VBA – A Quick Review
advertisement

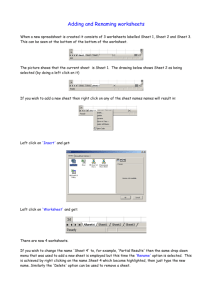
VBA – A Quick Review Your Name Goes Here A VBA module consists of one or more __________. A procedure begins and ends with the ___ and _______ statements, respectively. _______ procedures are executed at any time. _____ procedures are executed only when a designated event occurs. VBA accomplishes its tasks by manipulating _______. Objects contain other objects; for example, the workbook object contains the _________ object which in turn contains the range object. The objects are arranged in a hierarchy known as the _____ ______ _____. Other applications in Microsoft Office have their own object models. A __________ is a group of similar objects within the object model. A period is used to separate (qualify) an object within the object model. For example, Workbooks(“January.xls”).Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“Expenses”) refers to the range called ________ in the worksheet ______ in the _______ workbook. If you omit a qualifier, Excel refers to the active object; e.g., Worksheets (“Sheet1”).Range(“Expenses”) is equivalent to the preceding statement provided you had selected the _______ ________ from the collection of open workbooks. Objects have __________ that describe attributes (or settings) of the object; for example, ActiveCell.Value = 10 sets the _____ property of the __________ object. The Value property is the default property of the ActiveCell object and thus it can be omitted; i.e., ActiveCell = 10 is equivalent to the previous statement. You can also set variables to the value of a property; for example, intNumber = ActiveCell.Value stores the value of the active cell into the variable intNumber. Objects also have _______ (actions) that are performed on an object. The statement ActiveSheet.Protect applies the _______ method to the ___________ object. In similar fashion, Sheets(“Expense Summary”).Select applies the ______ method to the Expense Summary worksheet in the worksheets __________.