Mutations
advertisement

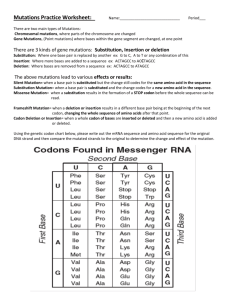
Mutations 1. Mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence 2. A mutation is an unpredictable and permanent change in DNA 3. Mutations are random There are 4 types of DNA mutations: 1. 2. 3. 4. Substitution Insertion Deletion Frame-Shift Mutation Substitution 1. A mutation that exchanges one base for another 2. A different codon, makes a different protein 3. Example – Sickle Cell Anemia 1. Inherited disease of red blood cells 2. Symptoms: pain, fatigue, breathlessness, rapid heart rate 3. Prognosis: Incurable. Some patients may live into their 50’s Insertion 1. Mutations in which extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in the DNA 2. Different codon, different protein 3. Example – Huntington’s Disease 1. Huntington's disease is an inherited disorder in which some brain cells waste away, or degenerate. 2. Symptoms: Uncontrollable body movements, Dementia, Disorientation. 3. Prognosis: Incurable. Death by 15-20 years old. Deletion 2. Different codon, different protein 3. Example - Cri du Chat Disease 1. Cri du Chat disease is a genetic disorder caused by a missing piece of chromosome #5. 2. Symptoms: Severe mental, speech, and motor delays. 3. Prognosis: Many will have normal life expectancy. Frameshift 1. A genetic mutation caused by a deletion or insertion in a DNA sequence that shifts the way the sequence is read. 2. Different codon, different protein 3. Example – Tay-Sachs Disease 1. Inherited as a recessive gene 2. Symptoms: A relentless deterioration of mental and physical abilities 3. Prognosis: Usually results in death by the age of four. 1. Radiation includes x-rays, radioactivity from nuclear power plants, and UV radiation from the sun. 2. In large doses, radiation is a proven cause of cancer and death. 3. Tanning is the body’s defense against UV radiation because exposure to UV radiation can cause cancer. 1. Mutagenic chemicals are chemicals that cause genetic mutations which often lead to cancer and death. 2. Example: BPA in plastic food containers including water bottles.