Document 14139754
advertisement

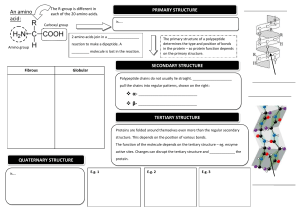
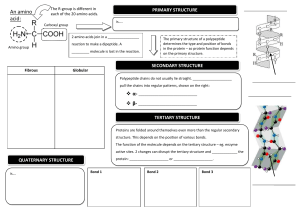
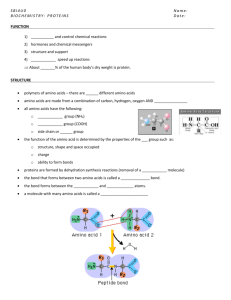
Proteins • Monomer: amino acid – Only twenty found in nature – Each has an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) – Monomers are joined together by peptide bonds. • Polymer: polypeptide – A protein is made up of one or more polypeptides. How can there be so many different proteins when there is only 20 amino acids? Proteins • Function: – Controls the rate of a reaction – Form bones and muscles – Transport substances – Fight disease • A combination of ionic, covalent, hydrogen and Van der Waals are responsible for 3D shape. • Any change in the shape of a protein will make it ineffective. Levels of protein organization Levels of protein organization A protein’s shape depends on four levels of structure 1. Primary Structure Is the sequence of amino acids forming its polypeptide chains 2. Secondary structure Is the coiling or folding of the chain, stabilized by hydrogen bonding 3. Tertiary Structure Is the overall three dimensional shape of a polypeptide 4. Quaternary Structure Results from the association of two or more polypeptide chains together-collagen