Introductions to Genetics Mendel and all that…

Introductions to Genetics
Mendel and all that…
Questions for you
•
•
•
In your notes, answer these ?s:
Who in your family do you most look like ?
In what ways do you NOT look like that person?
Who in your family has interests and preferences most like yours?
Who Is This??
Mrs. Hunter’s relative….
Which relative?
Yep, you guessed it…
It’s Mrs. Hunter’s…….
Grandmother!
I. Some terms
A. Genetics = study of heredity
B. Heredity = passing traits to offspring
C. Traits
1. = characteristics that parents can pass to offspring
2. Examples of traits :
Eye color
Hair color
Shape of eyebrows
What traits do you share?
3. What traits do share with your parents?
siblings?
cousins?
II. Gregor Mendel
(1822-1884)
A. Who was he?
Austrian monk
Studied the traits of pea plants
“Father” of modern genetics http://www.scienceshorts.com/gmendel.htm
B. Mendel’s Work
1. Background a. In peas, ♂ & ♀ parts are in every flower b.
Pollen = plant sperm c.
Self-pollination = flower fertilizes itself d.
Cross-pollination = flower fertilized by another flower http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?articleID=F4604E0F-E7F2-99DF-30C88C9489BD83A2
1. Background e. Peas have a lot of traits f. Can’t study them all at once g. Mendel studied one at a time http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/mendel/heredity.htm
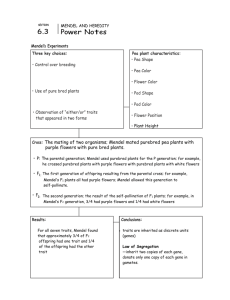
2. Mendel’s Experiments a. Mendel controlled the pea pollination b. ¿ How did he do this?
2. Mendel’s Experiments
• Removed ♂ parts from a flower
• Dusted ♀ parts with pollen from another flower
• ¿ Was this self-pollination or cross-pollination?
cross-pollination
2. Mendel’s Experiments c. First Mendel crossed: purebred purebred white flowered plant x purple flowered plant
(P1 generation) (P1 generation) all offspring were purple
(F1 generation)
2. Mendel’s Experiments d. Then, he crossed the F1 generation with itself (self-cross)
F1 X F1
3 offspring were purple
1 was white
(F2 generation)
2. Mendel’s Experiments e. What happened?
Did the traits blend?
Why were all the F1 flowers purple ?
Why did we get 3 purple
& 1 white in F2? http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/images/heade rnotes.gif
2. Mendel’s Experiments f. Vocabulary we need:
Gene = part of a chromosome that codes for a trait or a protein
(we have two genes for every trait)
Allele = a form of a gene
E.g. white or purple flowers http://www.healthsystem.virginia.edu/internet/huntdisease/geninfo.cfm
http://www.csulb.edu/~kmacd/361-6-Ch2.htm
Vocabulary
Dominant = if present, is always expressed
Recessive = both recessive alleles must be present for expression
g. Back to Mendel
Let B = purple
Let b = white
P1 x P1
P1
BB bb
F1
Bb http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k4ch10genetics.html
g. Back to Mendel
F1 x F1 (self-cross)
Bb x Bb
1 BB (purple)
2 Bb (purple)
1 bb (white)
3 purple
1 white http://uz.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetika
Questions
Which allele is dominant?
Purple flowers or white flowers?
Did the alleles blend ?
NO , flowers were either white or purple, but not in between
Why were all the F1 flowers purple ?
purple is dominant
Why did we get 3 purple & 1 white in F2?
purple is dominant
More Vocabulary
Homozygous =
2 of SAME alleles for the same trait
(BB or bb)
Heterozygous =
2 different alleles for the same trait
(Bb)
Practice
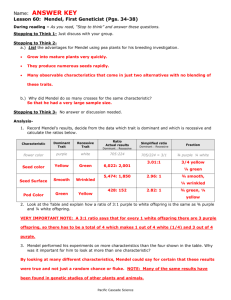
Copy the table in the Quick Lab on page 166 of the textbook into your notes
Circle your phenotype (physical appearance)
for each trait
Count the # in class with each trait
Write the numbers in the boxes
Questions
4.
5.
1.
2.
3.
How many cleft chins: no clefts?
How many dimples: no dimples
How many hair above knuckles : hairless fingers?
How many freckles: no freckles?
For which phenotypes do we know the genotype (which genes are present)?
Bibliography
6.
7.
3.
4.
5.
Graphics
1.
2.
Mendel picture http://www.scienceshorts.com/gmendel.htm
11/3/07
Garden pea picture http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?articleID=F4604E0F-E7F2-99DF-30C88C9489BD83A2
11/3/07
Pea characters http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/mendel/heredity.htm
11/3/07
F1 cross http://www.biology.iupui.edu/biocourses/N100/2k4ch10genetics.html
11/3/07
Punnett Square http://uz.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetika 11/3/07
Alleles http://www.csulb.edu/~kmacd/361-6-Ch2.htm 11/4/07
DNA, genes, chromosomes http://www.healthsystem.virginia.edu/internet/huntdisease/geninfo.cfm
11/4/07