Document 13036285

Key Concepts:
- Cells are the Basic Unit of Life
Cell Theory, Surface to Volume
- 2 Cell Types
Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic
- Cell Membrane
Fertilization of a human _____ cell
M embrane Structure
- Cell Organelles
Endomembrane system,
*Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria
*
Learn these from text/connect1
Microinjection of stem cells into mouse fertilized egg.
( Chronicle photo by Chris Stewart, 2002)
1 !
Microscopes Reveal the World of Cells
The Cell theory
–
All living things are made of cells
–
All cells come from ‘parent’ cells
Why are cells so small?
–
Most cells are bt. 1-100 um
(micrometers)
The size range of cells and related objects
2 !
Small Cell Size => Efficient Exchange
Which shape has more !
Surface area to Volume?
!
Small cell has more surface area relative to volume
High surface to volume ratio increases rates of exchange
— substances moving across the cell membrane
3 !
Clicker Question #1
!
Which cell shape has the highest ratio of surface area to volume?
!
A.
!
B.
!
C.
!
D.
!
© 1996 PhotoDisc, Inc./Getty Images/RF
!
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
!
4 !
The 3 Domains of Life Have 2 Cell Types
What are the names of the 2 cell types?
5 !
Prokaryotic cells
6 !
Eukaryotic cells
All cells have a plasma membrane , 1 or more chromosomes, cytoplasm, and ribosomes
Prokaryotes do not have a ___________, instead they have a nucleoid
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus , and other organelles
7 !
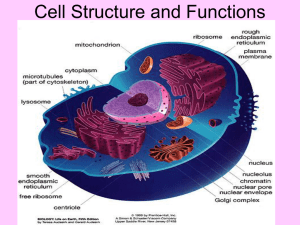
The Anatomy of an Animal Cell
8 !
The Anatomy of a Plant Cell
Plant cells are also eukaryotic, but note the cell wall and chloroplasts.
9 !
3.2 Mastering Concepts
In what two ways do prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells?
10 !
A Membrane Surrounds Each Cell
Composed of
–
A phospholipid bilayer ,
–
Have embedded and attached proteins
–
Commonly described as a fluid mosaic
The plasma membrane of an animal cell
11 !
Cell membranes are composed of molecules called phospholipids !
A phospholipid has two regions: !
Hydrophilic head:
(polar bonds) attracted to water !
Hydrophobic tails:
(nonpolar bonds) repel water !
12 !
Because of their chemical structure, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers in water.
13 !
Membrane video : <http://www.youtube.com/watch?
v=Rl5EmUQdkuI&feature=related>
14 !
Clicker Question #3
!
Cholesterol is a molecule in animal cell membranes. Since cholesterol is hydrophobic, where is it most likely to occur?
!
A.
region X !
B.
region Y !
15 !
3.3 Mastering Concepts
!
How does the chemical structure of phospholipids enable them to form a bilayer in water? !
16 !
Eukaryotic Organelles Divide Labor
Membranes w/in eukaryotic cells form compartments
–
Each compartment maintains conditions that favor particular metabolic processes
Organelles (& other cell structures) perform 4 basic functions
–
Genetic control of cell ( Which organelle does this?
)
–
Manufacture, distribution and breakdown of molecules
–
Energy processing
–
Structural support, movement, and communication bt. cells
17 !
The Endomembrane System
Endomembrane system = a collection of internal membranes
– work together in synthesis, storage, & export of molecules
Some are physically connected, some are functionally connected by tiny vesicles
What is meant by “functionally connected”?
!
18 !
Endoplasmic Reticulum
–
A Molecular Factory
2 kinds of ER
–
Smooth ER
–
Rough ER
Smooth ER !
Rough ER !
Nuclear !
envelope !
Ribosomes !
19 !
Smooth ER – no attached ribosomes. Involved in a variety of metabolic processes
– synthesis of lipids, oils, phospholipids, and steroids
–
In liver cells, enzymes from smooth ER break down alcohol and drugs
Rough ER – attached _____________, makes membrane for itself and proteins destined for secretion
–
Once proteins are made, transported in tiny
___________ to other parts of the endomembrane system
20 !
Transport vesicle !
buds off !
4 !
Ribosome !
3 !
1 !
Polypeptide !
2 !
Glycoprotein !
Secretory !
protein !
inside trans!
port vesicle !
Sugar !
chain !
Rough ER !
21 !
Golgi Apparatus Finishes & Ships Products
The Golgi apparatus functions in conjunction with the ER by modifying products of the ER
–
Products travel in transport vesicles from ER to Golgi
–
One side of Golgi functions as a receiving dock and the other as a ___________ dock
– Products are modified as they go from one side to the other
– Products “shipped” in vesicles to other sites
22 !
“Receiving” side of !
Golgi apparatus !
Transport !
vesicle !
from ER !
New vesicle !
forming !
“Shipping” side !
of Golgi apparatus !
Golgi !
apparatus !
Transport the Golgi !
!
vesicle from !
Golgi apparatus !
23 !
Lysosomes = Garbage Disposal of Cells
Lysosomes = sacs of digestive enzymes budded off of the Golgi
They digest food particles engulfed by cell
– The enzymes & membrane are produced by ______ ___ and transferred to Golgi for processing
Food”
Plasma membrane
3
Engulfment of particle
Food vacuole
Rough ER
1
Transport vesicle
(containing inactive hydrolytic enzymes)
Golgi apparatus
2
Lysosomes
Lysosome engulfing damaged organelle
4
Digestion
5
Lysosomes in a white blood cell
24 !
Review of Endomembrane System
The organelles of the endomembrane system are interconnected structurally and _____________
Rough ER
Transport vesicle from ER to Golgi
Transport vesicle from
Golgi to plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
Nucleus
Vacuole
Lysosome
Smooth ER Nuclear envelope Golgi apparatus
Connections among the organelles of the endomembrane system
25 !
Mitochondria – Power House of Cells
Cellular respiration occurs inside mitochondria
Mitochondrion
–
Cellular respiration = converts energy in food to ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) energy
Intermembrane space
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
– 6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O
Outer membrane
✶
Double membrane
Inner membrane
Cristae
Matrix
—
Inner membrane highly folded
Figure 4.15
What does the increased folding do to surface area?
!
26 !
Chloroplasts Convert Sunlight to Sugar
Chloroplasts – organelles of plant cells, contain a green colored pigment = _______________
–
Photosynthesis = the conversion of _______ energy to chemical energy (produces sugar molecules)
Double membrane
Inside are stacks of membranes = granum
Chloroplast
Stroma
Inner and outer membranes
Granum
Intermembrane space
Figure 4.14
The chloroplast
27 !
Endosymbiosis – The Origin of
Mitochondria & Chloroplasts
Endosymbiont theory = mitochondria & chloroplasts evolved from small prokaryotes that began living w/in larger host cells
–
Symbiosis benefited both symbiont and host cells
Evidence that supports theory
–
Mitos & chloros have their own unique DNA and ribosomes
–
DNA and ribosomes very similar to prokaryotic cells
–
Mitos & chloros replicate like prokaryotic cells
How is a theory different from a hypothesis?
!
28 !
Mitochondrion !
Engulfing !
of aerobic !
prokaryote !
Host cell !
Mitochondrion !
Some !
cells !
Engulfing of !
photosynthetic !
prokaryote !
Chloroplast !
Host cell !
29 !
Membranes are selectively permeable
–
Not all molecules can cross the cell membrane
–
Small non-polar molecules (carbon dioxide and oxygen) diffuse freely
–
Polar molecules (water, glucose and other sugars), ions, and large molecules can not diffuse through membrane
Transport proteins allow molecules that can not diffuse to enter and leave a cell
30 !
Ribosomes Build Cell Proteins
Ribosomes - involved in protein synthesis
–
Cells that synthesize lg. amounts of protein have a lg. # of ribosomes
Some ribosomes are free; others are bound
–
Free ribosomes are suspended in the cytoplasm
–
Bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
What cells in your body might produce lots of protein?
!
31 !
Ribosomes !
ER !
Cytoplasm !
TEM showing ER !
and ribosomes !
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) !
Free ribosomes !
Bound ribosomes !
Large !
subunit !
Small !
Diagram of !
subunit !
a ribosome !
32 !