Freshwater - Saltwater Interactions Freshwater - Saltwater Interface
advertisement
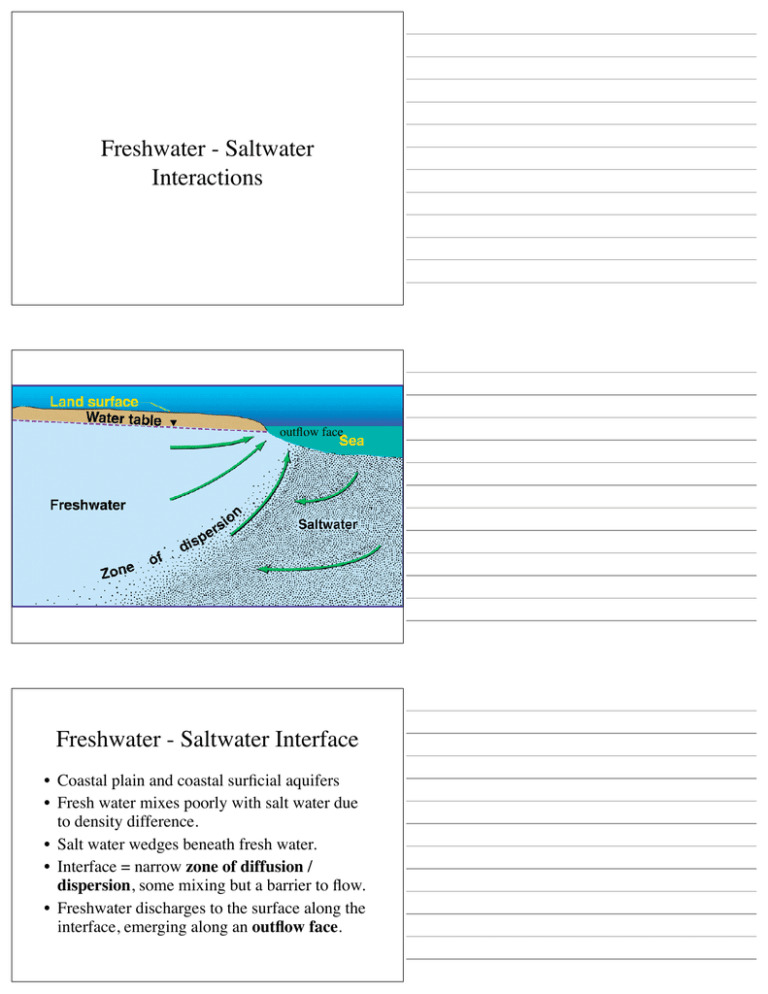
Freshwater - Saltwater Interactions outflow face Freshwater - Saltwater Interface • Coastal plain and coastal surficial aquifers • Fresh water mixes poorly with salt water due to density difference. • Salt water wedges beneath fresh water. • Interface = narrow zone of diffusion / dispersion, some mixing but a barrier to flow. • Freshwater discharges to the surface along the interface, emerging along an outflow face. Ghyben-Herzberg principle water table h Depth to interface is 40X water table elevation. z salty face fresh inter z = h (ρw / ρs - ρw) z = 40 h ocean Outflow Face • Freshwater is not static at interface. • Freshwater is flowing upward along the interface. • Creates a zone of freshwater discharge at the shoreline = outflow face. Ghyben-Herzberg principle water table h salty fresh face z Ideal inter z = h (ρw / ρs - ρw) z = 40 h ocean Outflow Face water table fresh Low Tide freshwater outflow face Cape Ann, Mass. inter Due to groundwater movement. face ocean salty Actual outflow face outflow face Paulson et al., 1998 Effect of tide on outflow seepage Salt water intrusion • Movement of the fresh-salt interface landward. • Passive encroachment – reduction in freshwater discharge – lowering of water table – interface moves slowly inland • Active encroachment – reversal of hydraulic gradient – interface moves rapidly inland – usually caused by pumping Passive encroachment Active encroachment Chloride ion concentration in water from a public supply well in Great Neck, Long Island. Stumm, 2001 Chloride ion concentration in water from a public supply well in Great Neck, Long Island (well was shut off due to salt contamination). Stumm, 2001 Saltwater wedge in North Shore Aquifer, Great Neck Long Island fresh salt Stumm, 2001 Saltwater upconing