Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference
advertisement

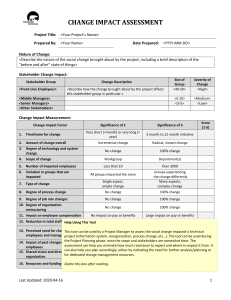
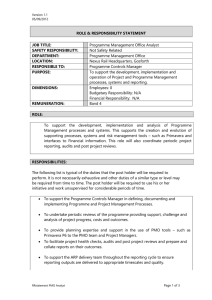
Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 Criteria for Evaluation of e-GovernanceToolkit Ahmed Al Arabi1 and K. Vizaya Kumar2 Bahrain has implemented e-Governance providing several services online to the people and the way the Government employees perform their duties have been drastically changed. Government has spent large sums of money in procuring and implementing the tool kit for e-Governance. However, there is not evaluation of the performance of the tool kit in terms of the functional performance as well as the economic performance. Though several authors have studied e-Governance, rarely any study has concentrated on the tool kit performance. It is also found that there are no standardized or accepted criteria for evaluation of the tool kit. Therefore, the authors have attempted as a beginning of comprehensive research on e-governance, to identify the criteria for evaluation of the e-Governance tool kit. The authors carried out the study in three stages, first, analysis of the literature and other reports to explore the existing knowledge through the works of other authors, second, in-depth interviews with the executives closely related to the use of eGovernance tool kit to draw the information from their mental models on the criteria to evaluate the tool kit. This resulted in near agreement of about 45 items. The authors have compiled them into nine constructs. In the third stage, the authors carried out Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) with about 16 Executives to determine the relative importance of the constructs inferred through the in-depth interviews and to develop the weightage to be given to each construct. This paper presents results of all the three stages and the finalized list of constructs and criteria under each construct to measure the performance of e-Governance tool kit. 1. Introduction: PMO considered as a new initiative when it comes to manage and execute a Program, program can be defined as “Group of projects that are related to each other in which the outcomes of these projects is contributing in the success of achieving the program objectives”. E-government Authority (eGA) is taken the credit for implementing such newly proposed concept within the Government sector because this concept is fully support the nature of work within the eGA as it is considered a project based organization. Recently eGA contracted with an expert consultancy firm (Booz&Co) to develop the new eGovernment Strategy for the upcoming five years 2011 - 2016, one of eGA strategic initiatives was to fully set up the PMO as part of this initiative the consultancy company proposed the new PMO toolkits to regulate the eGovernment Program. In General toolkits can be defined as “set of tools, especially one kept in a bag or box and used for a particular purpose” another definition is that Toolkits are “set of process, templates, guidelines and procedures that are bundled together to help in the process of executing a business function within an organization”, the concept of toolkits is wildly used in many organization to ensure the proper execution of the business functions and improvement when required. _______________________________________________________ 1 Post-Graduate Scholar and Professor of Industrial Management Ahlia University, MANAMA, Kingdom of Bahrain. E-mail: vkarumanchi@ahlia.edu.bh.; Phone: 00973 33709282. 2 Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 National eGovernment Strategy focuses on three toolkits that are expected to be implemented before the finalization of the national strategy 2016, one of them is the Smart Program Management Toolkit accordingly the PMO office with the support of the consultancy company developed the new PMO toolkit to streamline the PMO functions and improve the project management activities within the organization. Before the new PMO toolkit proposed the eGovernment PMO team was monitoring the execution of the program using an adhoc and structured method which was causing a lot of issues in terms of monitoring and controlling the execution of the project within the eGovernment Program. The usual practice was that each project will have project management plans (communication plan, issue management plan, risk management plan and other plans) based on the module proposed by the vendor executing the project, this approach is associated with a lot of issues that are impacting the nature of management and controlling the project also the quality of the deliverables might be impacted. Moreover, this technique was causing the eGovernment Authority and major issue of not been able to control the planning activities of the project because the vendor usually create the project plans based on his prospective which will have a negative impact on the control over the project execution activities. In later stages the project managers of the eGovernment Authority started to provide their input on the plans provided by the vendor but still another issues was occurring which is the in compliance with project plans prepared, for example usually the issue management plan will provide the project manager and project stakeholder with the direction on how the issues should be treated based on impact of the risk, what the PMO team have notice in the period before the new PMO toolkit proposed is that must of the project manager were dealing with issues (for example) without keeping in mind the instructions agreed and documented in the plans. Having said that PMO was not applying the roles as expected in terms of having an umbrella view (Program View) on the projects because of the lack of processes, Templates and procedures to regulate the way of running and monitoring the eGovernment program. Newly Proposed toolkit consist of processes and templates that will be used by the project stakeholder to ensure the proper execution, Monitoring, Control and escalation of the projects within the eGovernment Program also it will help the eGA in obtaining a good compliance Project Management Institute (PMI) Standard as they are considered as the governance body for Projects and Programs Management in the world (www.pmi.com). This study intended to identify the criteria evaluate the performance of the PMO toolkit. 2. Problem Definition & Opportunities: Some of the problems highlighted by the PMO chief during the preliminary interview can be summarized as follows; Unprepared users Adoption difficulties of the new toolkit and processes (resistant to change) Lack of Change management strategy Lack of awareness between the users on the benefits However, it is necessary to make a thorough study to evaluate the performance of the tool kit. But no standard criteria are available for evaluation. Therefore, the purpose of Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 this study is to identify the criteria to evaluate the performance of the new PMO toolkit and processes. These criteria will help the organization to Compare the old way of conducting the projects management with the New toolkit Measure the performance of the toolkit Share the constraint and drawbacks of the new PMO toolkit Improve the strategy of implementing the new PMO toolkit 3. Methodology and Data Collection: The study was conducted based on a customized methodology: A. Content analysis: A full analysis of the situation covering both the old way of running the PMO and new toolkit is carried out and also the existing literature is probed to identify overall criteria that may be useful to measure the performance of the tool kit. The major criteria identified are Number of projects completed (within Budget, scope and time line) Efficiency and effectiveness of PMO toolkit (Processes, Templates and guidelines) Improvement on delivery of projects after the implementation of the Toolkit “Quality” Compliance with best practices in PMO Improvement over the reporting functionalities (Internally and Externally) % of PMO objectives achieved (strategically or operationally) Internal Capabilities (project management and Program management) Services offered Return on Investment (ROI) However, as these are not validated or standardized criteria, it is not possible to use them as it is unless they are validated. Added to that, this is a first attempt for such a task in Bahrain and there is no precedence. This content review has given good insight to the problem and the criteria. B. Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is one of Multi Criteria decision making method that was originally developed by Prof. Thomas L. Saaty. In short, it is a method to derive ratio scales from paired comparisons. The input can be obtained from actual measurement such as price, weight etc., or from subjective opinion such as satisfaction feelings and preference. AHP allow some small inconsistency in judgment because human is not always consistent. The ratio scales are derived from the principal Eigen vectors and the consistency index is derived from the principal Eigen value Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 It uses pair wise comparison between the factors/variables and therefore pairs will be very large if there are more factors/variables. It uses a matrix with the same factors horizontally and vertically and requests the respondents to fill up upper half of the matrix filling the cells with a score between 1 to 9 or 1/9 to 1 (generally, 1/9, 1/7, 1/5, 1/3, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9) as a comparative measure (no. of times larger or smaller) between a pair of factors/variables. The matrix is given in appendix 1. The respondents are from the e-Government Authority consisting of various levels of executives who use the toolkit such as Project managers Program coordinators and officers Project leaders Project Owners Totally 20 executives who were using the old tool kit as well as the new tool kit were chosen but only 16 have responded within acceptable time. 4. Results and Discussion: The analysis of the responses have shown that the respondents have preferred only six factors/constructs as important to measure the performance of the tool kit, namely, Efficiency and effectiveness of PMO toolkit (Processes, Templates and guidelines) Compliance with best practices in PMO % of PMO objectives achieved (strategically or operationally) Internal Capabilities (project management and Program management) Services offered Return on Investment (ROI) They have ranked them in the following order: 1. Return on Investment (ROI) 2. Services offered 3. Internal Capabilities 4. Compliance with best practices in PMO 5. Efficiency and effectiveness of PMO toolkit and 6. % of PMO objectives achieved In the next sage, sub items are developed for each factor/construct and the opiniojs of the respondents are obtained on the utility of these items for measurement of the performance of the tool kit. The results are shown in Appendix 2. Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 References: Rakesh Belwal and Khalid Al-Zoubi, 2008, Public centric e-governance in Jordan: A field study of people‟s perception of e-governance awareness, corruption, and trust, Journal of Information, Communication & Ethics in Society, Vol. 6 No. 4, 2008, pp. 317-333 Whasun Jho and Kyong-jae Song, 2007, Governance in the Information Age: A comparative analysis of e-Governance in major Asian countries, Korea Observer, vol. 38, No. 1, pp. 127-161. Saxena, K. B. C., 2006, Towards excellence in e-Governance, International Journal of Public Sector Management, Vol. 18, No. 6, pp. 498-513. Gurmeet Singh, R.D. Pathak, Rafia Naz, and 2010, Rakesh Belwal, Egovernance for improved Public sector service delivery in India, Ethiopia and Fiji, International Journal of Public Sector Management, Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 254-275. Malathi Subramanian, and Anupama Saxena, 2008, e-Governance in india: from Policy to reality. a Case study of Chhattisgarh online information system for Citizen empowerment (CHoiCe) Project of Chhattisgarh state of India, International Journal of Electronic Government Research, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 1226. Hilmar Westholm, 2005, Models of Improving e-Governance by Back Office ReOrganization and Integration, Journal of Public Policy, Vol. 25, No. 1, pp. 99-132. Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 Appendix 1: Stage 2: Evaluation of New Toolkit for monitoring of eGovernment Program and its Projects – Case Study Introduction: We are in the process of performing a detailed analysis of the PMO proposed toolkit performance in order to specify the criteria to measure the performance. We have developed the below questionnaire to collect more information from the actual users on what are the evaluation criteria that will be used to measure the performance of the toolkit. The second step in the analysis will be to create another questionnaire that will focus more on the performance of the toolkit based on the criteria collected at the first step. You are requested to kindly spare your valuable time to peruse over the questions area and then provide us with your valuable opinion and suggestions. Your input will help us to formulate our work in a better manner and to make the research output useful to all the stakeholders Instructions for audience: You are expected to rank the options from the important to less importance based on your professional opinion and interaction You should fill up only one copy of the questionnaire to ensure that the results are accurate If the you have conflict between two answers for the same question the you should select the “other” option and clearly mention the details of the conflict in the open text area All the information collected will be used for research and educational purposes only, no information will be exposed or shared outside the boundaries of this research The answers should be selected based on your professional point of view without any personal forces The last section is an open question and please feel free to include any additional things out of the questionnaire context within the same subject Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 Intensity of Definition Importance 1 Equally importance Explanation Two criteria are equally important The criteria is 3 times better than The criteria with the the other criteria score of “3” is slightly better than the other criteria The criteria is 5 times better than The criteria with the the other criteria score of “5” is strongly better than the other criteria The criteria is 7 times better than The criteria with the the other criteria score of “7” is strongly better in based on practice The criteria is 9 times better than The criteria with the the other criteria score of “9” is the best criteria 3 5 7 9 Y axis X axis Number of projects completed (within Budget, scope and time line) Efficiency and effectiveness of PMO toolkit (Processes, Templates and guidelines) Number of projects completed (within Budget, scope and time line) Efficiency and effectiveness of PMO toolkit (Processes, Templates and guidelines) 1 7 1/7 1 Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 Questions: Participant Information: * Department: ______________________ * Job Title: _________________________ ^ Contact details: Phone:_____________________ Email:______________________ - Field marked by „*‟ are considered to be mandatory - Field marked with „^‟ are considered to be optional How would you rate your experience with the PMO after the implementation of the new PMO toolkit? Very Bad Bad Good Very good If your answer is (very bad or bad) kindly explain the reasons that drive the decision of having such perception: __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ How would you define your interaction level with the PMO after the implementation of the new PMO toolkit? Very less (Not even once in a month) Less (Once to Zero a month) Moderate (3 to 5 times a month) High (6 to 10 times a month) Very High (More than 10 times a month) Do you think that the current setup of the PMO is serving the purpose of the eGovernment Authority? Yes No If you answer is No please select the best option from the below type of PMO as per your experience in the field of project and program management: Program management office with an authority to provide policies, methodologies, processes and templates for managing project Program management office with a clear rule of supporting and guiding the other in the organization on how to perform project management (support role) Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 Program management office with an authority to provide project managers for different projects Hyped options were the PMO merge between the above three roles Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 Based on your interaction with the PMO how would you rank the below criteria from the most important to less important for measuring the performance of the new proposed PMO toolkit? X axis Y axis Number of projects completed (within Budget, scope and time line) Efficiency and effectiveness of PMO toolkit (Processes, Templates and guidelines) Improvement on delivery of projects after the implementation of the Toolkit “Quality” Compliance with best practices in PMO Improvement Number of projects completed (within Budget, scope and time line) Efficiency and effectiveness of PMO toolkit (Processes, Templates and guidelines) Improvement on delivery of projects after the implementatio n of the Toolkit “Quality” Compliance with best practices in PMO Improvement over the reporting functionalities (Internally and Externally) % of PMO objectives achieved (strategically or operationally) Internal Capabilities (project management and Program management) Services offered Return on Investmen t (ROI) Other Proceedings of 7th Asia-Pacific Business Research Conference 25 - 26 August 2014, Bayview Hotel, Singapore ISBN: 978-1-922069-58-0 over the reporting functionalities (Internally and Externally) % of PMO objectives achieved (strategically or operationally) Internal Capabilities (project management and Program management) Services offered Return on Investment (ROI) Other ________ ________ ________ ________ The idea is for you to compare every option on the ‘X’ dimension with all the option in ‘Y’ dimension As for the other option you are allowed to include any other criteria that support to be included in the analysis and then compare it with the other options