Document 14118623
advertisement

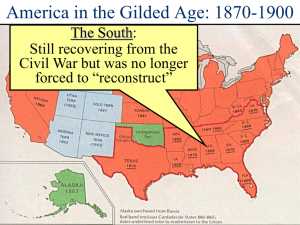
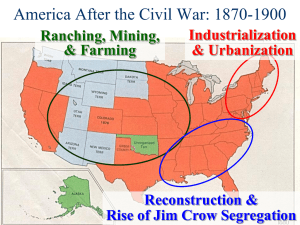
THE POST CIVIL WAR WEST RUGGED INDIVIDUALISM: Look back to your notes for page 461. Draw a picture of what a part of the Great Plains would look like based on the information: Railroad Growth, and the Federal Government’s role: “When it came to a choice between giving a particular tract to railroads or homesteaders, the homesteaders nearly always lost out.” Land Grants were given to railroad companies (49 million acres between 1850-­‐1870) 4 transcontinental railroads were thus created: Union Pacific/Central Pacific Line (1869) 3 others completed in 1883. Pacific Railway Act established a pattern for these grants. Between 1864-­‐1896, 10 new states were added to the Union: • Colorado, • Idaho, • Kansas, • Montana, • Nebraska, • Nevada, • North Dakota, • South Dakota, • Utah, • Wyoming. Plains Indians and U.S. Government Policy: -­‐various tribes with similar lifestyles. (hunting buffalo) “although they seemed the epitome of freedom, pride, and self-­‐reliance, the Plains Indians had begun to fall under the sway of white power.” Examples: Use of horses Metal good and tools Rifles, swords “however, like the whites’ liquor and diseases, horses and guns caused problems.” Policy of concentration: vague yet respected guidelines and borders instituted by whites to curb tribal warfare and keep Indian life in existence. -­‐an example of recognition of Indian tribes as sovereign nations. Indian Conflicts and Resistance: Government not interested in honoring agreements with Indians. 1. Sand Creek/ Chivington Massacre 2. Red River War Scanned by CamScanner 3. Wounded Knee 4. Battle of Little Big Horn/Custer’s Last Stand Most warfare against Indians was similar to Guerilla Warfare. Usually only one side of the battles were known to Americans. Violence shifted American Indian policy from concentration to reservation. Which was the last Indian tribe to “abandon the unfair battle”? Who was their leader? Dawes Severalty Act, 1887: reservation policy that broke up Indian land in to allotments. Had to stay in Indian tribal families for 25 years. Forced “Assimilation” of Native Americans. The Mining Boom: Discoveries of gold and silver created new towns very quickly. Most towns went “boom” then “bust” in favor of another one. Pikes Peake Comstock Lode Snake River Valley Black Hills “get rich quick” mentatlity for miners/prospectors. Deadwood, South Dakota prime example of a mining town. If so much gold and silver was found by prospectors and miners, why then were they not the chief beneficiaries of their OWN discoveries? Who WERE the chief beneficiaries of these discoveries? *For better or worse, mining was instrumental in the growth of America politically, economically, and socially. Cattle Kingdom: -­‐Industrial growth created a higher demand for food and crops. -­‐railroads made it easier to move food and crops. -­‐the idea of “The Long Drive” was born. Charles Goodnight and Oliver Loving: cattle drivers that drive 2000 cattle throughout the West. Techniques of the Long Drive: (pg. 469) -­‐Some famous Cattle Towns: Abilene, Wichita, Ellsworth, Dodge City, Caldwell. Open Range Ranching: -­‐Cowboys took out homestead claims along waterways to expand their ranches. Ranchers collaborated, thus creating huge tracts of open range land in which to raise cattle, sheep, etc… This system worked well: everyone profited, the land was kept free, and the animals stayed healthy. Overcrowding eventually became a problem, and ranchers got greedy. 1874, Joseph Glidden, Barbed Wire is invented. Drastically changes ranching, herding, long drives, etc… “Barbed Wire Wars” resulted. this, and overproduction brought an end to the boom times by 1888. What did the Homestead Act intend to do for American citizens? The Land Bonanza: -­‐homesteaders and businessmen competed for land and businesses usually won. Timber Culture Act of 1873 attempted to help homesteaders. Land laws overall were cleverly circumvented by wealthy businesses in addition to being poorly enforced. *Go back to your drawing of the Great Plains. Add as many new things to your picture that have been discussed in Chapter 15.