Math 1070 Final Exam Review
advertisement

Math 1070
Final Exam Review
This exam will last 2 hours. Write your answers in the space provided. All
solutions must be sufficiently justified to receive credit. You may use a
scientific or graphing calculator, and a letter-size sheet of paper with notes
on it. You may not use any other notes or texts. Good luck!
Name:
Section:
Section I
Instructions: Circle the letter of the best answer choice. For extra practice, correct the
false statements so that they are true.
1. (2 points) A 95% confidence interval contains 95% of all of the data from any SRS.
A. True
B. False
2. (2 points) A 90% confidence interval for µ, calculated from many different SRS’s of the
same size, will contain the true population mean approximately 90% of the time.
A. True
B. False
3. (2 points) A 90% confidence interval for µ will exclude 0 exactly when a hypothesis test
for
H0 : µ = 0 vs. Ha : µ 6= 0
will reject H0 at the α = 0.05 significance level.
A. True
B. False
4. (2 points) A 99% confidence interval for µ will exclude 0 exactly when a hypothesis test
for
H0 : µ = 0 vs. Ha : µ > 0
will reject H0 at the α = 0.01 significance level.
A. True
B. False
5. (2 points) If A and B are any two events, then P {A or B} (the probability that A or
B occurs) is equal to P (A) + P (B).
A. True
B. False
6. (2 points) If the probability of an outcome is
out of every two trials.
1
2
then the outcome will occur exactly once
A. True
B. False
7. (2 points) If the probability of an outcome is said to be 1, then that outcome occurs
every time without fail.
A. True
B. False
8. (2 points) If A and B are disjoint events, then P {A or B} = P {A} + P {B}.
A. True
B. False
9. (2 points) If the correlation of two variables is 1 or -1, there is a cause-effect relationship
between them.
A. True
B. False
10. (2 points) If the correlation of two variables is non-zero, then there is a cause-effect
relationship between them.
A. True
B. False
11. (2 points) If the correlation of two variables is zero, then they are independent.
A. True
B. False
12. (2 points) If the correlation of two variables is positive, the least squares regression line
will have positive slope.
A. True
B. False
13. (2 points) An outlier is any value that lies above the third quartile or below the first
quartile.
A. True
B. False
14. (2 points) When an observation is decided to be an outlier, it should always be discarded
immediately.
A. True
B. False
Page 2
15. (2 points) A histogram is used to analyze the distribution of a categorical variable.
A. True
B. False
16. (2 points) The total area under a density curve is 1.
A. True
B. False
17. (2 points) The P-value gives the probability that the null hypothesis is true.
A. True
B. False
18. (2 points) A smaller P -value means the results of the experiment are more significant.
A. True
B. False
19. (2 points) All distributions are normal.
A. True
B. False
20. (2 points) The Normal distribution completely determined by its mean µ and standard
deviation σ.
A. True
B. False
21. (2 points) If a distribution is skewed left, the median is larger than the mean.
A. True
B. False
22. (2 points) The mean and the median of a symmetric distribution are the same.
A. True
B. False
23. (2 points) In any hypothesis test, the P -value is the area under the density curve to the
left of the statistic.
A. True
B. False
24. (2 points) In any hypothesis test, our test statistic is calculated assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Page 3
A. True
B. False
25. (3 points) A random variable can take any (real number) value between 0 and 1. What
type of random variable is it?
A. Discrete
B. Continuous
26. (3 points) A random variable is Normally distributed with mean 10 and standard deviation 2. What type of random variable is it?
A. Discrete
B. Continuous
27. (3 points) A sample space for a random event contains 10 possible outcomes. What
type of probability model is this?
A. Discrete
B. Continuous
28. (3 points) The most important condition for sound conclusions from statistical inference
is usually
A. that the population distribution is exactly Normal.
B. that the data contain no outliers.
C. that the data can be thought of as a random sample from the population of interest.
29. (3 points) A population is known to have standard deviation σ. A group of 10 volunteers
are given a relaxation exercise and then have their blood pressure measured. Which of
the following must be true in order to use statistical methods to analyze the data?
A. The sample standard deviation is no more than twice as large as σ.
B. There is a control or placebo group in the experiment.
C. The subjects are a random sample from the population of interest.
D. All of the above.
30. (3 points) A researcher is testing the hypothesis that tomato plants grow faster when
they are given sugar water than when they are fed MiracleGro. She randomly chooses
15 plants to feed with sugar water and 15 plants to feed with Miracle Gro, and measures
their height after 1 week. She finds that the sugar-fed plants grew an average of 2.65
inches with standard deviation 0.56 inches, while the Miracle-Gro plants grew an average
of 2.87 inches with standard deviation 1.24 inches. To test her hypotheses, she should
use
A. z Test
Page 4
B. One-Sample t Test
C. Two-Sample t Test
D. Chi-Square Test
31. (3 points) A researcher wants to know whether majoring in a STEM (science, technology,
engineering, mathematics) field results in a higher starting salary (regardless of career
track). He chooses a random sample of 100 recent graduates from the University of
Utah and asks about their majors and current salaries. What procedures should he use
to compare the two groups (STEM & non-STEM) majors?
A. z Test
B. One-Sample t Test
C. Two-Sample t Test
D. Chi-Square Test
32. (3 points) A class survey in a large class for first-year college students asked, “About
how many minutes do you study on a typical weeknight?” The mean response of the
269 students was x = 137 minutes. Suppose that we know that the study time follows
a Normal distribution with standard deviation σ = 65 minutes in the population of all
first-year students at this university. Is there good evidence that students claim to study
more than 2 hours per night on average?
A. z Test
B. One-Sample t Test
C. Two-Sample t Test
D. Chi-Square Test
33. (3 points) Which of the following theorems or rules allows us to calculate the sampling
distribution of x for a population with known mean and standard deviation?
A. Law of Large Numbers
B. Right-Hand Rule
C. Central Limit Theorem
D. Fundamental Theorem of Statistics
34. (3 points) A quantitative variable x is Normally distributed in a certain population,
with mean 36 and standard deviation 2.7. What is the distribution of the sample mean
x in samples of size 9?
A. N(36, 2.7)
B. N(13, 2.7)
C. N(36, 0.9)
D. N(13, 0.9)
Page 5
35. (3 points) Mr. Miller wants to test the hypothesis that he is a better teacher than Mrs.
Reed against the alternative that they are equally good teachers. He carries out a twosample t-test using their students’ exam scores and calculates that the P -value is 0.052.
What conclusion should he make?
A. Accept the null hypothesis at both α = 0.05 level and α = 0.01 level.
B. Reject the null hypothesis at both α = 0.05 level and α = 0.01 level.
C. Accept the null hypothesis at α = 0.05 level but reject at α = 0.01 level.
D. Reject the null hypothesis at α = 0.05 level but accept at α = 0.01 level.
36. (3 points) A medical organization is trying to estimate the proportion of the population
who are carriers of the Tay Sachs gene. In an SRS of 600 young adults, it is found that
4 of them are carriers. Which variant of the population proportion procedures should
be used to create a confidence interval?
A. Large sample confidence interval
B. Plus four confidence interval
37. (3 points) A pollster wants to determine whether a majority (more than 50%) of Canadian citizens are affiliated with the Conservative party. She asks a random sample of
100 residents about their party affiliation, and finds that 53 of them belong to the Conservative party. When she is calculating the test statistic, she accidentally uses n = 10
instead of n = 100. Based on this incorrect statistic, her P value will be
A. larger than the correct P value.
B. smaller than the correct P value.
C. equal to the correct P value.
38. (3 points) Jane wants to determine whether teachers educated at a teachers’ college
earn higher salaries than teachers educated elsewhere. The Board of Education reports
that teacher salaries are normally distributed with mean $525 per week and standard
deviation $34. A random sample of 10 teachers’ college graduates who are now teachers
has mean weekly salary of $594. Let µ be the mean salary for all graduates. Jane should
test the hypotheses:
A. H0 : µ = 594 vs. Ha : µ > 594
B. H0 : µ = 525 vs. Ha : µ > 525
C. H0 : µ = 525 vs. Ha : µ 6= 525
D. H0 : µ > 525 vs. Ha : µ = 525
39. (3 points) Can changing diet reduce high blood pressure? Vegetarian diets and low-salt
diets are both promising. Men with high blood pressure are assigned at random to four
diets: (1) normal diet with unrestricted salt; (2) vegetarian with unrestricted salt; (3)
normal with restricted salt; and (4) vegetarian with restricted salt. This experiment has
Page 6
A. one factor, the choice of diet.
B. four factors, the four diets being compared.
C. two factors, normal/vegetarian diet and unrestricted/restricted salt.
40. (3 points) A committee on community relations in a small town plans to survey local
businesses about the importance of avid readers as customers. From telephone book
listings, the committee chooses 210 businesses at random. Of these, 113 return the
questionnaire mailed by the committee. The sample for this study is
A. the 210 businesses chosen.
B. the 113 businesses that returned the questionnaire.
C. all businesses in the town.
41. (3 points) The Community Intervention Trial for Smoking Cessation asked whether a
community-wide advertising campaign would reduce smoking. The researchers located
11 pairs of communities, each pair participated in the advertising campaign and the
other did not. This is
A. an observational study.
B. matched pairs experiment.
C. a Control group experiment.
D. a completely randomized experiment.
42. (3 points) When rolling a fair die, each digit {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} is equally likely to occur.
What is the probability that you roll the die and get a six?
A.
5
36
B.
1
36
C.
1
6
D.
1
2
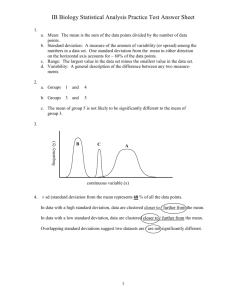
43. (3 points) The picture below is a histogram which describes the distribution of a quantitative variable. Which of the following answer choices best describes this distribution?
A. Uniform
B. Symmetric
C. Skewed to the left
D. Skewed to the right
44. (3 points) Suppose that a student earns 10, 12, 8, and 13 points on her first four quizzes,
respectively. What must she get on her fifth quiz so that her mean quiz score is 14
points?
Page 7
A. 13
B. 20
C. 32
D. 27
E. 17
Page 8
Section II: Short Answer
Instructions: Answer each question in the space provided. Show all of your work to receive
credit.
45. The following is the 5-number summary calculated from a data set:
1 6 12 14 22
(a) (5 points) Determine whether the maximum (22) is an outlier.
Solution:
IQR = 14 − 6 = 8
14 + 1.5(8) = 14 + 12 = 26
Since 22 is not larger than Q3 + 1.5(IQR), it is not an outlier.
(b) (5 points) Draw a box plot of the data.
Solution:
46. (10 points) Calculate the standard deviation of the following data, given that the mean
is 10:
7 12 13 8
Solution:
1
(7 − 10)2 + (12 − 10)2 + (13 − 10)2 + (8 − 10)2
3
1
= (9 + 4 + 9 + 4)
3
50
=
3
r
50
σ=
3
σ2 =
Page 9
47. Low-back-pain (LBP) is a serious health problem in many industrial settings. The article
“Isodynamic Evaluation of Trunk Muscles and Low- Back Pain Among Workers in a Steel
Factory” (Ergonomics, 1995) reported the accompanying summary data on lateral range
of motion (degrees) for a sample of workers without a history of LBP and another sample
with a history of this malady.
Condition
No LBP
LBP
Sample Size
28
31
Sample Mean
91.5
88.3
Sample SD
5.5
7.8
(a) (5 points) Calculate a 90% confidence interval for the difference between population
mean extent of lateral motion for the two conditions.
Solution:
(b) (5 points) Does the interval suggest that the population mean lateral motion differs
for the two conditions?
Solution:
48. (20 points) The College Alcohol Study interviewed a simple random sample of 14,941
college students about their drinking habits. Of the students in the sample, 10,010
supported cracking down on underage drinking. Use the population proportion procedures to estimate the proportion of all college students who feel this way with 99%
confidence.
Solution:
(1 − α) × 100%CI for p :=
=
10, 010
± 2.576
14, 941
10,010
(1
14,941
p̂ ±
−
∗
Z1−α
10,010
)
14,941
p̂(1 − p̂)
n
1/2
!1/2
14, 941
= 0.67 ± (2.576)(0.00385) = 0.67 ± 0.00991
= [0.6601, 0.6779]
49. The placebo effect is particularly strong in patients with Parkinson’s disease. To understand the workings of the placebo effect, scientists measure activity at a key point in the
brain when patients receive a placebo that they think is an active drug and also when
no treatment is given. The same six patients are measured both with and without the
placebo, at different times. The six differences (treatment minus control) had sample
Page 10
mean x = −0.326 and sample standard deviation s = 0.181. Is there evidence of a
difference between treatment and control at the level α = 0.01?
(a) (5 points) State the null and alternative hypothesis.
Solution: Let µ be the mean difference (placebo minus control) between brain
activity with and without the placebo.
H0 : µ = 0
Ha : µ 6= 0
(b) (5 points) Which test statistic would you use, and what assumptions must be met?
Solution: You should use the single sample t-statistic. This is a matched pairs
experiment, with only one independent sample. The population standard deviation σ is unknown.
50. (10 points) Pretend that you are rolling two fair, six-sided dice.
(a) Is this a discrete or continuous distribution?
Solution: Discrete
(b) What is the probability of rolling the two dice and having the sum be 1, 4, or 5?
Solution:
P (1) + P (4) + P (5) =
0+3+4
7
=
36
36
(c) What is the probability of rolling the dice and not having the sum be even?
Solution:
1 − (P (2) − P (4) + P (6) + P (8) + P (10) + P (12))
1+3+5+5+3+1
=1−
36
18
1
=1−
=
36
2
51. (10 points) A researcher wishes to use students IQ’s to predict their SAT scores. There
is a correlation of 0.82 between SAT score and IQ score. The average SAT Verbal score
Page 11
is 500, with a standard deviation of 100. The average IQ score is 100, with standard
deviation 15. Calculate the equation for the least squares regression line.
Solution:
52. (10 points) A teacher wishes to predict his students’ performance in a class based on
their scores on an aptitude test. He calculates that the least squares regression line is
ŷ = 26.768 + 0.644x. Use this equation to predict a student’s grade in the course if they
received a score of 80 on the aptitude test.
Solution:
ŷ = 26.768 + 0.644x = 26.768 + (0.644)(80) = 26.768 + 51.52 = 78.288
Page 12
Section III: Long Answer
Instructions: Answer each question in the space provided. Show all of your work to receive
credit.
53. (20 points) An experiment to help determine if insects sleep gave caffeine to fruit flies
to see if it affected their rest. The three treatments were a control, a low caffeine dose
of 1 mg/ml of blood, and a higher caffeine dose of 5 mg/ml of blood. Nine fruit flies
were assigned at random to three treatments, three to each treatment, and the minutes
of rest measured over a 12-hour period was recorded. The data are below:
Level
Control
Low
High
N Mean
3 427.00
3 440.33
3 328.00
StDev
20.07
23.46
62.02
Assume that the data are three independent SRSs, one from act of the three populations
of caffeine levels, and that the distribution of the resting time is Normal. An ANOVA
F test was run on the data. The following shows a portion of the results:
(a) State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses. Explain whether the assumptions are satisfied or not.
Solution: H0 : Caffeine does not affect rest in fruit flies.
Ha : Caffeine affects rest patterns in fruit flies. The assumptions for the ANOVA
test are not satisfied: We do have three independent SRSs from Normally distributed populations, but the assumption that the standard deviations are the
same does not seem to hold, since the largest standard deviation is more than
twice as large as the smallest.
(b) Fill in the rest of the table.
Source DF Sums of Squares Mean Squares
Group
22598
Error
9601
Total
F-ratio P-value
0.026
Solution:
Source
Caffeine
Error
Total
DF
SS
MS
F-ratio
P
2 22598 11299
7.06
0.026
6
9601 1600
8 32199 12899
Page 13
54. (20 points) In a study to investigate the effects of regular exercise on raising HDL (good
cholesterol) levels, a random sample of six male subjects known to have low HDL levels
had their HDL measured at the beginning of the study and then after six months on a
regular exercise schedule. The changes in HDL levels for the 6 subjects are given below:
12 − 7 − 1 7 4 2
A researcher is interested in testing the null hypothesis that “Initial and final HDL
measurements have the same distribution” against the alternative that “Final HDL
levels are systematically higher.”
(a) Calculate the value of the Wilcoxon signed rank statistic W + .
Solution: First, rank the data (negative values are in bold).
Value 1 2 4 7
7 12
Rank 1 2 3 4.5 4.5 6
W + = 2 + 3 + 4.5 + 6 = 15.5
(b) Calculate the mean (µW + ) and standard deviation (σW + ) of W + if the null hypothesis is true.
Solution:
n(n + 1)
6(7)
=
= 10.5
4
4
r
r
n(n + 1)(2n + 1)
6(7)(13) √
=
=
= 22.75 = 4.77
24
24
µW + =
σW +
(c) Calculate the z-score.
Solution:
z=
15.5 − 10.5
= 1.048
4.77
(d) Calculate the P -value.
Solution: One sided alternative hypothesis, that mean change is positive:
P = P {Z ≥ 1.048} = 1 − .8531 = .1469
(e) What conclusion should the researcher make about the null and alternative hypotheses?
Page 14
Solution: The data provide some evidence against the null hypothesis. However, the researcher should accept the null hypothesis at the level α = 0.10 or
smaller. He could reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative at level
α = 0.15 or higher.
Page 15