATIONS • INFUSE DRUGS SLOWLY OVERTIME. • ASSESS VITAL SIGNS. • STRICT I&O. • STRICT BEDREST. • HAVE VALIUM AND CALCIUM GLUCONATE AT BEDSIDE PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3 MCN 102 REVIEWER 4 CREATED BY: JERLYN R. ANTIHYPERTENSIVES: HYDRALAZINE HCL (APRESOLINE) AND DIAZOXIDE (HYPERSTAT) MECHANISM OF ACTION RELAXES ARTERIAL SMOOTH MUSCLE TO REDUCE BP PERIPHERAL VASODILATOR USED FOR SEVERE HYPERTENSION SIDE EFFECTS: HEADACHE, DIZZINESS, DROWSINESS, EPIGASTRIC PAIN HYPOTENSION, TACHYCARDIA, ANGINA, HYPERGLYCEMIA AND SODIUM AND WATER RETENTION NURSING IMPLICATIONS MONITOR VITAL SIGNS ESP. PR AND BP CHANGE POSITIONS SLOWLY AND AVOID SUDDEN POSITION CHANGES. LIE DOWN FOR A WHILE IF DIZZINESS PERSISTS. SMALL, FREQUENT FEEDINGS. REPORT IMMEDIATELY IF SEVERE CONSTIPATION PERSISTS, UNEXPLAINED FEVER. MALAISE MUSCLE OR JOINT ACHES CHEST PAIN SKIN RASH, TINGLING AND NUMBNESS. PROPERTY OF JEFEM <3