Population Genetics Review Problems
advertisement

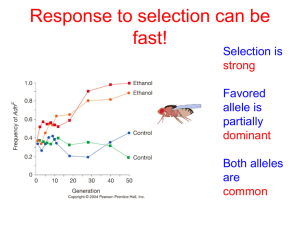
Population Genetics Review Problems 1. Albinism is a recessive trait. 1 in 4,000 individuals are affected. a. What percentage of individuals is affected? b. What is the frequency of the albino allele? c. What is the frequency of normal allele? d. What is the frequency of the carriers for albinism? e. How many individuals in this population are homozygous dominant? 2. 27,000 males in Colorado Springs (population 600,000) suffer from X-linked red-green color blindness. How many color blind females would you expect in this town? (Assume that the population of Colorado Springs is 50% male and 50% female) 3. The frequency of the R allele for red color in snapdragons is 85%. (Reminder: Snapdragons exhibit incomplete dominance. RR - red, Rr - pink, rr – white) a. How many flowers will be white out of 5,000? pink? red? b. I have a mixed bag of seeds and need to raise 3,000 white snapdragons for summer weddings. i. How many seeds should I plant? ii. How many pink flowers will I have to sell? iii. How many red flowers will I have to sell? 4. In a population of elk, consisting of 4,000 individuals, the frequency q of a recessive allele controlling atypical antlers is 0.35. 300 elk from a different population B, where the frequency qm of the same allele is 0.25, migrate over a mountain pass and join population A. a. What is the q? b. What will be the new frequency of q in population A? 5. Elk that are heterozygous for antler shape are only partially atypical. After one generation a wildlife biologist finds that 45% of the elk are partially atypical. He suspects that inbreeding is the cause and calculates the inbreeding coefficient for the new population. What is the inbreeding coefficient? Is inbreeding occurring in the new population?