The Nervous System Poudre High School By: Ben Kirk
advertisement

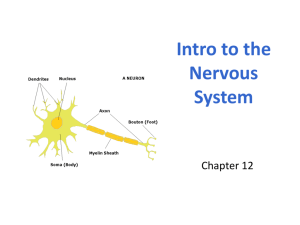
The Nervous System Poudre High School By: Ben Kirk Functions Regulation of all body function Sensory: Information reception Response: Response transmission Integrate: Integrate and interpret all body changes/stimuli Organization Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and Spinal Cord Control center for the entire nervous system Receives, processes, integrates and produces responses to all stimuli Higher Functioning (the brain primarily): intelligence, memory, thought, emotion and learning The Central Nervous System http://www.sruweb.com/~walsh/cns_pns.jpg Organization Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): All neural tissue outside the CNS Delivery of sensory information from sensory glands/organs to the CNS Transmission of motor information from the CNS to effectors glands/organs Organization Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System: Voluntary Controls voluntary muscle contractions (skeletal muscle) Autonomic Nervous System: Involuntary Involuntary movements, processes and reflexes Visceral organs, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands (heart rate, vessel diameter, digestion, etc…) Organization Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Nervous System: Expenditure of energy Fight or Flight Increased Heart Rate Parasympathetic Nervous System: Restoration and conservation of energy Rest and Digest Slows Heart Rate http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html Histology Neuroglia: Glial Cells 6 Types of glia cells Primary Function is to protect and support neurons Smaller and more numerous (5-10X) than neurons Common source of tumors (Gliomas) 40-45% of all brain tumors Histology Neurons: Conduct impulses from one part of the body to another Cell Body (Soma): Large, pronounced nucleus No myotic apparatus in cytoplasm Neuron reproduction/regeneration is compromised Dendrites: Highly branched processes extending from cell body Each neuron in the CNS has 10,000-100,000 dendrite branches. Each branch has 100,000-1million sensory inputs!!! Histology Neurons: Axon: Single thin extension that sends electrical impulses to other neurons or tissues 1mm-1meter in length Axon Terminal contains neurotransmitters that are released to trigger subsequent impulses Axon Hillock: Where all electrical impulses are summated to trigger an impulse, or not. The Neuron Histology Neuron: Myelin (myelin sheath): Multiple layered, lipid and protein sheath covering neuron axons (not all axons are myelinated) Electrically insulates axon and increases conduction speed (Ex. Leaky garden hose) Multiple Sclerosis: Autoimmune disease that breaks down the myelin sheath in the CNS. Tremors: Unregulated electrical impulses Histology Neurons: Myelin: Myelin Production Schwann cells (PNS): Myelinate a single segment of a single axon. Have limited ability to regenerate PNS neural tissue Oligodendrocyte (CNS): A single oligodendrocyte can myelinate multiple segments of multiple axons CNS neuron regeneration is very complex and relatively nonexistent. Myelination = White Unmyelinated = Gray Classification of Neurons Structural: Based on the # of processes extending from the cell body Multipolar: many dendrites and one axon Most cells of the CNS Bipolar: One dendrite and one axon Retina of eye, inner ear and nose Unipolar: Has one continuous branch with both an axon and a dendrite (cell body off to side) Dorsal root ganglia (sensory cell bodies of spinal nerves) Classification of Neurons Functional: Based on the direction of impulse propagation Sensory (Afferent): Transmit impulses from receptors in skin, muscles, sensory organs, joints, and viscera to the CNS Motor (Efferent): Transmit impulses from the CNS to peripheral effectors (muscles and glands) Interneuron (Association): Carry impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons within the CNS Make up the majority of human neurons Grouping of Neural Tissue Nerve Fiber: Any process projecting from a cell body Axon or dendrite Nerve: A group of many fibers within the PNS Not a neuron Usually contain both sensory and motor nerve fibers sciatic nerve, ulnar nerve Ganglia: Group of cell bodies and synapses within the PNS. Grouping of Neural Tissue Tract: Bundle of fibers within the CNS May run long distances up or down the spinal column or connecting parts of the brain Ascending tracts carry information upward (sensory) Descending tracts carry information downward (motor) White Matter: Group of myelinated axons from many neurons Look white due to myelination Grouping of Neural Tissue Gray Matter: Unmyelinated axons, dendrites, or cell bodies within the CNS Found covering the outer surfaces and in the deeper regions (nuclei) of the brain Compose the “horns” of the spinal cord