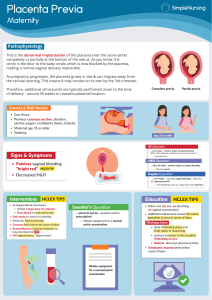
Placenta Previa in Pregnancy Case study Presented to the College of Nursing In partial fullfilment of the requirements in NCM 109 RLE Care of mother and Child at Risk or with Problems OBW Submitted to: Sonia Adefuin Delantar, RN, MAN,LPT Submitted by: Gleisy G. Saguno BSN 2 1 Table of Contents Title page………………………………….………………………………..………….………..1 Tale of Contents…………………………………………………………………………………2 Foreword……………………………………………………………...…………………….…...3 Dedication…………………………………………...…………………………………………..3 Objectives………………………………………………………………………………………..3 Introduction……………………………………………………………………………………...4 Patients Data…………………………………………………………………………………….6 Physical Assessment…………………………………………………………………………….7 Laboratory Result/Diagnostic Result……………………………………………………………9 Anatomy and Physiology……………………………………………………………………….12 Pathophysiology………………………………………………………………………………...13 Medical Management…………………………………………………………………………...14 Nursing Care Plan………………………………………………………………………………17 FDAR…….……………………………………………………………………………………..21 Drug Study……………………………………………………………………………………..22 Discharge Plan…………………………………………………………………………………27 Prognosis………………………………………………………………………………………28 Reference………………………………………………………………………………………29 2 I. Foreword Placenta previa is a severe complication of pregnancy and is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage, which often endangers the lives of pregnant women. In recent years, an increasing number of researchers believe that the placenta previa position has an important influence on the pregnancy outcome. In 80% cases it is found in multiparous women. The incidence increase beyond the age of 35, with high birth order pregnancies and in multiple pregnancy. The incidences approximately 4-5 per thousand pregnancies. During the course of clinical treatment of placenta previa, nursing student should be aware of not only the types of placenta previa (complete and partial or marginal placenta previa) but also the position of placental attachment (e.g., anterior uterine wall, posterior wall, whether the placenta overlaps a surgical scar from a previous caesarean section). Some researchers have suggested that complete placenta previa, which is characterized by placental attachment to the anterior wall covering the uterine scar, should be defined as pernicious placenta previa. Placenta previa is a medical emergency that needs immediate management because it can lead to serious maternal and fetal complication, even death of one or both of them. Once diagnosed, close observation must be done to monitor the status of both the mother and the baby. Any untoward attending physcian. Complications can be diminished if the diagnosis and management are done at an early stage. II. Dedication This Case study is wholeheartedly dedicated to my beloved parents, who have been my source of inspiration and gave me strength when I thought of giving up, who continually provide my moral, spiritual, emotional, and financial support. To my clinical Instructor Ma’am Sonia Delantar, who help me and provide a format to make a final output . To Almighty God, thank you for guidance, strength, power of mind, protection, skills and for giving me a healthy life. To the Nursing student and Future researcher’s, who can use this case study as their guide or reference. III. Objectives To define Placenta Previa and its causes. To Identify possible risk factors for Placenta Previa Describe appropriate prevention and treatment of Placenta Previa. Describe the implications of Placenta Previa on the health and well-being of the mother and her new baby. 3 IV. Introduction Placenta previa The placenta is a structure that develops in the uterus during pregnancy, providing oxygen and nutrition to and removing wastes from your baby. The placenta connects to your baby through the umbilical cord. The placenta grows during pregnancy and feeds the developing baby. The cervix is the opening to the birth canal. In most pregnancies, the placenta is located at the top or side of the uterus. In placenta previa, the placenta is located low in the uterus. The placenta might partially or completely cover the cervix, as shown here. Placenta previa can cause severe bleeding in the mother before or during delivery. A C-section delivery might be required. Placenta previa occurs when a baby's placenta partially or totally covers the mother's cervix the outlet for the uterus. Placenta previa can cause severe bleeding during pregnancy and delivery. Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix. Causes During pregnancy, the placenta moves as the womb stretches and grows. It is very common for the placenta to be low in the womb in early pregnancy. But as the pregnancy continues, the placenta moves to the top of the womb. By the third trimester, the placenta should be near the top of the womb, so the cervix is open for delivery. Sometimes, the placenta partly or completely covers the cervix. This is called a previa. There are different forms of placenta previa: Marginal: The placenta is next to the cervix but does not cover the opening. Partial: The placenta covers part of the cervical opening. Complete: The placenta covers all of the cervical opening. Placenta previa occurs in 1 out of 200 pregnancies. It is more common in women who have: An abnormally shaped uterus Had many pregnancies in the past Had multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets Scarring on the lining of the uterus due to a history of surgery, C-section, or abortion In vitro fertilization Women who smoke, use cocaine, or have their children at an older age may also have an increased risk. 4 Symptoms Bright red vaginal bleeding without pain during the second half of pregnancy is the main sign of placenta previa. Some women also have contractions. In many women diagnosed with placenta previa early in their pregnancies, the placenta previa resolves. As the uterus grows, it might increase the distance between the cervix and the placenta. The more the placenta covers the cervix and the later in the pregnancy that it remains over the cervix, the less likely it is to resolve. Risk factors Placenta previa is more common among women who: Have had a baby Have scars on the uterus, such as from previous surgery, including cesarean deliveries, uterine fibroid removal, and dilation and curettage Had placenta previa with a previous pregnancy Are carrying more than one fetus Are age 35 or older Are of a race other than white Smoke Use cocaine Complications If you have placenta previa, your health care provider will monitor you and your baby to reduce the risk of these serious complications: Bleeding. Severe, possibly life-threatening vaginal bleeding (hemorrhage) can occur during labor, delivery or in the first few hours after delivery. Preterm birth. Severe bleeding may prompt an emergency C-section before your baby is full term. Exams and Tests Your health care provider can diagnose this condition with a pregnancy ultrasound. Treatment Your provider will carefully consider the risk of bleeding against early delivery of your baby. After 36 weeks, delivery of the baby may be the best treatment. Nearly all women with placenta previa need a C-section. If the placenta covers all or part of the cervix, a vaginal delivery can cause severe bleeding. This can be deadly to both the mother and baby. If the placenta is near or covering part of the cervix, your provider may recommend: 5 Reducing your activities Bed rest Pelvic rest, which means no sex, no tampons, and no douching Nothing should be placed in the vagina. You may need to stay in the hospital so your health care team can closely monitor you and your baby. Other treatments you may receive: Blood transfusions Medicines to prevent early labor Medicines to help pregnancy continue to at least 36 weeks Shot of special medicine called Rhogam if your blood type is Rh-negative Steroid shots to help the baby's lungs mature An emergency C-section may be done if the bleeding is heavy and cannot be controlled. V. Patients Data Name: Patient G Age: 30 y.o. Sex: Female Birthdate: January 12, 1990 Marital Status: Married Address: Bgry. 6 Evangelista St. Lucena City, Quezon Province Religion: Roman Catholic Citizenship: Filipino Height:5’6 ft Weight: 57 kg Parity (GP): G3 P2 LMP: May 1, 2020 EDC: February 7, 2021 AOG: 42 weeks 2/7 days age of gestation Chief complaints upon admission: Painless vaginal bleeding with bright red blood. Diagnosis: Placenta Previa Attending Physician: Dr. Maria Teresa Obispo Corpuz Date Initiated: October 10, 2021 6 Care plan by: Gleisy G. Saguno Date admitted: October 10, 2020 VI. Physical Assessment Head and Neck: Facial symmetry Absence of scalp tenderness Absence of lesions nor masses noted Iris are black, pupils are equally round and reactive to light accomodation With white and clear sclera Pinna is the same as color with the fscial skin, smooth and aligned with eye level Able to hear sound clearly as claimed Absence of pain, inflamation or drainages With patent and clear nostrils Absence of nasal flaring, congestion or drainages Tongue and uvula are centrally positioned Lingual tonsils at the posterior portion of the tongue. Has good oral hygiene, no halitosis Jugukar vain not destended No swollen lymph nodes as palpated Thorax: Symmetrical chest wall upon movement and breathing on room air Breath sounds are clear Cardiovascular: Absence of chest pain Normal peripheral pulse Genitourinary: Minimal vaginal sotting up to 2-3 pads per day No discharges nor foul smell 7 Able to void freely Urine is clear No pain in urination Gastrointestnal: Mild hypogastrip pain Abdomen is soft With mild to moderate uterine contraction With active bowel sounds No abdominal tenderness Musculoskeletal: No Physical deformities nor paralysis With active ROM Joints can move freely without any resistance or pain Neurologic: Awake, alert and orianted to time, person and place Understands written and spoken language and responds accurately Able to follow commands General Appearnace: Well Cooperative Weak-looking Vital Signs: Temperature:36.9 PR:60 RR:14 BP:100/60mmHg 8 VII. Laboratory Result/ Diagnostic Result DIAGNOSTIC TEST/PROCEDURE PATIENT’S RESULT NORMAL VALUE/RESULT CBC: WBC 14.64 3.98-10.04 RBC 4.22 3.93-5.22 HGB 11.8 11.2-15.7 HCT 34.6 34.1-44.9 PLT 403 182-369 PATIENT 11.7 10-17 PT: CONTROL 14.8 INR 0.83 2-4(therapeutic) PATIENT 36.2 26.1-36.3 CONTROL 35.1 APTT: ABO RH O POSITIVE ANTI BODY SCREEN NEGATIVE NEGATIVE RPR NON-REACTIVE NON- REACTIVE HBSAG NON-REACTIVE NON-REACTIVE 9 Diagnostic Result Transvaginal Ultra Sound in plancenta Previa Placenta covers internal os and extends over the os by over 5 cm. This type will not migrate sufficiently by term and will likely require a cesarean section. Placenta covers internal os and extends over the os by under 2 cm. This type will often migrate sufficiently by term and allow vaginal delivery. 10 Pitfall in the Diagnosis of Placenta Previa A prominent myometrial contraction in the lower uterine segment adjacent to the placenta may simulate a previa. The echotexture of the contaction is usually slightly different to the placenta, and resolution over time will usually help distinguish contraction from previa. 11 VIII. Anatomy and Physiology The placenta is normally implanted into the wall of the uterus where there are many blood vessels that supply the baby with oxygen and nutrients. Placenta is normally located in the upper part of the uterus. With marginal placenta previa, the placenta implants near the bottom part off the uterus and may block part of the cervix. The baby may need to be delivered by caesarean section. 12 IX. Pathophysiology 13 X. Medical Management 14 15 Medical Management- Depends on the Gestational age and severity of bleed. A. Strict bedrest B. IV - large bore catheter (16 gauge) C. CBC, type & screen, platelet count, fibrinogen, bleeding time D. If HCT less than30% tranfuse E. No Pelvic Examinations F. Adequate hydration, accurate I & O G. Frequent Vital Signs H. Ultrasound I. Restore blood loss, correct coagulation defect Treatment of placenta previa involves bed rest and limitation of activity. Tocolytic medications, intravenous fluids, and blood transfusions may be required depending upon the severity of the condition. 16 XI. Nursing Care Plan Deficient Fluid Volume related to Active Blood Loss Secondary to Disrupted Placental Implantation Assessment Diagnosis Planning Subjective: Deficient Fluid Volume related to Active Blood Loss Secondary to Disrupted Placental Implantati on Within 8 hours of Nursing intervention the Patient will maintain fluid volume at a functional level possibly evidenced by adequate urinary output and stable vital signs. “Ang dami pong lumalabas na dugo sa puerta ko, di parin tumitigil yung pagdaloy at pag agos ng dugo”.- As verbalized by the patient. Objective: Bleeding episodes (100 ml), 24 hrs duration Abdomen hard when palpated Manifests body weakness Intervention Independent Establish Rapport Monitor Vital Signs Assess color, odor, consistency and amount of vaginal bleeding; weigh pads. Assess hourly intake and output. To gain patient’s trust To obtain baseline data Provides information about active bleeding versus old blood, tissue loss and degree of blood loss. Provides information about maternal and fetal physiologic compensation to blood loss. Assessment provides information about possible infection, placenta previa or abruption. Warm, moist, bloody environment is ideal for growth of microorganisms. Assess abdomen Detecting for tenderness or increased in rigidity- if present, measurement of measure abdomen abdominal girth at umbilicus suggests active (specify time abruption. interval) Assess baseline data and note changes. Monitor FHR. Rationale Assess SaO2, skin color, temp, Evaluation The Goal Met after 8 hours of nursing intervention the: Patient maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by adequate urinary output and stable vital signs. T:37°C RR:18 cpm PR: 80 bpm BP:120/80 mmHg Assessment provides 17 Fetal heart rate less than normal (90 bpm) moisture, turgor, capillary refill. Decreased urine output Increased urine concentratio n Pale, cold, clammy skin Vital Signs: Temperature: 36.9 °C PR:60 RR:14 BP:100/60m mHg Assess for changes in LOC: note for complaints of thirst or apprehension Dependent: Provide supplemental O2 as ordered via face mask or nasal cannula at 10-12 L/min. Initiate IV fluids as ordered. information about blood vol., O2 saturation and peripheral perfusion. To detect signs of cerebral perfusion. Intervention increases available O2 to saturate decreased hemoglobin. For replacement of fluid vol. Loss. Position decreases pressure on placenta and cervical os. Left lateral position improves placental perfusion. Monitor lab. Work Lab Work provides as obtained: Hgb & information about Hct, Rh and type, degree of blood loss; cross match for 2 prepares for possible units RBCs, transfusion. urinalysis, etc. Ultrasound provides Scheduled for info about the cause ultrasound as of bleeding ordered. Position Pt. in supine with hips elevated if ordered or left lateral position. 18 Decreased cadiac output related to altered contractility Assessment Subjective: “Ang dami pong lumalabas na dugo sa puerta ko, di parin tumitigil yung pagdaloy at pag agos ng dugo”.- As verbalized by the patient. Objective: Dysrhythmi as Prolonged capillary refill cold clammy skin Diagnosis Decreased cadiac output related to altered contractilit y Planning Intervention Within the 8 Independent: hours of Establish Rapport nursing Monitor Vital intrvention Signs the: History taking will Patient Assess patient participate condition and Review lab data demonstrate activities that reduce Monitor BP & the workload Pulse frequently of the heart. Provide will information on test Patient procedures manifest Provide adequate hemodynami rest & Reposition c stability. client Encourage relaxati on techniques Elevate HOB Encourage use of relaxation techniques Rationale Evaluation The Goal To gain patient’s Met after trust the 8 To obtain baseline hours of data nursing To determine intrvention contributing factors the: To assess contributing factors For comparison Patient can with current participate normal values and To note response to activity demonstra To gin patient’s te participation activities that reduce To promote venous the return workload of the To alleviate stress heart. & anxiety To promote circulation To decrease tension level Dyspnea Restlessness Variations in BP reading Vital Signs: T: 36.9°C PR:60 RR:14 Patient can manifest hemodyna mic stability as evidenced by a vital sign of BP: 120/80 mmHg PR: 80 bpm 19 BP:100/60m mHg Ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased HgB concentration in blood and hypovolemia Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Subjective: “Ang dami pong lumalabas na dugo sa puerta ko, di parin tumitigil yung pagdaloy at pag agos ng dugo”.- As verbalized by the patient. Ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased HgB concentrati on in blood and hypovole mia Within 8 hours of nursing intervention the: Patient will demonstrate behaviors to impove circulation. Patient will demonstrate increased perfussion as individually appropriate Independent : Establish Rapport Objective: Restlessness Confusion Irritability Manifest Body Weakness Capillary refill more than 3 sec Oliguria Vital Signs: Monitor Vital Signs Assess patient condition Note customary baseline data, BP, weight, lab. Determine presence of dysrhythmias Perform blanch test Rationale To gain patient’s trust To obtain baseline data To assess contributing factors For comparison with current findings To identify alterations from normal To identify and determine adequate perfusion Check for To determine Homan’s Sign presence of thrombus formati on. Encourage quiet & To lessen O2 restful environment demand Elevate HOB To promote circulation Encourage use of To decrease relaxation tension level techniques Evaluation The Goal was met after the 8 hours of nursing intervention the: Patient demonstrat e behaviors to impove circulation . Patient demonstrat e increased perfussion as individuall y appropriat e as evidence by a vital signs of T:37°C PR: 80 bpm RR:18 cpm BP:120/80 mmHg 20 T: 36.9 °C PR:60 RR:14 BP:100/60m mHg FDAR Date 10/10/20 9:00 am Focus Deficient Fluid Volume related to Active Blood Loss Secondary to Disrupted Placental Implantation Data, Action, Responce D:“Ang dami pong lumalabas na dugo sa puerta ko, di parin tumitigil yung pagdaloy at pag agos ng dugo”.- As verbalized by the patient. Appears pale, cold, clammy skin, manifests body weakness. Has decreased urine output and increased urine concentration. With the bleeding episodes of 100 ml in 24 hrs duration. The abdomen is hard when palpated. Fetal heart rate less than normal (90 bpm).Vital signs of T:36.9°C, PR:60, RR:14 BP:100/60mmHg. A: Establish Rapport, monitor Vital Signs, assess color, odor, consistency and amount of vaginal bleeding; weigh pads, assess hourly intake and output, assess baseline data and note changes. monitor FHR, assess abdomen for tenderness or rigidity- if present, measure abdomen at umbilicus, assess SaO2, skin color, temp, moisture, turgor, capillary refill, assess for changes in LOC: note for complaints of thirst or apprehension, provide supplemental O2 as ordered via face mask or nasal cannula at 10-12 L/min., Initiate IV fluids as ordered, position Pt. in supine with hips elevated if ordered or left lateral position, monitor lab., work as obtained: Hgb & Hct, Rh and type, cross match for 2 units RBCs, urinalysis, etc. Scheduled for ultrasound as ordered. R: Patient maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by adequate urinary output and stable vital signs. T:37°C, RR:18 cpm, PR: 80 bpm, BP:120/80 mmHg 21 XII. Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate Therapeutic Action Contraindication Generic name: Ferrous Conditions: Ferrous sulfate replaces A high amount of Sulfate iron, an oxalic acid in essential urine component in Iron metabolism the formation disorder causing of hemoglobin. increased iron Brand storage name:Feosol iron supplement Sickle cell used to treat or anemia Anemia from Classification: prevent low pyruvate kinase Iron Products blood levels of iron and G6PD deficiencies an overload of iron in the blood A type of blood disorder where the red blood cells burst called hemolytic anemia An ulcer from too much stomach acid Ulcerative colitis An inflammatory condition of the intestines Problems with food passing through the esophagus Diverticular disease Excess iron due to repeated blood transfusions Toxicity Constipation Dark stools Diarrhea Stomach pain Stomach cramps Indication Irondeficiency anaemia Safe Dose Dosage: mg Route:PO Frequency: TID Upset stomach Nausea Vomiting 22 27 Sodium Chloride Therapeutic Generic name: Sodium Chloride 0.9 % Brand Name: Sterile Saline Diluent TipLok Syringe Syrex Classification: Normal Saline Action Contraindication Sodium Chloride used as an additive for total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and carbohydratecontaining IV fluids. Contraindicated in patients with: Absorb and transport nutrients Maintain bloo d pressure Maintain the right balance of fluid Transmit nerve signals Congestive heart failure Severe renal impairment Toxicity Conditions of sodium retention Edema Liver cirrhosis Redness Pain Swelling at the injection site Swelling hands/ankles / Feet Irrigation during electrosurgical procedures Contract and relax muscles Muscle cramps unusual wea kness headache Nausea Extreme drowsiness Mental/moo d changes (such as confusion) Indication Safe Dose Indicated for As directed by the treatment a physician. of hypertonic extracellular dehydration Dosage is or dependent hypovolaemi upon the age, a weight and clinical Sodium Chlo condition of ride Injection the patient as . well as laboratory Indicated as a source of determinatio water and ns. electrolytes. Dosage 250 to 500 Indicated for use as a ml/hour. priming Route: IV solution in hemodialy Frequency: sis procedure PRN s. Seizures Vein irritation Thrombophl ebitis Extravasatio n of solution may cause tissue injury. Allergic 23 reaction, including: ra sh, itching/s welling (especially of the face/tongue/t hroat) Severe dizzi ness Trouble breathing Magnesium Sulfate Therapeutic Generic Name: Magnesium Sulfate Brand name: MgSO4 Classification: Mineral and electrolyte replacements/ supplements Action Contraindication Toxicity Magnesium Conditions: Circulatory sulfate is a collapse amount of High nutritional Respiratory supplement in magnesium in the paralysis hyperalimentat blood ion. It is a Low amount of Hypothermia cofactor in calcium in the Pulmonary enzyme blood edema systems involved in Myasthenia gravis Depressed neurochemical reflexes A skeletal muscle transmission disorder Hypotension and muscular Progressive excitability. Flushing muscle weakness Drowsiness with carcinoma Decreased kidney function Severe renal impairment Indication Safe Dose Indicated for replacement therapy in magnesium deficiency Dosage: 12g/h intravenously (IV) Route: IV Frequency: STAT Depressed cardiac function Diaphoresis Hypocalcem ia 24 Hypophosph atemia Hyperkalemi a Visual changes Dexamethasone Acetate Therapeutic Action Contraindication Generic name: Dexamethaso ne Acetate Dexamethasone may be given to promote the development of the lungs in the fetus. Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug or its components and in those with systemic fungal infections. Brand name: Decadron DSC Dexamethasone stimulates the synthesis of Classification enzymes needed to decrease the :antiinflammatory inflammatory response. immunosuppr essant Toxicity Increased appetite Irritability Difficulty sleeping (insomnia) Indication Inflammatory conditions, allergic reactions, neoplasias, dexamethason e (systemic) Safe Dose Injectable suspension 4mg/mL (generic) 10mg/mL (generic) Swelling in your ankles and feet (fluid retention) Dosage:10 mg Heartburn Route: Oral Muscle weakness Impaired wound healing Frequency: TID Increased blood sugar levels 25 Medication Card 26 XIII. Discharge Plan Patient Education: Counsel patients with placenta previa about the risk of recurrence, and instruct them to notify the obstetrician caring for their next pregnancy regarding their history of placenta previa. Medicines: Tocolytics: Tocolytics are given to stop contractionsbecause your baby is not ready to be born. Contractions are when the muscles of your uterus tighten and loosen. Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be given to help treat or prevent an infection caused by bacteria. Antibiotics may be needed before you give birth if you have an infection in your uterus. You may also need antibiotics after your baby has been born. Blood thinners: Blood thinners prevent clots from forming in your blood. They may be given if you are at risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT is a condition in which clots form inside your blood vessels. Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell him or her if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency. Follow up with your obstetrician as directed: You may need to return for repeat ultrasounds. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits. Manage placenta previa: You may need to be on bedrest until your baby is born. Ask your healthcare provider which activities you may do while you are on bedrest. Do not douche or have sex. These may cause bleeding. Safety plan: You will need to have a safety plan until your baby is born. Make sure you live, or are staying a short distance away from the hospital. You will also need to make sure someone is ready to take you to the hospital if needed. Contact your obstetrician if: You feel abdominal cramps, pressure, or tightening. Your heart is beating faster than normal for you. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care. 27 Seek care immediately or call 911 if: You have any amount of bleeding from your vagina. You are having severe abdominal pain or contractions. You feel faint or too weak to stand up. You suddenly feel lightheaded and short of breath. You have chest pain when you take a deep breath or cough. You cough up blood. Further information Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. XIV. Prognosis Patient G was diagnosed with Placenta Previa after several diagnostic procedures. After 2 days of applying intervention to patient G in the hospital, the patient was stable and reduce further signs and symptoms occurred. Reduce the pain and bleeding of the cervix. Patient G maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by adequate urinary output and stable vital signs.Patient G demonstrate behaviors that impove circulation. Upon discharge, patients VS are as follow: BP 120/80, HR 85 bpm, RR 20 bpm and temperature of 36.8 degrees celsius. This concludes that the patient has a good prognosis. 28 XV. Reference rancois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18. Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46. Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000900.htm?fbclid=IwAR24TI6Gy8BoSYb78vapkvCx13y0Aa1nVGj9jZmt0Xms58I8q2JKrlBPkc http://www.fetalultrasound.com/online/text/33032.htm?fbclid=IwAR1Xztiu2bPh7fR_ieG2ZpZqOO8szCh8JNpTOHCwjeHPSvOgokmWu_oOs4 https://www.drugs.com/cg/placenta-previa-discharge-care.html https://nurseslabs.com/3-placenta-previa-nursing-care-plans/ https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/abnormalities-ofpregnancy/placenta-previa https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/262063-medication#1 https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000900.htm https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/placenta-previa/symptoms-causes/syc20352768#:~:text=Placenta%20previa%20(pluh%2DSEN%2D,pregnancy%20and%20during%2 0your%20delivery. https://www.medscape.com/answers/260998-168209/what-are-the-most-common-tocolyticagents-used-to-treat-preterm-labor https://go.drugbank.com/categories/DBCAT000759 https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/sodium-chloride-injection-route/description/drg20068846 https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-145556/sodium-chloride-0-9-intravenous/details https://www.parents.com/pregnancy/complications/health-and-safety-issues/placenta-previa/ 29