University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics
advertisement

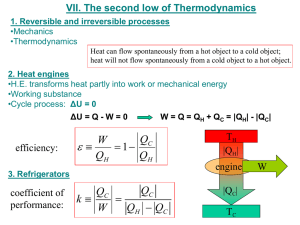
University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics Evaluation of Entropy a) At constant volume ( isomeric) dW 0 dU dQRev. CV dT TdS S CV ln T2 T1 Isobaric process dH dQRe v. C P dT TdS S C P ln T2 T1 b) Isothermal process dU 0 dQRe v. dW TdS PdV S RT ln V2 V1 c) Adiabatic process dQ 0 dS 0 d) Polytropic process dU dQRe v. dW CV dT TdS PdV T2 V2 dT R TdS CV dT PdV S CV dV T V T1 V1 S CV ln Heat pump T2 V R ln 2 T1 V1 University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics Operate between the same to temperature level but direction of heat transfer are reversible and work is required ( e.g., refrigeration cycle) ∆ U = Q net + W ( first law) 0 = QC – QH + W W = Q H - QC ……. (1) Entropy analysis S H ∆S QH TH T otal = ∆S H , S C QC and , ∆S pump = 0 TC + ∆S C + ∆S pump = 0 STotal 0 QH QC 0 TH TC ….. (2) TH 1 From equations 1 and, 2 : Wheatpump QC TC COP QC TC outlet W pump inlet TH TC COP :coefficient performance pump Ex: Thermodynamic device cools small refrigerator and discards heat to the surroundings at 298.15K .The maximum electric power to which the device is designed is 100 W , the heat load on the refrigeration is 350 W what is the maximum temperature that can be maintained in the refrigerator? If Carnot engine is connected to Carnot pump (refrigerator) so that all the work produced by engine is used by refrigerator University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics Q1 is he heat rejected by Carnot engine Q2 is the heat rejected by Carnot refrigerator WE=WP Engine WP T WE T 1 1 and, pump QH TH QC TC WE = QH –Q1 and , WP = Q2 -QC T QH 1 TH T QC 1 TC T T QH H TH T TC QC TC T TC TH QH QC T T H TC Relation between QH and QC Q QH QC TH T QH TH TH T QH TH T TC QC TC T TC (Q QH ) TC T TC QH Q TH TC TH T Relation between Q H ( hot reservoir)and Q(heat sink)