File
advertisement

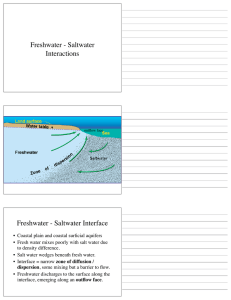
Science 8 Freshwater and Saltwater Systems Knowledge Objectives 1) Generally describe the distribution of water in Alberta, Canada and the world and understand water characteristics (glaciers, snow, polar icecaps, ground water, oceans) 2) Interpret graphs showing how much water is available for us to use. 3) Understand that fresh and salt water contain varying amounts of dissolved materials, particulates and biological parts and interpret information about the presence or amount of these in a water body. 4) Identify factors used to decide if water is potable (able to be consumed by humans) and understand water quality tests (do them and interpret them.) – clarity, salinity, hardness, invertebrates 5) Describe, in general terms, how to get fresh water from salt water using evaporation, distillation and reverse osmosis. 6) Describe the process of erosion and deposition due to wave action and water flow by: - identifying dissolved solids and sediment loads and identifying sources and endpoints for these materials - describing how waves and tides are made and how they affect the shoreline 7) Investigate and describe stream characteristics (slope, flow rate, stream profile) 8) Describe the process leading to the ocean basins and continental drainage systems (continental shelves and trenches) 9) Identify evidence of glacial action and analyze factors that affect growth and attrition (shrinking) of glaciers and polar ice caps. Student Notes 10) Describe the movement of ocean currents and their influence on regional climates (Gulf Stream, Labrador Current, El Nino and La Nina) 11) Investigate life forms found in fresh and salt water and identify and interpret examples of adaptations to these environments (describe fish and invertebrates found in a local freshwater environment) 12) Analyze factors that lead to the development of adaptations in species found in saltwater and freshwater environments. 13) Investigate and interpret examples of seasonal, short-term and long-term changes in populations of living things in aquatic environments (algae blooms, fish populations, cod and salmon depletion) 14) Analyze relationships between water quality and living things and judge (infer) the quality of water based on the life supported by it. 15) Analyze human water uses and identify the impacts resulting from different uses (pollution in ground and surface water from home and industrial use, effects of agriculture and forestry of stream flow and water quality.) 16) Identify current practices and technologies that affect water quality, evaluate environmental costs and benefits and identify and evaluate alternatives - Research - ways of ensuring safe water - an issue related to water – extension of Agrium gypsum pile or landfill site - use of secondary and tertiary water treatment - protection of a natural waterway - salinization of soils due to irrigation - eutrophication of ponds and streams due to excess phosphates used in fertilizer and detergents - proposal to export water resources 17) Learn about the role of scientific research in monitoring environments and supporting development of appropriate environmental technologies (aquatic monitoring) – guest speaker 18) Provide examples of problems that cannot be solved using science and technology alone (the need to prevent pollutants from entering aquatic environments, the need to avoid damage from ice sheets and ice bergs)