Designing Enterprise Decisions A model of a real company, ADI Research goals
advertisement
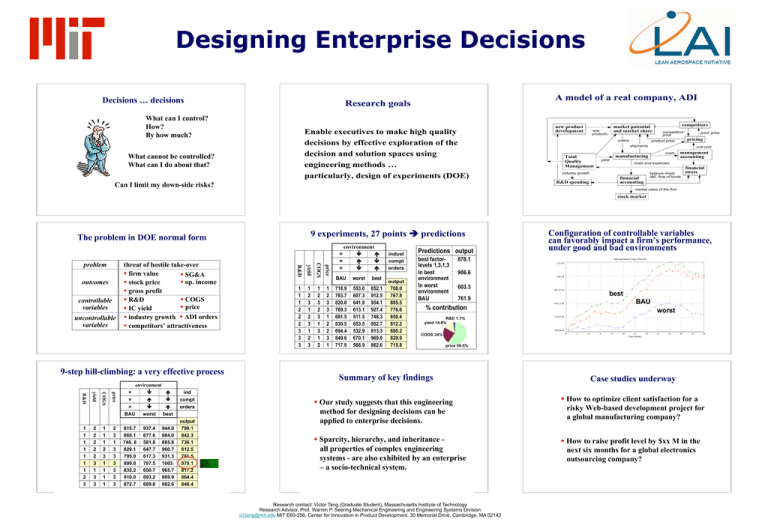
Designing Enterprise Decisions Decisions … decisions A model of a real company, ADI Research goals What can I control? How? By how much? Enable executives to make high quality decisions by effective exploration of the decision and solution spaces using engineering methods … particularly, design of experiments (DOE) What cannot be controlled? What can I do about that? Can I limit my down-side risks? new product development competitors market potential and market share new products orders competitors’ price prod. price pricing product price shipments Total Quality Management unit cost manufacturing yield management accounting costs costs and expenses industry growth balance sheet, I&E, flow of funds financial accounting R&D spending financial stress market value of the firm stock market 9 experiments, 27 points predictions The problem in DOE normal form 9-step hill-climbing: a very effective process 1 1 1 2 3 1 1 1 1 price 2 2 2 2 2 3 1 3 3 COGS yield R&D 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 2 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 environment = = = BAU worst best 815.7 865.1 740. 8 829.1 795.9 899.8 835.2 910.0 872.7 937.4 677.6 581.8 647.7 617.3 707.5 650.7 693.2 689.8 944.0 984.0 885.8 960.7 931.3 1003. 965.7 989.9 982.6 ind compt orders output 799.1 842.3 736.1 812.5 781.5 870.1 817.2 864.4 848.4 1 2 3 2 3 1 3 1 2 price uncontrollable variables 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 COGS controllable variables 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 yield outcomes threat of hostile take-over firm value SG&A op. income stock price gross profit COGS R&D price IC yield industry growth ADI orders competitors’ attractiveness R&D problem 1 2 3 3 1 2 2 3 1 environment = = = BAU 718.9 783.7 820.6 789.3 691.5 830.5 694.4 849.6 717.9 worst 553.0 607.3 641.9 613.1 511.5 653.5 532.9 670.1 566.9 best 852.1 912.5 954.1 927.4 748.3 952.7 813.3 969.9 862.6 indust compt orders output 708.0 767.8 805.5 776.6 650.4 812.2 680.2 829.9 715.8 Predictions output best factorlevels 1,3,1,3 In best environment In worst environment BAU 878.1 Configuration of controllable variables can favorably impact a firm’s performance, under good and bad environments Indicated Market Value of the firm 1.215 B 3 3 906.6 3 1.091 B R&D 1.7% yield 14.8% 967.22 M 3 3 3 3 719.03 M 2 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 3 3 2 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 worst 1 1 1 1 source: experiment L27 including full factorial 1 3 2 2 1 1 BAU 2 2 3 2 2 2 0 Summary of key findings 2 2 2 3 3 3 843.13 M 594.94 M price 59.5% 3 best 1 COGS 24% 2 2 3 761.9 % contribution 3 2 2 3 603.3 2 3 3 3 3 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 6 Indicated Market Value of the firm : 110L81-61 Indicated Market Value of the firm : 110L81-41 Indicated Market Value of the firm : 110L81-21 1 1 1 8 1 10 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 12 Time (Month) 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 14 1 2 3 16 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 18 1 2 3 1 2 3 20 1 2 3 1 2 3 22 1 2 3 1 2 3 24 1 2 3 1 2 3 3 Case studies underway Our study suggests that this engineering method for designing decisions can be applied to enterprise decisions. How to optimize client satisfaction for a risky Web-based development project for a global manufacturing company? Sparcity, hierarchy, and inheritance all properties of complex engineering systems - are also exhibited by an enterprise – a socio-technical system. How to raise profit level by $xx M in the next six months for a global electronics outsourcing company? Research contact: Victor Tang (Graduate Student), Massachusetts Institute of Technology Research Advisor, Prof. Warren P. Seering Mechanical Engineering and Engineering Systems Division victang@mit.edu MIT E60-256, Center for Innovation in Product Development, 30 Memorial Drive, Cambridge, MA 02142