analog vs digital • digital world

digital images
analog vs digital
• media content in the ‘real world’ is analog
– Quantities in a continuous domain
– Infinite range of values
• digital world
– Values are based upon counting discrete entities.
– Operates on single bits of information - ‘0’ or ‘1’
binary
• Single ‘bit’ can represent only 2 values (0 or1). Using binary representation bits can be used together to represent larger values.
Place
Place Value
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
binary numbers
• Single ‘bit’ can represent only 2 values (0 or 1). Using binary representation bits can be used together to represent larger values.
• for example
– 10110 = 1*2 4 + 0*2 3 + 1*2 2 + 1*2 1 + 0*2 0
– = 16
– = 22
+ 0 + 4 + 2 + 0
• for example
– 75 = 64 + 8 + 2 + 1
– = 1*2 6 + 0*2 5
– = 1001011
+ 0*2 4 + 1*2 3 + 0*2 2 + 1*2 1 + 1*2 0
16 bit sample
• 65535 possible values for each sample
4 bit
• 16 possible values for each sample sample
image basics
• pixels (PIcture ELementS): Grid of small dots.
• bitmap: matrix of pixels
• two types of images
– raster images (made of pixels)
– vector images (mathematically defined)
1
digital images
• raster
• vector
vector images
• calculated to display
• small filesize
• resizable
• high resolution
raster images
• pixel grids
• colours
• high quality
• large filesize
• compressible
image attributes
• resolution
– ppi
– 100 x 100 = 10000 pixels
• pixel depth
– 8 bit colour 256 colours
– 16 bit colour thousands of colours
– 24 bit colour millions of colours
pixelation
• If the size of the image is increased and the number of pixels is unchanged, then the pixel size increases
file formats
• BMP
• TIFF
• Pict
• JPEG
Win bit map
Cross platform bitmap
Mac bitmap / object
High compression (WWW)
• GIF
» suited to large graphics (24 bit colour)
Moderate compression (WWW)
» 256 colours/8 bit colour
• Interlaced GIF, GIF89a
2
file formats
• gif
– 256 colours
– lossless
– interlaced
– suited to graphics
• jpg
– millions of colours
– lossy
– variable file size
– suited to photographs
• png
– millions of clours
– high comppression
1 bit
Good for B&W line art - 34 K
8 bit
B&W ‘Continuous Tone’ or ‘ Contone’ image - 385 K
bit depth
• Number of bits of information per pixel
• This resolution determines how much colour information is allocated for each pixel
– Usually 8, 16, or 24 bit depth
– 1 : B&W
– 2 : B& W + Two greys
– 8 : 256 greys, ‘Continuous Tone’ or ‘Contone’ smooth images
– 8 : 256 colours
– 24 : 8 bits for each of RGB, gives 256 levels each of RGB giving over 16 million colours
– 32: 8 bits for each of CYMK
2 bit
Low quality greyscale - 68 K
8 bit
Low quality colour - 385K
3
16 bit
Thousands of color - 760K
colours
• 24 bit
– 8 bits for red, 8 bits for green, 8 bits for blue,
– rr gg bb
– 0-255, 0-255, 0-255
– hexadecimal codes
• hue
• saturation
• brightness
32 bit
high quality - 1.4M
colours image file size
• image size (cms x cms)
• resolution (ppi)
• bit depth
• file format
image capture
• digital camera
• scanning
• Web
• drawing
4
device resolution
• Number of dots or pixels represented per unit length of output
– dots per inch/pixels per inch
• Devices have different resolution
– Laser printers: 300 - 1200 dpi
– Scanners: 300 - 1200 dpi
– Monitors: 72 - 90 dpi
Sound Basics amplitude
• amplitude governs loudness
The height of the waveform
wavelength
The distance between peaks
frequency
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
• The frequency of a waveform is defined by the number of periods per sec.
• Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz) or kilohertz (kHz)
pitch
• The height of the note
• The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch
5
In other words...
digitising sound
• Convert sound from analogue to digital
• An approximation (dynamic to static)
– conversion to values
– reconstruction to playback
• Quality of sound
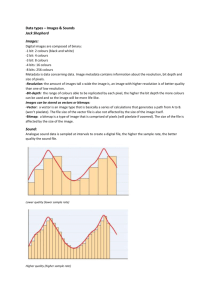
– Sampling rate
– Sampling resolution
– Compression ratio
011010110111
110010111000
sampling sound
• 48.000 kHz (DAT)
– Digital Audio Tape, also DVD
• 44.100 kHz (CD)
– Compact Disk - typical quality of most sound cards
• 22.255 kHz
– Medium quality
• 11.025 kHz
– Low quality (frequently used for speech)
sampling resolution
• Digitiser assigns an integer value to each sample that reflects the sample’s amplitude
• 8 bit sound: values 0 to 255
– most widely supported resolution
• 16 bit sound: values 0 to 65,535
– CD quality requires 16 bits
• Think of sample resolution as the amount of information able to be stored per sample. The more information, the better the quality (just like graphics)
• Compression also affects quality of sound
the prodigy
• 8 bit mono 11 kHz: 159 KB
• 8 bit Stereo 22 kHz: 637 KB
• 16 bit stereo 44 kHz: 2.5 MB
recording sound
• Cool Edit
• Sound Edit 16
• Midi Software (eg Cakewalk, Cubase, Trax)
6
sound formats
• SoundEdit 16—16 bit format (Mac)
• Audio IFF: Standard and cross platform
• Wave: Windows standard
• MP3 - High quality compressed format (Internet)
• QuickTime Movie Audio - variety of formats including MP3
• Quicktime Musical Instrument: Midi information contained in
QuickTime movie
• General MIDI - supports more sounds, becoming a cross platform standard
midi files
• Multiple/Musical Instrument Digital Interface
• Notes, not values... Synthesised
• Quality of final sound depends on quality of sound card or external keyboard synthesiser
Canyon.mid - 36Kb
7