Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chem I
advertisement

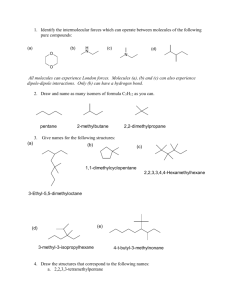
Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chem I 1. The most stable carbocation is: 2. Which of the following statements is true of transition states? A. A transition state represents a minimum on the reaction path diagram and can be isolated. B. A transition state represents a maximum on the reaction path diagram and can be isolated. C. A transition state represents a minimum on the reaction path diagram and cannot be isolated. D. A transition state represents a maximum on the reaction path diagram and cannot be isolated. 3. Which of the following is the least stable conformation of butane? 4. Which of the following compounds is/are meso? I A. I only B. II only IV III II C. III only D. II and III 5. Which of the following compounds would react the fastest in an SN1 reaction? A. (C6H5)3CCl B. (C6H5)3CCH2Cl C. (C6H5)2CHCl D. (CH3)3CCl 6. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? A. 4-bromo-4-ethyl-2,5-dimethyloctane B. 5-bromo-4-ethyl-2,4-dimethyloctane C. 4-bromo-3-isobutyl-3-methylheptane D. 3-bromo-3-ethyl-5-methyl-2-propylhexane 7. The most stable conformation of the following compound has the methyl group in the ______ position and the tert-butyl group in the __________ position. A. Equatorial, Axial B. Equatorial, Equatorial C. Axial, Axial 8. What is the relationship of the following compounds? OH CH2CH3 H OH CH3CH2 H OH CH3 CH3 A. Enantiomers C. Constitutional isomers H OH H B. Diastereomers D. Same compound D. Axial, Equatorial 9. Which statement is true for the reaction shown here? NaOH + CH3CO2H → H2O + CH3CO2Na A. NaOH is the base and CH3CO2Na is its conjugate base B. NaOH is the acid and H2O is its conjugate base C. CH3CO2H is the acid and CH3CO2Na is its conjugate base D. CH3CO2H is the base and CH3CO2Na is its conjugate acid 10. Which of the following changes will speed up the following reaction? Br + SH + SH Br I. Replace SH with H2S II. Replace (CH3)2CHCH2Br with CH3CH2CHBrCH3 III. Replace (CH3)2CHCH2Br with (CH3)2CHCH2OH IV. Use the solvent DMSO instead of methanol A. I and III B. II C. I and IV D. IV 11. What is the energy of activation for the reaction of BC? kJ/mol 35 30 25 C Series1 20 A 15 10 B 5 reaction coordinate A. 6 kJ/mol B. 3 kJ/mol C. 9 kJ/mol D. 23 kJ/mol 12. Which of the following statements correctly describes the molecule shown below: A. B. C. D. It is achiral It is meso Its chirality center possesses the R configuration The mirror image of this molecule is its enantiomer 13 . For the following reaction step, indicate which pattern it belongs to. A. B. C. D. Proton Transfer Loss of Leaving Group Nucleophilic Attack Rearrangement 14. Which of the following is/are the most likely product(s) for the following reaction? 15. What is the IUPAC name of: OH H H I A. trans-1-iodo-2-cyclohexanol C. trans-2-iodocyclohexanol B. cis-1-iodo-2-cyclohexanol D. cis-2-iodocyclohexanol 16. What is the configuration of the following molecule? 17. What is wrong with the following mechanism? A. There is no leaving group, so there should be no arrows. B. The arrow should be removing a proton from the H2O group. C. An arrow is also needed to indicate the loss of the leaving group. D. The arrow indicating the formation of the C-Br bond (nucleophilic attack) should start at the bromide anion. 18. What is the product of the following SN1 reaction? 19. What is the relationship between the following molecules? A. diastereomers C. enantiomers B. conformers D. constitutional isomers 20. Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point? 21. Give the IUPAC name for the following compound. OH A. (S)-4-methyl-2-hexanol C. (S)-4-methyl-2-pentanol B. (R)-4-methyl-2-hexanol D. (R)-4-methy-2-pentanol 22. The major compound that will be formed in the following SN1 reaction will be: 23. Your sample of Compound-X was found to have a specific rotation of +20o. A sample of pure Compound-X has a specific rotation of +100o. What is the composition of the sample? A. B. C. D. 20% (+) isomer and 80% (-) isomer 80% (+) isomer and 20% (-) isomer 60% (+) isomer and 40% (-) isomer 40% (+) isomer and 60% (-) isomer 24. Which of these statements is false? A. Angle strain is a major problem in cyclopropane. B. Gauche butane has torsional strain. C. Boat cyclohexane is destabilized with respect to chair cyclohexane, partly due to flagpole steric strain. D. On a cyclohexane, 1,3-diaxial interactions are an example of steric strain. 25. What is the correct priority of these groups with respect to R/S determination in stereochemistry, with highest priority group first? Assume these groups are all bonded to the same chirality center. A. -CH2CH2F > -CH2OH > -CH=CH2 > -C(CH3)3 B. -CH2OH > -C(CH3)3 > -CH=CH2 > -CH2CH2F C. -CH2OH > -C(CH3)3 > -CH2CH2F > -CH=CH2 D. -C(CH3)3 > -CH=CH2 > -CH2OH > -CH2CH2F