Mendel's Genetics: Pea Plant Traits & Ratios Worksheet
advertisement
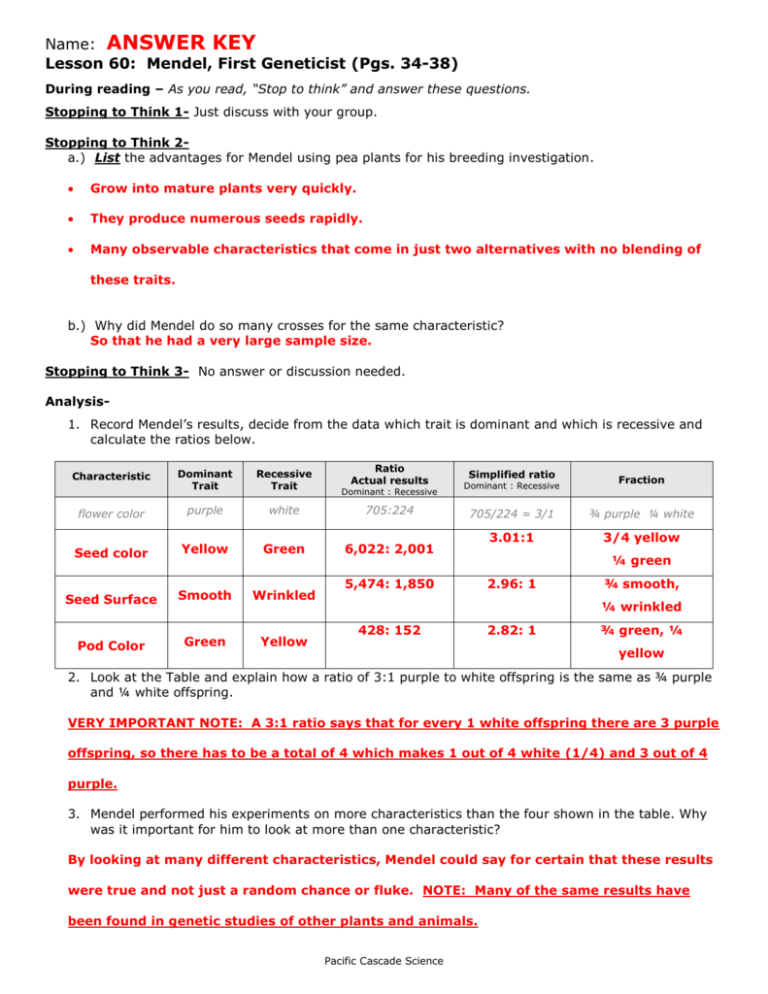
Name: ANSWER KEY Lesson 60: Mendel, First Geneticist (Pgs. 34-38) During reading – As you read, “Stop to think” and answer these questions. Stopping to Think 1- Just discuss with your group. Stopping to Think 2a.) List the advantages for Mendel using pea plants for his breeding investigation. Grow into mature plants very quickly. They produce numerous seeds rapidly. Many observable characteristics that come in just two alternatives with no blending of these traits. b.) Why did Mendel do so many crosses for the same characteristic? So that he had a very large sample size. Stopping to Think 3- No answer or discussion needed. Analysis1. Record Mendel’s results, decide from the data which trait is dominant and which is recessive and calculate the ratios below. Ratio Actual results Dominant : Recessive white 705:224 705/224 = 3/1 ¾ purple ¼ white Yellow Green 6,022: 2,001 3.01:1 3/4 yellow Seed Surface Smooth Wrinkled Pod Color Green Yellow Dominant Trait Recessive Trait flower color purple Seed color Characteristic Dominant : Recessive Simplified ratio 5,474: 1,850 Fraction ¼ green 2.96: 1 ¾ smooth, ¼ wrinkled 428: 152 2.82: 1 ¾ green, ¼ yellow 2. Look at the Table and explain how a ratio of 3:1 purple to white offspring is the same as ¾ purple and ¼ white offspring. VERY IMPORTANT NOTE: A 3:1 ratio says that for every 1 white offspring there are 3 purple offspring, so there has to be a total of 4 which makes 1 out of 4 white (1/4) and 3 out of 4 purple. 3. Mendel performed his experiments on more characteristics than the four shown in the table. Why was it important for him to look at more than one characteristic? By looking at many different characteristics, Mendel could say for certain that these results were true and not just a random chance or fluke. NOTE: Many of the same results have been found in genetic studies of other plants and animals. Pacific Cascade Science