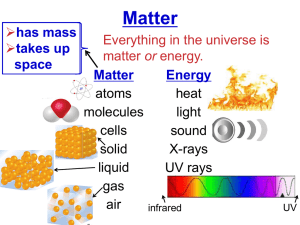
REVIEW!! # Protons = Atomic # Every element has specific physical properties
advertisement

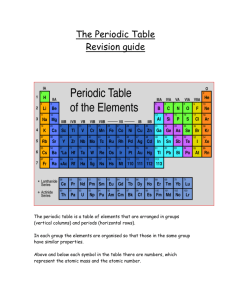
REVIEW!! 50 26 Fe 3 Sn Li Every element has specific physical properties created from the: # Protons = Atomic # The number of ELECTRON shells & the number of VALENCE electrons differ for each element. The Updateable Periodic Table Metal Nonmetal Metalloid Metals Nonmetals Good Conductors Poor Conductors Shiny Dull Malleable Brittle Opaque May be transparent Ductile Brittle All Solid (except 4) Solids, Liquids & Gases Metals: Malleable = bend without breaking Nickel can be hammered into thin sheets, making it malleable Ductile = can be made into wires Alloy = A metal composed of more than one element Examples: Brass Cu + Zn Sterling Silver Ag + Cu Steel Fe (97%), Mg + C Bronze Cu + Sn Tooth Filling Ag + Hg 85% of the elements are metal 75% Earth’s crust & atmosphere are nonmetals!! Liquid Nitrogen Metalloids = elements (6) that have both metal & nonmetal characteristics (semiconductors). (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te) Boron Rod Your turn!! Color in the metals, nonmetals & metalloids on the note sheet! Elements are organized into Groups (columns) & Periods (rows). Mendeleev Developed periodic table based on trends & characteristics Increase atomic number in horizontal rows = PERIODS Elements with similar properties are lined up in columns = GROUPS Common Groups Names 1.Alkali Metals • Low Density & Melting Point • Good Conductors Li • React violently with water • Soft – can be cut with knife Na K Rb Common Group Names 2.Alkali-Earth Metals • Less reactive with water than alkali • Harder than alkali Common Group Names 3.Boron Family Boron can be used to create a distinctive green color in fireworks. Boron open pit, Kern Co, California, USA. Common Group Names 4.Carbon Family Common Group Names 5.Nitrogen Family Common Group Names 6.Oxygen Family Common Group Names 7.Halogens • All nonmetals • Form various salts Common Group Names 8.Noble Gases • Extremely unreactive • Tend not to combine with other elements