China Review Global Studies Name
advertisement

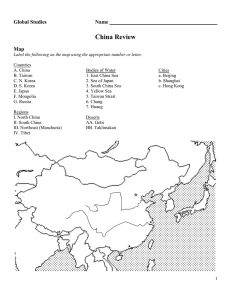
Global Studies Name China Review ***FILL IN THE MAPS ON YOUR OWN**** Map Label the following on the map using the appropriate number or letter. Countries A. China B. Taiwan C. N. Korea D. S. Korea E. Japan F. Mongolia G. Russia Regions I. North China II. South China III. Northeast (Manchuria) IV. Tibet Bodies of Water 1. East China Sea 2. Sea of Japan 3. South China Sea 4. Yellow Sea 5. Taiwan Strait 6. Chang 7. Huang Cities a. Beijing b. Shanghai c. Hong Kong Deserts AA. Gobi BB. Taklimakan 1 Geography & General Information Size in Relation to About the same size United States Capital City Beijing Description of Eastern 1/3 of the country is low-lying, fertile land. Region known as the Eastern Topography heartland because food is grown and most of population lives there Description of Western Mountains and desert; less population Topography Huang (Other Name) Chang (Other Name) Total Population Yellow River Largest Ethnic Group Han Traditional China Middle Kingdom Mandate of Heaven Scholar Elite Gentry Peasants Yangtze River Over 1 billion (approx. 1.2 billion) Term used by traditional Chinese dynasties to describe China- because they felt they were surrounded by less civilized people The Chinese belief that heaven and the gods granted the ruler a right to rule; The Zhou dynasty first used this idea Education allowed people to move up in society by passing imperial examinations and obtaining government positions Land owners Majority of the people who farmed the land; some owned plots of land; most were subsistence farmers Religion/Philosophy Confucianism (General Description) Filial Piety Founded by Confucius; it is a code of behavior based on the superiorinferior relationships where the superior teaches the inferior and the inferior honors and obeys the superior. Emphasizes education Respect for parents and elders Analects Book of Confucius’ teachings Taoism (General Description) Emphasized living in harmony with nature; its most recognizable symbol is the Yin/Yang which symbolizes balance 2 Lao Tzu Most famous Taoist philosopher Tao Te Ching Writings of Taoism supposedly authored by Lao Tzu Tao “the way of nature” Yin/Yang Symbol of Taoism representing the balance of opposites Ch’I Cosmic energy; the energy in all living things Buddhism (General Description) Siddhartha Gautama Religion that follows the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path; goal is to end suffering and reach Nirvana. It emphasizes living life following the Middle Way; its symbol is an eight-spoke wheel Prince from ancient Nepal; he set out to find and end to suffering and as a result established Buddhism. Became the Buddha. 1. Everyone suffers 2. Wants and desires cause suffering 3. If you stop wanting, you will end suffering 4. To end wanting, you need to follow the eightfold path Living life in the middle, avoiding extremes; according to Buddhism, if you live this way, you will not want anything and end suffering A philosophy that believes that people should be kept in line with strict rewards and punishments. Four Noble Truths Middle Way Legalism (General Description) Dynasties First Emperor’s Dynasty First Emperor’s Construction Projects Golden Age Dynasties Barbarian Invaders Name of Imperial Palace Name and Origin of Last Dynasty Qin Dynasty; Shi Huangdi declared himself first emperor of China after uniting it Built the First Great Wall. Had terracotta soldiers that guarded his tomb Tang and Song (time of prosperity and peace) Huns, Mongols, and Manchu The Forbidden City Qing (Manchu) They invaded China from the north (Manchuria) 3 Last Dynasty Opium War British wanted to balance trade with China so it sold opium (an addictive drug) to China. When the Chinese destroyed the opium, Britain attacked Treaty of Nanjing First of the unequal treaties; ended the Opium War; China had to pay $ to Britain, give up Hong Kong; led to foreign countries to establish spheres of influence Hong Kong British gained control of Hong Kong after China lost the Opium War; it remained under British control until 1997 Spheres of Influence Areas within a country where foreign countries have economic, political, or cultural control (NOT a colony) Taiping Rebellion Rebellion led by Hong Xiuquan who thought he was Jesus’ brother; took over 1/3 of China; 20 million died; crushed by Europeans; weakened China Boxer Rebellion Attempt to get foreigners out of China; secretly supported by Ci Xi; also crushed by Westerners; further weakened China Ci Xi A.K.A. Dowager Empress; ruled through son and nephew; opposed reforms that would have modernized China Pu Yi Last emperor of China; chosen by Ci Xi; lost position in Republican Revolution Republican China Republican Revolution Sun Yatsen Sun’s 3 Principles of the People The emperor was overthrown and a constitution established a republic Leader of the Republican Revolution; physician; he is considered father of the Chinese republic 1. democracy 2. nationalism 3 livelihood (jobs) Revolutionary China Nationalists Political party established by Sun Yatsen; battled Communists for control of China; lost and fled to Taiwan Chiang Kai-shek Leader of the Nationalists after Sun Yatsen Communists Mao Zedong Long March Rape of Nanking After years of chaos, warlords, and poor conditions for most of the people, established People’s Republic of China Leader of the Communists Communists fled attack by the Nationalists; Communists survived, regrouped and spread their ideas; inspirational story of birth of Communist China Horrible and violent attack by the Japanese on the Chinese city of Nanking during World War II 4 Karl Marx German philosopher who created Marxism/Communism Proletariat The working class; according to Marx, the workers would rise up, overthrow the bourgeoisie, and create a classless society China Under Mao Totalitarian State When the government has total control over the lives of the people. This occurred in communist China Propaganda Information, ideas, or rumors deliberately spread to help or harm a person, group, movement, institution, nation, etc. Great Leap Forward Mao’s attempt to modernize China quickly; huge communes formed; steel made in backyard furnaces; this plan was a failure; many starved Collectives & People farmed together to try to increase production; communes were Communes huge with dormitories and communal kitchens Cultural Revolution Mao’s attempt to revitalize communist spirit and win power struggle against moderates/experts; it was a failure; many jailed or even killed Red Guard The youth that were involved in the Cultural Revolution China After Mao Deng Xiaoping Tiananmen Square Uprising Moderate leader of China after Mao; opened China to foreign investment and made capitalist reforms Students organize a demonstration in the square to demand more democracy/freedom of speech; the government reacted violently 5