India & South Asia Review Global Studies Name _____________________________
advertisement

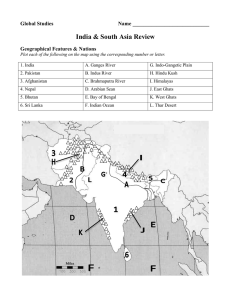
Global Studies Name _____________________________ India & South Asia Review Geographical Features & Nations Plot each of the following on the map using the corresponding number or letter. 1. India A. Ganges River G. Indo-Gangetic Plain 2. Pakistan B. Indus River H. Hindu Kush 3. Afghanistan C. Brahmaputra River I. Himalayas 4. Nepal D. Arabian Sean J. East Ghats 5. Bhutan E. Bay of Bengal K. West Ghats 6. Sri Lanka F. Indian Ocean L. Thar Desert Geography Size in Relation to US Subcontinent Monsoons General Total Population National Language Capital City India is 1/3 size of the U.S. Large, distinguishable part of a continent (South Asia is a subcontinent of Asia) Seasonal winds; the wet monsoon brings necessary rains to South Asia 1.3 billion Most commonly spoken is Hindi New Delhi Major Religious Majority – Hinduism; 2nd most common – Islam Groups Hinduism Reincarnation When, after death, the spirit is reborn into another living thing Karma One’s deeds in this life will affect one’s fate in a future life Dharma A person’s duty Atman A person’s soul or essence Moksha Sacred Animal When a person’s atman stops being reincarnated and becomes one with the Universal Spirit Cow Hindu Deities Brahman Universal Spirit Brahma Creator god Vishnu Preserver god that helps people do their dharma Shiva Destroyer god that ends life and then reincarnates it India & South Asia Review 2 Ganesh Civilizations Chronological Order of Indian Civilizations God that removes obstacles; God of journeys Indus, Aryan, Maurya, Gupta, Mughal Indus River Civilizations Location Indus River Valley (modern-day Pakistan) Cities Harappa and Mohenjo-daro Achievements Planned cities, plumbing, picture writing Aryans Description Light-skinned herders who came from from the northwest Impact on culture of India Hinduism, Sanskrit writing, caste system, cow being sacred Maurya Empire Asoka India’s greatest king who converted to Buddhism and then became nonviolent Gupta Empire Significance India’ Golden Age Mughal Empire Religion Islam (Muslim) Akbar Shah Jahan Leader that promoted religious tolerance and showed this by marrying a Hindu woman Mughal leader that built the Taj Mahal Taj Mahal Built by Shah Jahan, it was a tomb for his favorite wife India & South Asia Review 3 Caste System Caste System Hindu social organization based on spiritual purity What Determines Caste You are what your parents are Brahmins Highest caste; priests Untouchables Lowest group at the bottom of caste system Colonial Period East India Company Motivations for Imperialism European Colonial Power Direct & Indirect Rule Sepoy Rebellion Changes Made After Sepoy Rebellion Independence Mohandas Gandhi Mahatma British company that first to establish a relationship with India Make money and gain resources Britain Direct – when the country sends its own people to rule a colony Indirect – rules through local native rulers The British were trying to change Indian culture; the rumor that gun cartridges were greased with beef and pork fat started the fighting Britain made India a colony, Indians given British citizenship and freedom of religion Lawyer that started fighting for Indian rights in South Africa; moved back to India; Goals included: eliminating the Untouchable caste; peace between Hindus and Muslims; and Indian independence Means, “Great Soul”; nickname for Gandhi Civil Disobedience Satyagraha Refusal to obey unjust laws Amritsar Massacre Salt March British opened fire on crowd of peaceful Indian protesters; Indians became even more motivated to work towards independence Indian act of civil disobedience against the British tax on salt and British restrictions on salt production. Gandhi’s civil disobedience and peaceful protest India & South Asia Review 4 Partition of India Reason for Partition Year of Independence Modern India Indian National Congress India’s Main Rival Jawaharlal Nehru Cold War Nonalignment Kashmir Hindu India and Muslim Pakistan Muslim minority was afraid Hindu majority would not treat them fairly 1947 Hindu group that lead the Indian independence movement; after independence, the INC became India’s majority party Pakistan Leader of the INC and first prime minister of India India did not choose a side in the Cold War despite receiving aid form both the U.S. and the Soviet Union Northern region that is divided between India and Pakistan Indira Gandhi Daughter of Nehru; prime minister; way she addressed the Sikh minorities was controversial; assassinated Sikh Separatist Sikh religion has some Hindu and some Muslim aspects, but is a Movement minority and feel discriminated against; many want their own country Independence of West Pakistan was slow to help after a typhoon, India helped Bangladesh Bangladesh become independent from Pakistan Green Improving farming technology to increase output Revolution Rajiv Gandhi Indira’s son, prime minster; more capitalist; assassinated Current Government Type Government of India’s Claim To Fame Countries with nuclear weapons Parliamentary democracy Largest democracy in the world India and Pakistan India & South Asia Review 5