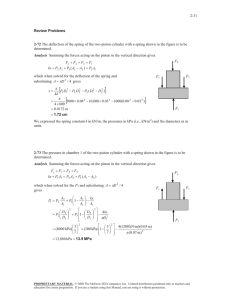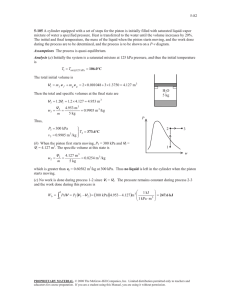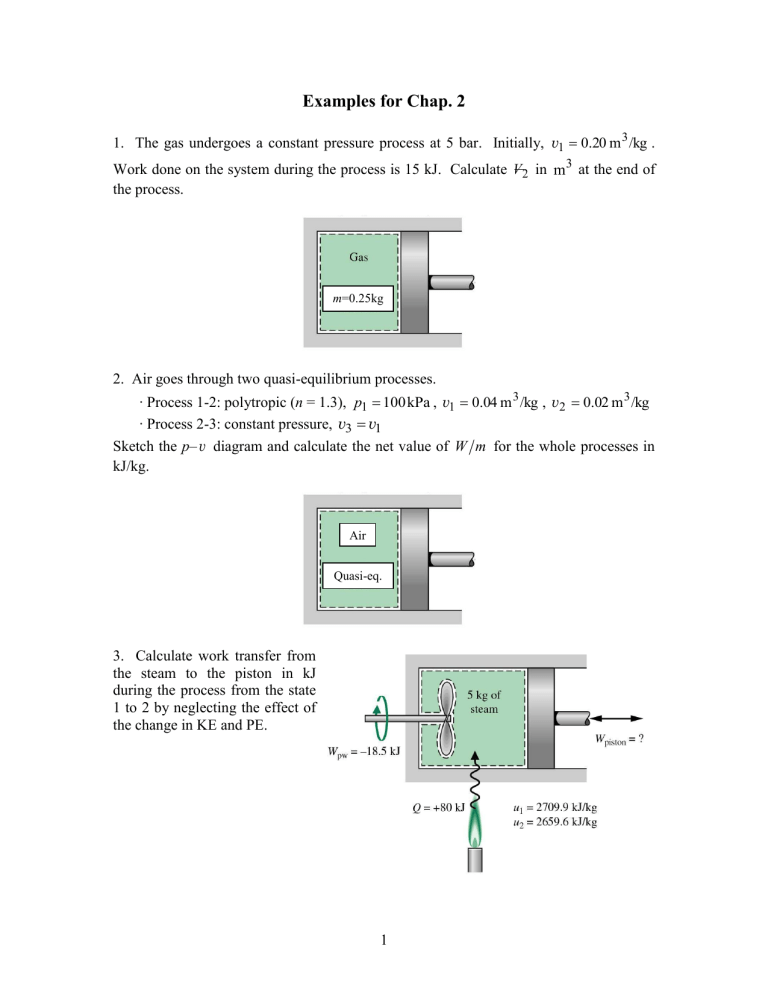
Examples for Chap. 2 1. The gas undergoes a constant pressure process at 5 bar. Initially, v1 0.20 m 3 /kg . Work done on the system during the process is 15 kJ. Calculate V 2 in m3 at the end of the process. m=0.25kg 2. Air goes through two quasi-equilibrium processes. ∙ Process 1-2: polytropic (n = 1.3), p1 100 kPa , v1 0.04 m 3 /kg , v2 0.02 m 3 /kg ∙ Process 2-3: constant pressure, v3 v1 Sketch the p– v diagram and calculate the net value of W m for the whole processes in kJ/kg. Air Quasi-eq. 3. Calculate work transfer from the steam to the piston in kJ during the process from the state 1 to 2 by neglecting the effect of the change in KE and PE. 1 4. The mass of air is 2 kg and the volume is 0.6 m3. The paddle wheel transfers work to air at a constant rate of 10 W for 1 hour. Neglecting the effect of change in KE and PE, calculate (a) v2 at t = 1 hour. (b) u 2 u1 in kJ/kg. Thermally insulated rigid container Air 2