Genetic Mutations Frame-shift and point mutations
advertisement

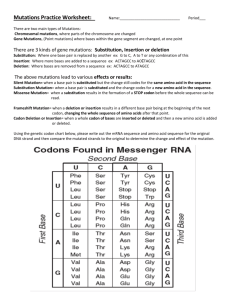
Genetic Mutations Frame-shift and point mutations Point mutations – substitution These only affect a small part of the gene. Substitution normal mutant g g c c t c c t c DNA c c g g a g g a g mRNA pro val glu glu glu g g c c a c c t c c c g g u g g a g protein pro Only one amino acid is affected in the primary structure. Frame shift mutations – insertion and deletion These can affect a large part of the gene. Insertion normal mutant a g a g t c t t c DNA u c u c a g a a g mRNA ser pro glu glu lys a g a g g t c t u c u c c a g a a protein ser All the amino acids after the insertion will be affected in the primary structure of the protein. Frame-shift mutations – insertion and deletion These can affect a large part of the gene. Deletion normal mutant a g a g t c t t c DNA u c u c a g a a g ser ser glu mRNA lys a g a g c t t c g u c u c c a g a a protein ser arg All the amino acids after the deletion will be affected in the primary structure of the protein. Summary Point mutation Occurs at a single point – substitution. Generally not too harmful, most of the protein remaining unaffected. Only one amino acid affected so the protein will probably be functional. (single nucleotide polymorphism) Summary Frame-shift mutation After a deletion or insertion the open reading frame is moved one base pair forward or backward. This is generally harmful since all the amino acids in the primary structure of the protein will have changed from the mutation onwards. The protein will probably be non-functioning. Mutation Naturally occurring mutations are rare, they occur randomly and spontaneously. Mutations can be induced by mutagenic agents such as gamma rays, X-rays and UV light. Tar in cigarettes, certain food additives and many chemicals are thought to induce mutations. Some mutagens are also carcinogens – cancer-causing mutations. Mutation Most mutant alleles are recessive so are only seen in the phenotype when two recessive alleles are present. However, some are dominant (achondroplasia) and some are sex-linked (haemophilia). Some mutations give rise to better genes and provide alternative choices on which natural selection can act. They are considered to be the raw material of evolution.