ABSTRACT THESIS An Exploratory Research Study to Investigate the Effect of Geographical
advertisement

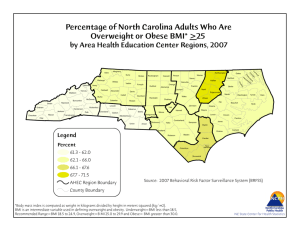
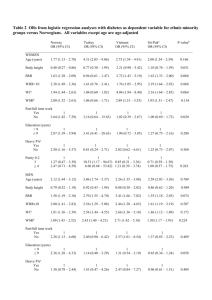
ABSTRACT THESIS: An Exploratory Research Study to Investigate the Effect of Geographical Residency (United States and China) on Structured Physical Activity Patterns and Body Mass Index of Chinese Students attending Two Midwestern Universities STUDENT: Caitlyn Zimmerman DEGREE: Master of Science in Nutrition and Dietetics COLLEGE: Applied Sciences and Technology DATE: May 2014 PAGES: 86 This research compared structured physical activity patterns to changes in body mass index (BMI) of Chinese university students. Chinese students attending Midwestern universities completed a 26-itemized, validated and reliable physical activity questionnaire. The questionnaire assessed demographics, time spent in various physical activities, BMI, and perceived barriers to exercise prior to and after residing in the U.S. for at least three months. Analysis of variance revealed that, after residing in the U.S., males had a greater increase in time spent in moderate-intensity physical activity compared to females (p < .01), while females had a greater increase in time spent in vigorous-intensity physical activity when compared to males (p < .01). Also, students 21 years of age or older were more likely to increase their time spent in moderate- and vigorous-intensity physical activities combined than those 20 years of age or younger. Lastly, change in BMI appeared to be affected by geographical region of origin (p < .05), where participants from the Eastern region of China had a greater increase in BMI than those from the Western, Northern, and Southern regions. Overall, educating Chinese university students on the importance of incorporating structured physical activities may help prevent future increases in BMI after immersion into the U.S lifestyle.