Lecture 20: Multiple Comparisons, Residuals Summary
advertisement

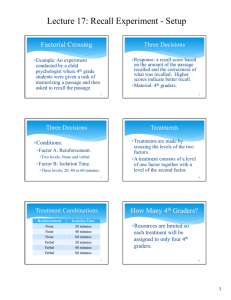
Lecture 20: Multiple Comparisons, Residuals Summary Summary Response: Recall score Conditions: Reinforcement (None, Verbal) and Isolation Time (20, 40 or 60 minutes) Experimental Units: 24 fourth graders. Treatments are made up of levels of two factors; Reinforcement and Isolation Time. Treatments are assigned randomly to the fourth grade students. 1 Analysis 2 Results There are statistically significant effects of some treatments. Because of the factorial structure look at individual factors and their interaction. Informal: Look at averages and plots. Formal: Analysis of variance. 3 Factors 4 Factors Reinforcement is a statistically significant factor. Isolation time is a statistically significant factor. Verbal reinforcement produces a higher average recall (26) than no reinforcement (22). 40 minutes produces a statistically higher mean recall (28) than either 20 minutes (21.5) or 60 minutes (22.5) 5 6 1 Lecture 20: Multiple Comparisons, Residuals Recommendation? Interaction Use Verbal Reinforcement and 40 minutes of Isolation Time. This recommendation ignores the statistically significant interaction. Because the interaction between Reinforcement and Isolation Time is statistically significant, the effect of Isolation Time on Recall is different for different levels of Reinforcement. 7 Best Combination? 8 Best Combination? The combination that gave the highest mean Recall in the experiment was Verbal Reinforcement and 60 minutes of Isolation Time. In order for a combination to be best it must be statistically different from other combinations. 9 Multiple Comparisons 10 Multiple Comparisons Tukey HSD There are (6*5)/2=15 pairs of comparisons between treatment means that can be made. Use Tukey’s HSD to avoid a high probability of false positives (declaring treatments to be different when they are really the same). 1 1 3.17803 13.0 1 4 3.17803 2.54951 11 1 4 8.1 12 2 Lecture 20: Multiple Comparisons, Residuals Multiple Comparisons Level V, 60 N, 40 V, 40 N, 20 V, 20 N, 60 Mean 31.5 A 30.5 A 25.5 A B 22.0 B 21.0 B C 13.5 C Multiple Comparisons There is no one treatment that is clearly better than all the others. Remember that we have only 4 experimental units for each treatment so we can only detect very large differences in treatment means. Levels not connected by the same letter are significantly different 13 14 Residuals Residuals vs Factors 7.5 7.5 The analysis of residuals proceeds much in the same way as we have done before. 5 Residual Recall Residual Recall 5 2.5 0 -2.5 2.5 0 -2.5 -5 -5 -7.5 -7.5 N V Reinforce 20 40 15 Interpretation 60 IsoTime 16 Fisher Conditions The variation for either level or Reinforcement is about the same. The variation for all three levels of Isolation Time are about the same. The Fisher Condition of equal error standard deviations is satisfied. 17 18 3 3 .99 2 .95 .90 Distribution of Residuals .75 .50 1 0 .25 .10 .05 .01 Look at the histogram, box plot and Normal Quantile plot to assess whether the residuals could have come from a Normal distribution. Normal Quantile Plot Lecture 20: Multiple Comparisons, Residuals -1 -2 -3 4 Count 6 2 19 Description -7.5 -5 -2.5 0 2.5 5 7.5 20 Description The histogram is slightly skewed to the right with a mound between –2.5 and 0. The box plot looks fairly symmetric with the mean and median being equal. The Normal quantile plot has residuals following the diagonal (Normal model) line. 21 22 Fisher Conditions Comment Although not perfect, the residuals could have come from a Normal distribution. The Fisher Condition of Normally distributed errors is satisfied. Even if the Fisher Conditions were not satisfied, it would not affect the conclusions about the impact of Reinforcement and Isolation Time on Recall. 23 24 4