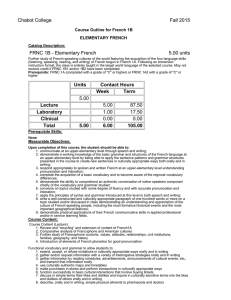
Chabot College Fall 2015 FRNC 1A - Beginning French 5.00 units
advertisement
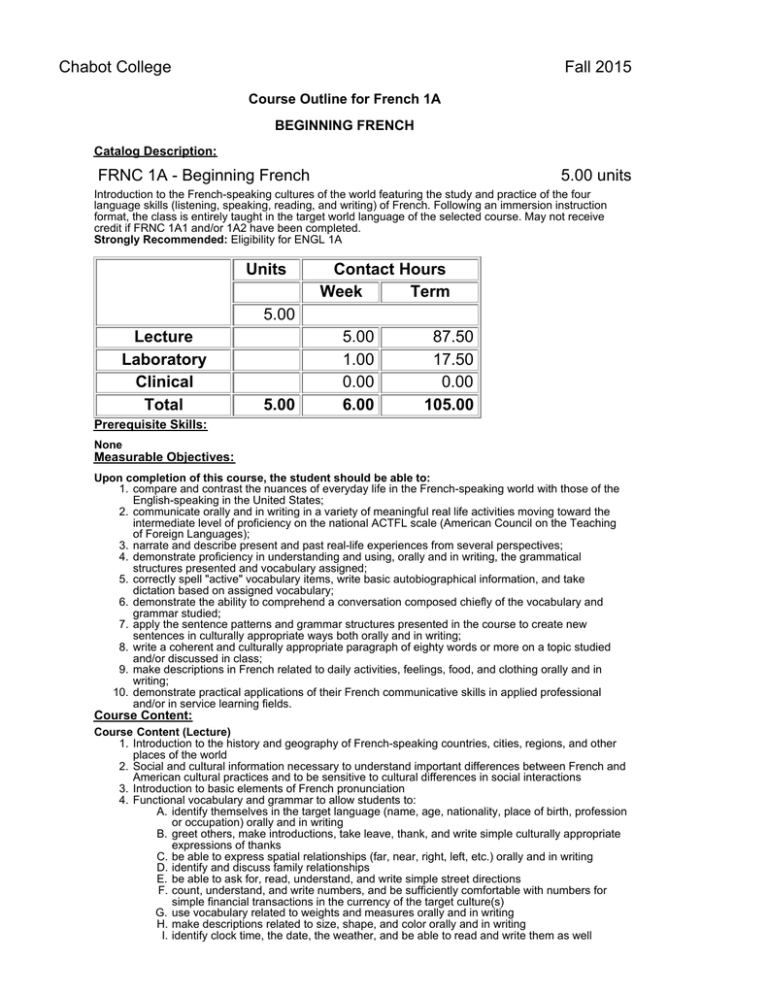
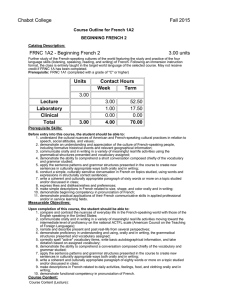
Chabot College Fall 2015 Course Outline for French 1A BEGINNING FRENCH Catalog Description: FRNC 1A - Beginning French 5.00 units Introduction to the French-speaking cultures of the world featuring the study and practice of the four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing) of French. Following an immersion instruction format, the class is entirely taught in the target world language of the selected course. May not receive credit if FRNC 1A1 and/or 1A2 have been completed. Strongly Recommended: Eligibility for ENGL 1A Units Contact Hours Week Term 5.00 Lecture Laboratory Clinical Total 5.00 5.00 1.00 0.00 6.00 87.50 17.50 0.00 105.00 Prerequisite Skills: None Measurable Objectives: Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to: 1. compare and contrast the nuances of everyday life in the French-speaking world with those of the English-speaking in the United States; 2. communicate orally and in writing in a variety of meaningful real life activities moving toward the intermediate level of proficiency on the national ACTFL scale (American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages); 3. narrate and describe present and past real-life experiences from several perspectives; 4. demonstrate proficiency in understanding and using, orally and in writing, the grammatical structures presented and vocabulary assigned; 5. correctly spell "active" vocabulary items, write basic autobiographical information, and take dictation based on assigned vocabulary; 6. demonstrate the ability to comprehend a conversation composed chiefly of the vocabulary and grammar studied; 7. apply the sentence patterns and grammar structures presented in the course to create new sentences in culturally appropriate ways both orally and in writing; 8. write a coherent and culturally appropriate paragraph of eighty words or more on a topic studied and/or discussed in class; 9. make descriptions in French related to daily activities, feelings, food, and clothing orally and in writing; 10. demonstrate practical applications of their French communicative skills in applied professional and/or in service learning fields. Course Content: Course Content (Lecture) 1. Introduction to the history and geography of French-speaking countries, cities, regions, and other places of the world 2. Social and cultural information necessary to understand important differences between French and American cultural practices and to be sensitive to cultural differences in social interactions 3. Introduction to basic elements of French pronunciation 4. Functional vocabulary and grammar to allow students to: A. identify themselves in the target language (name, age, nationality, place of birth, profession or occupation) orally and in writing B. greet others, make introductions, take leave, thank, and write simple culturally appropriate expressions of thanks C. be able to express spatial relationships (far, near, right, left, etc.) orally and in writing D. identify and discuss family relationships E. be able to ask for, read, understand, and write simple street directions F. count, understand, and write numbers, and be sufficiently comfortable with numbers for simple financial transactions in the currency of the target culture(s) G. use vocabulary related to weights and measures orally and in writing H. make descriptions related to size, shape, and color orally and in writing I. identify clock time, the date, the weather, and be able to read and write them as well J. discuss in simple terms their likes and dislikes and to inquire in culturally sensitive terms into likes and dislikes of others, orally and in writing K. describe features and contents of homes and other residences L. identify body parts and communicate about health conditions and medical treatments M. communicate about food, beverages, dining, and table utensils N. identify articles of clothing and accessories and communicate about shopping experiences O. communicate about actions in progress, characteristics and conditions of people and things P. use vocabulary related to weights and measures orally and in writing Q. make descriptions related to weights and measures, size, shape, and color orally and in writing 5. Syntax and grammar that allows students to correctly use orally and in writing: A. subject, object, interrogative, demonstrative, and disjunctive pronouns in both formal and informal social contexts B. regular –er, -re, and –ir verbs and the irregular verbs être, avoir, aller, faire, venir, revenir, devenir, pouvoir, vouloir, prendre, apprendre, comprendre, mettre, promettre, permettre, boire, sortir, dormir, mentir, partir, sentir, servir, devoir, voir, croire, recevoir, and spelling-change –er verbs all in the indicative present and passé composé tenses with both avoir and être as auxiliaries in the latter C. the negative verb constructions ne . . . pas, pas du tout, pas encore, plus, and jamais D. the conjugated verb + infinitive (with no intervening preposition) construction E. the expression il y a affirmatively and negatively F. the future tense using the present tense of aller G. the affirmative and negative imperative verb constructions H. the pronominal verbs I. nouns in singular and plural forms, regular and irregular J. definite, indefinite, partitive articles and expressions of quantity K. singular, plural, regular, and irregular adjectives, their proper placement, and possessive and interrogative adjectives L. the expression of possession with the preposition de M. interrogative forms involving intonation, subject-verb inversion, est-ce que, the expressions n’est-ce pas?, non?, c’est ça?, je suppose?, d’accord? OK?, and the adverbs où, quand, pourquoi, comment, and combien de 6. Introduction to the basic elements of French phonetics for functional pronunciation Course Content (Laboratory): 1. Activate lecture content using interactive audio and audiovisual programs on iLrn Motifs (online course content). Motifs iLrn passkey which includes access to: A. Motifs electronic Student Activities Manual (workbook + lab manual = homework) B. Textbook assignments (part of homework) C. Motifs eBook (online textbook) D. Video Library (part of homework) E. Enrichment- flashcards, web quizzes, games, glossary, Internet activities, Google Earth coordinates, interactive learning games, Heinle iRadio, grammar & vocab tutorials, verb conjugator. F. Diagnostic exams with personalized learning plans 2. DVDs, CD ROMS, target language websites, etc., featuring culturally authentic and contextual guided speaking, reading, and writing activities such as cued repetition of native speech, dictations, cued oral responses, listening comprehension, and interactive realia (culturally authentic texts). 3. Organized laboratory activities including conversation groups. 4. Fundamentals of French pronunciation: A. syllabification and rhythm B. final consonants: pronounced and unpronounced C. vowels and spelling D. the vowels /a/, /i/, and /u/ (all symbols between slashes are International Phonetic Alphabet symbols) E. the o in closed and open vowels F. the vowels /e/ and /E/ G. the vowels /œ/ and /ø/ H. the vowels /y/ and /u/ I. nasal vowels J. the unstable (mute) e K. the vowels /i/, /u/, and /y/ followed by other vowels (semi-vowels) L. the consonants /p/, /t/, and /k/ Methods of Presentation 1. 2. 3. 4. Lecture/Discussion Group Activities Laboratory Class and group discussions Assignments and Methods of Evaluating Student Progress 1. Typical Assignments A. Write a paragraph reporting in the past in a variety of contexts that focuses on the narration of a series of events such as a short report about a recent shopping trip. B. Demonstrate "ordering" skills in a restaurant skit. C. Demonstrate aural understanding of street directions by tracing examples of such directions on a map. D. Laboratory assignment: After studying nasal vowels, make a recording of the poem “Jonathan le Pélican” by Robert Desnos 2. Methods of Evaluating Student Progress A. Exams/Tests A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Exams/Tests Quizzes interviews to evaluate the four language skills in relation to material presented Student participation in class activities Homework Final Examination Recordings from the language laboratory to evaluate pronunciation skills Textbook (Typical): 1. K. Jansman, and M. A. Kassen (2014). Motifs-An Introduction to French (6th/e). Heinle Cengage Learning. Special Student Materials