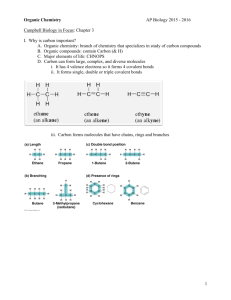
Document 11123969
advertisement
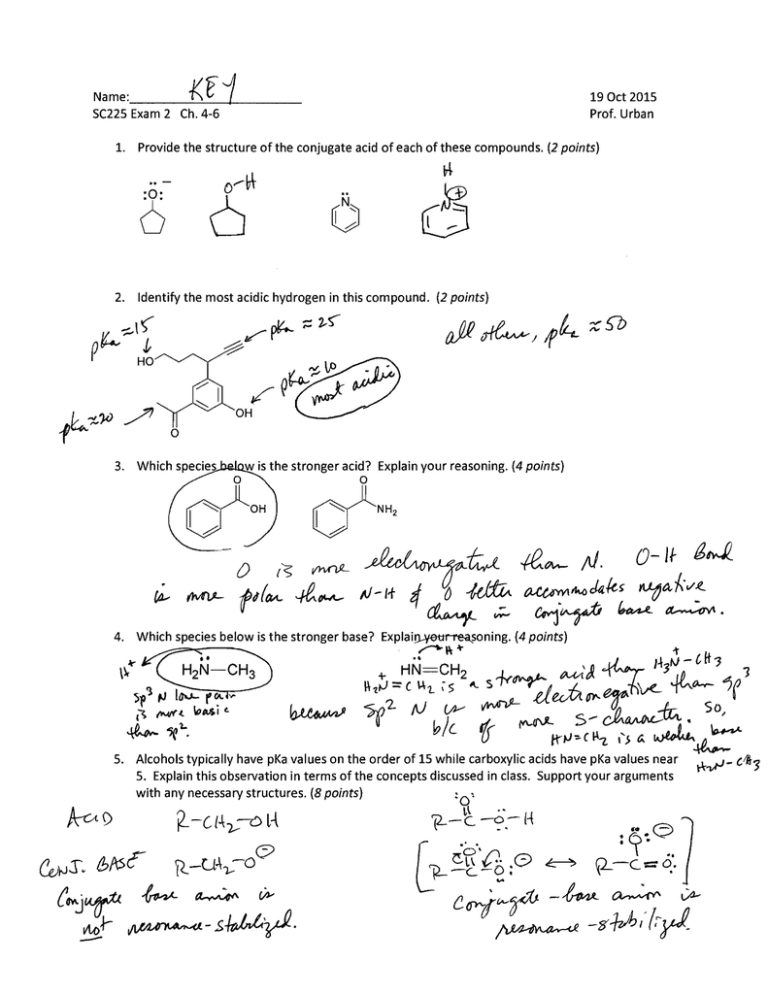
Name:_~-Kf--l--j_
19 Oct 2015
Prof. Urban
SC225 Exam 2 Ch.4-6
Provide the structure of the conjugate acid of each of these compounds. (2 points)
1.
.. ­
o
'0'
o
N
2.
Identify the most acidic hydrogen in this compound. (2 points)
3.
Which species
o
w is the stronger acid? Explain your reasoning. (4 points)
0
~OH
~NH'
~-IIf)
III
a-lf a~
{<; ~ ., ., ~ -;' av-lA,vA. 'f{A~ /\.(.
f,(/iA- 4.......... ill-If
~ -W::ft.. ~ ... ddk< ~a-kv::
~~ ~~~~.
o
i
rMV-
A
4
Which species below is the stronger base? Explai~oning. (4 points)
4.
\~...
~l:~HJJ-C~3
-~
r
,..........,,""
'>'P ~
i~ ~~
~
5.
(IV-
"If •
0\. .""
to
IoMi
_L~
+ HN=CHz
l\,ztJ = C
'1
~
5f'2
"1. ~$
tJ
vv
'fJ/c
A..
MA',}.
.,. ~ HJ~;lk1
S 'fYv- 7" AI -L
~ive.~ U eu<A P'-
't
t"--~
a.
'f\A~ 1()
,
'
s- ~~-fJ;." So,
1-t~~C "''l ,'> fA ~C
Alcohols typically have pKa values on the order of 15 while carboxylic acids have pKa values near
5. Explain this observation in terms of the concepts discussed in class. Support your arguments with any necessary structures. (8 points) c
t-\-~-
c-1t1
6.
Which species below is the stronger acid? Explain your reasoning. (4 points) -
F3C~OH H3C~OH
o
0
"O/~
II - -n.- ,t I\.(..
-r
r
..vt' OUA.. v'T
~ 7.
r: 's
t {-+e.-J-
0"'--
lJ.v
,*>0
~,¢
L:
~
-,'1(11
cf~ ~~
>H~ '6'~ +
~~
~ ~.
(.AI"
~
~
~6vr-
~
/
6 A: ¢
~ we~~ IoN~ ~,0J
a.
b.
\OJ"
~~~'-dl\_~\·I'fY.• _..A'.~
Consider the reaction acid-base reaction below. (8 pOints)
r
'0'-
~ ......
b,)--
\~
0
0 ~
~~
~(IY"
o\~
0­.L
Q
..
+
0
~~ ~J ~ 0-,,~
Use curved-arrow notation to show the movement of electrons in the reaction.
Which side of the reaction is favored at equilibrium, reactants or products? Explain your
A?~~ e..,.-:t. f
9. Provide structures for these compounds. (6 points)
(Z)-2-chloro-3-methylhex-2-ene ~f"-' U
Ou
6)
@~/
l~
3-methoxy-2-methylpentane
10. Define the following terms. (12 points)
a.
Stereoisomer
Is...........
"';+€.
A __
I-
~
u~r
c.
~
C4''''tKf.'v'1
.
~ cJ,~ Torsional Strain
11. Classify each of the labeled carbons as: primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary. (Terms may
be used multiple times or not at all.) (4 points)
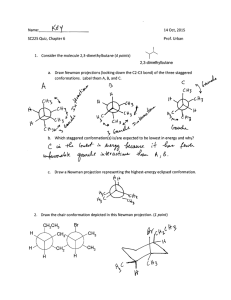
12. Provide the Newman projection for this structure when viewed down the C-C bond. (4 points)
F
0
F
:'
$.:"
H
OH
NH2 ../
.'
OH
13. Consider the stereoisomers~IOW: (12 points)
Isomer A ~
Isomer B
a. Draw the chair conformations for isomer A and explain which, if either, is lower in
energy and why.
b. Draw the chair conformations for
isomer B and explain which, if either, is lower in
energy and why.
c. Which stereoisomer is more stable, A or B? Explain your reasoning.
6
.tJ 11:­
IFf-CIt
t~
J
~
(;t.f
tJi,
tA.f)
~
J
-<
fJ-f.
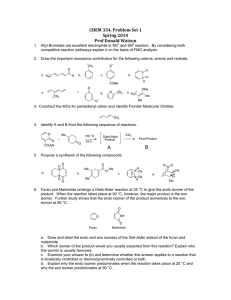
14. The axial penalty for an OH group on a cyclohexane is O. ca
e iaxia conformation of
isomer A is 1.8 kcal/mol higher in energy than the diequatorial. But, isomer B, the diaxial is
slightly lower in energy than the diequatorial. Explain this observation. (8 pOints)
J .. ' 0
OH
OH 1> t &.1;'tJ..- @ It-VI
I~
¢ Q
OH
OH A
* OM11V
A~ .\-~~ ~~l~
~~
:;;t ~1rJ.
?­
t},p_ .diflJ.v
B
~~r-t1)
MI. Q~-" 0\-\
\\'
#'Vr-G
lv1-r/~ u{ ~
e\'fI'i.' ~\~. ~
~
~
"fr'
\-\"
CI
I
I
H
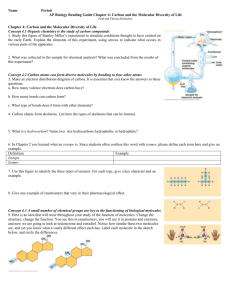
15. For l,l,2-trichloroethane:
a. Draw Newman projections of the three staggered conformations looking down the
bond and label them A, B, and C. Indicate their relative stability.
CI
I
H-C-C-H
I
\1<
B
~ ~~'
:*;
C.
U
~t~
~
A 1'-<;. ~ ~ ~ ~ 'il-~ ~ ~ Ct/eJ ('v\+ev~+il\1.>.
g ~ (a.M. ~ ~ i~ ~)u-J.- (~.-te..,~/T, b.t~ 4­
CI
in+t
fi~ ~ ~
efd.
I~~~.
b.
Draw Newman projections of the three eclipsed conformations looking down the
:r
bOn~! label them I, II and III. Ind~te ~elative stability.
::r: (.JL
\-\ .~.~.0~..P. ~f ...r
iV'<
~
~tf
e-e
I'-~.
!)J..
~~
R
CR..
.1
-KM.."7- .:.. ~ l~ ~ ~IiJ"t'- e.;;.. i etA/fS'7J
Ct/U IYvfJ:A.~ - III ~ ~ .;. ~
~ 1\0 eli ell (v(i fS\~ lAo ~"'"'+;~.
II)
I.11 ~;+
c. Sketch a plot of energy vs dihedral angle when viewed down the e-e bond.
d. Label the locations of A, B, e, and I, II, and III on your plot.
(10 points)
o
e-e
60
120
180
CI-C-C-CI dihehdral angle
240
300
360