Interferons Interferons (IFNs) are host-coded proteins that are members of the... cytokine family and which inhibit ...
advertisement
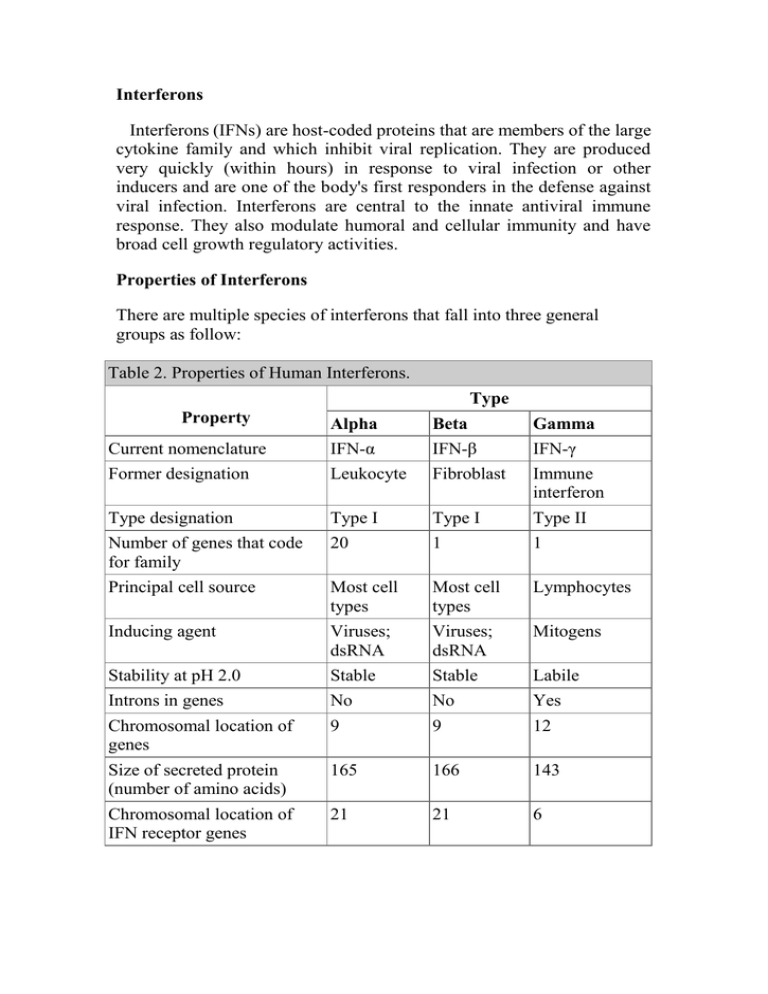
Interferons Interferons (IFNs) are host-coded proteins that are members of the large cytokine family and which inhibit viral replication. They are produced very quickly (within hours) in response to viral infection or other inducers and are one of the body's first responders in the defense against viral infection. Interferons are central to the innate antiviral immune response. They also modulate humoral and cellular immunity and have broad cell growth regulatory activities. Properties of Interferons There are multiple species of interferons that fall into three general groups as follow: Table 2. Properties of Human Interferons. Type Property Alpha Beta Gamma Current nomenclature IFN-α IFN-β IFN-γ Former designation Leukocyte Fibroblast Immune interferon Type designation Type I Type I Type II Number of genes that code for family 20 1 1 Principal cell source Most cell types Most cell types Lymphocytes Inducing agent Viruses; dsRNA Viruses; dsRNA Mitogens Stability at pH 2.0 Stable Stable Labile Introns in genes No No Yes Chromosomal location of genes 9 9 12 Size of secreted protein (number of amino acids) 165 166 143 Chromosomal location of IFN receptor genes 21 21 6 Viral Vaccines The purpose of viral vaccines is to utilize the immune response of the host to prevent viral disease. Several vaccines have proved to be effective at reducing the incidence of viral disease Vaccination is the most costeffective method of prevention of serious viral infections. Mucosal immunity (local IgA) is important in resistance to infection by viruses that replicate exclusively in mucosal membranes (rhinoviruses, influenza viruses, rotaviruses). Viruses that have a viremic mode of spread (polio, hepatitis, measles) are controlled by serum antibodies. Cell-mediated immunity also is involved in protection against systemic infections (measles, herpes). Table 3 Comparison of Characteristics of Killed and Live Viral Vaccines Characteristic Killed Vaccine Live Vaccine Number of doses Multiple Single Need for adjuvant Yes No Duration of immunity Shorter Longer Effectiveness of protection (more closely mimics natural infection) Lower Greater Immunoglobulins produced IgG IgA and IgG Mucosal immunity produced Poor Yes Cell-mediated immunity produced Poor Yes Residual virulent virus in vaccine Possible No Reversion to virulence No Possible Excretion of vaccine virus and transmission to No nonimmune contacts Possible Interference by other viruses in host No Possible Stability at room temperature High Low