Plant Structure & Function: Tissue Systems Explained
advertisement

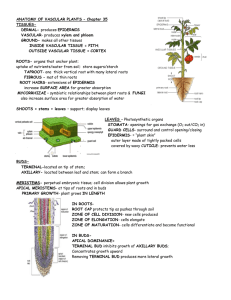
1. 2. 3. 4. Review What are the three main tissue systems of plants Compare and Contrast How do the three main functions of a plant’s tissue differ Form and Function How might the presence of meristems explain the ability of plants to regenerate from cuttings Infer With your prior knowledge of the circulatory system, write a paragraph comparing and contrasting the structure and function of the vascular system of a plant to the human circulatory system CH 23 PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 23.1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. Roots Anchor plant in ground Help prevent erosion Absorb water and nutrients and transport to rest of plant Store food Hold plant upright. Stems Support system for the plant body Transport system that carries nutrients Defensive system to protect against predators and disease Produces leaves and flowers. Leaves Main photosynthetic organs Regulates water by controlling air exchange. Plant Tissue Systems Three main tissue systems: Dermal Vascular Ground. Dermal Tissue Protective outer covering of a plant Epidermis Single layer of cells that makes up the dermal tissue May have tiny hair like projections on leaves and roots. Vascular Tissue Supports the plant body Transports water and nutrients Xylem Phloem Consist of long, slender cells that connect almost like sections of pipe. Xylem Tracheids Xylem cells Leave cell walls made of lignin when they die Openings allow water movement from cell to cell. Xylem Vessel elements Wider than tracheids and are arranged end After cell dies, cell walls allow water to move freely. Phloem Alive at maturity Transports sugar throughout plant Sieve tube elements Arranged end to end with ends having many small holes Lose nuclei and organelles as they mature Kept alive by companion cells. Phloem Companion cells Supports sieve tube element. Ground Tissue Produces and stores sugars Contributes to physical support of plant Neither dermal nor vascular Three types of ground tissue: Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma. Parenchyma Main type of ground tissue Have thin cell walls Contain many chloroplasts in leaves. Collenchyma Strong, flexible cell walls that help support plant organs Middle cell wall thickness. Sclerenchyma Extremely thick, rigid cell walls Makes ground tissue such as seed coats tough and strong. Meristems Regions of unspecialized cells in which mitosis produces new cells Found in tips of stems and roots. Apical Meristems Meristem at tip of a stem or root Cells divide rapidly Increases plants length. Floral Meristems Produces flowers specialized cells Develop from apical meristem.