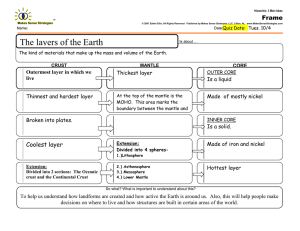
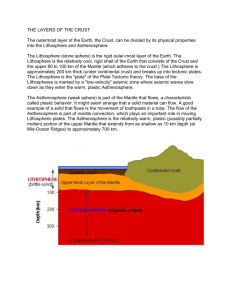
Isostasy dynamics of the Earth’s crust Isostasy:
advertisement

Isostasy and the dynamics of the Earth’s crust Isostasy: the condition of equilibrium, comparable to floating, of the units of the lithosphere on the asthenosphere. Lithosphere Asthenosphere Altitude (km) Area of Earth’s surface (106 km) Hypsographic Curve for the Earth Rigid mantle ρ = 3.3 g/cc Depth (km) continental crust oceanic crust mean altitude 823 m mean depth 3729 m Percentage of Earth’s surface Mars Earth Venus aesthenosphere The physical state (solid / partially solid / liquid) of the different layers of the Earth depends on which is higher - the melting temperature or the actual temperature. mantle core outer rock p.sol. solid liquid A=M A<M A>M inner iron Graph of Age vs. Depth of Ocean Floor Mid-Ocean Ridge Trench Why might the ocean floor sink as it gets older? Mid-ocean ridge time Trench Oceanic crust ρ = 3.0 g/cc lithosphere Rigid mantle ρ = 3.3 g/cc Asthenosphere mantle ρ = 3.25 g/cc ρlithosphere = ρcrust x %thicknesscrust + ρmantle x %thicknessmantle Mid-ocean ridge time Trench Oceanic crust ρ = 3.0 g/cc Rigid mantle ρ = 3.3 g/cc Asthenosphere mantle ρ = 3.25 g/cc age = 0 my ρlithosphere = 3.0 g/cc x 1.0 + 3.3 g/cc x 0 = 3.0 ρlithosphere << ρasthenosphere Mid-ocean ridge time Trench Oceanic crust ρ = 3.0 g/cc Rigid mantle ρ = 3.3 g/cc Asthenosphere mantle ρ = 3.25 g/cc age = 10 my ρlithosphere = 3.0 g/cc x .4 + 3.3 g/cc x .6 = 3.18 ρlithosphere < ρasthenosphere Mid-ocean ridge time Trench Oceanic crust ρ = 3.0 g/cc Rigid mantle ρ = 3.3 g/cc subduction Asthenosphere mantle ρ = 3.25 g/cc age = 100 my ρlithosphere = 3.0 g/cc x .06 + 3.3 g/cc x .94 = 3.28 ρlithosphere > ρasthenosphere Mid-ocean ridge time Oceanic crust ρ = 3.0 g/cc Rigid mantle ρ = 3.3 g/cc Trench Continent ρ = 2.7 g/cc ρ = 3.3 g/cc Asthenosphere mantle ρ = 3.25 g/cc Can continents be subducted into the mantle? Isostasy - equilibrium position of lithosphere “floating” on asthenosphere. continental lithosphere oceanic lithosphere Asthenosphere oceanic lithosphere Other ways to change the isostatic equilibrium of the crust • Heating / cooling of the lithosphere – Changes the density of the crust = buoyancy – Caused by passage of plates over mantle hot spots • Heating / cooling of the mantle – Rising plumes of hot mantle displace the lithosphere upward – Sinking slabs of cold mantle pull the lithosphere downward Continental Crust acrust sea level hcrust = acrust + dmantle dmantle tcrust ρ = 2.65 g/cc tmantle (displaced) ρ = 3.25 g/cc Archimedes’ principle: tcrust x ρcrust = tmantle x ρmantle Example acrust sea level dmantle tcrust ρ = 2.65 g/cc tmantle How much mantle will be displaced by 45 km of crust? tcrust x ρcrust = tmantle x ρmantle 45 x 2.65 = tmantle x 3.25 ρ = 3.25 g/cc Archimedes’ principle: tcrust x ρcrust = tmantle x ρmantle 45 x 2.65 = tmantle 3.25 36.7 = tmantle Example acrust sea level dmantle 36.7 km = tmantle 45 km = tcrust If dmantle = 8.0 km tcrust ρ = 2.65 g/cc tmantle How high above sea level will the crust be? acrust = tcrust - ( dmantle + tmantle) ρ = 3.25 g/cc Archimedes’ principle: tcrust x ρcrust = tmantle x ρmantle acrust = 45 - ( 8 + 36.7) acrust = .3 km