P 2a a Rigid
advertisement
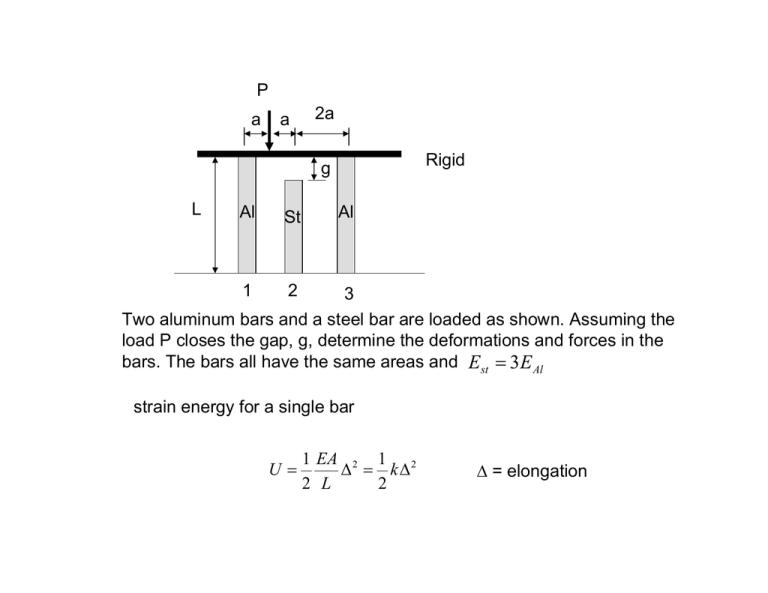
P a a 2a Rigid g L Al St 1 2 Al 3 Two aluminum bars and a steel bar are loaded as shown. Assuming the load P closes the gap, g, determine the deformations and forces in the bars. The bars all have the same areas and Est = 3E Al strain energy for a single bar U= 1 EA 2 1 2 ∆ = k∆ 2 L 2 ∆ = elongation 1 1 1 k Al ∆12 + k St ∆ 22 + k Al ∆ 32 2 2 2 1 3 1 = k Al ∆12 + k Al ∆ 22 + k Al ∆ 32 2 2 2 U= total strain energy 2a 2a x ∆1 ∆ g ∆3 ∆2 ∆ − ∆1 ∆ 3 − ∆1 = x 4a ∆= At the steel bar x ( ∆ 3 − ∆1 ) + ∆1 4 x = 2a ∆= ∆1 + ∆ 3 = ∆2 + g 2 U ( ∆1 , ∆ 3 ) = At the load 1 3 ⎡ ∆ + ∆3 ⎤ 1 k Al ∆12 + k Al ⎢ 1 − g ⎥ + k Al ∆ 32 2 2 ⎣ 2 ⎦ 2 2 x=a ∆ = ∆P = 3∆1 ∆ 3 + 4 4 Principle of virtual work δU = δW ∂∆ P ∂∆ P ∂U ∂U δ∆1 + δ∆ 3 = Pδ∆ P = P δ∆1 + P δ∆ 3 ∂∆1 ∂∆ 3 ∂∆1 ∂∆ 3 for all δ∆1 , δ∆ 3 ∂∆ ∂U =P P ∂∆1 ∂∆1 ∂∆ ∂U =P P ∂∆ 3 ∂∆ 3 U ( ∆1 , ∆ 3 ) = 1 3 ⎡ ∆ + ∆3 ⎤ 1 k Al ∆12 + k Al ⎢ 1 − g ⎥ + k Al ∆ 32 2 2 ⎣ 2 ⎦ 2 2 ∂∆ ∂U =P P ∂∆1 ∂∆1 ∆ = ∆P = 3∆1 ∆ 3 + 4 4 ∂∆ ∂U =P P ∂∆ 3 ∂∆ 3 ⎛ ∆1 + ∆ 3 ⎞ ⎛ 1 ⎞ 3P − g ⎟⎜ ⎟ = k Al ∆1 + 3k Al ⎜ ⎝ 2 ⎠⎝ 2 ⎠ 4 ⎛ ∆1 + ∆ 3 ⎞⎛ 1 ⎞ P − g ⎟⎜ ⎟ = k Al ∆ 3 + 3k Al ⎜ ⎝ 2 ⎠⎝ 2 ⎠ 4 or, equivalently 7 ∆1 3∆ 3 3P 3 g + = + 4 4 4k Al 2 3∆1 7 ∆ 3 3g P + = + 4 4 4k Al 2 Solving, we find 0.45 P ∆1 = + 0.6 g k Al ∆3 = −0.05 P + 0.6 g k Al (Compressional) forces in the bars are P1 = k Al ∆1 = 0.45 P + 0.6k Al g ⎡ ∆1 + ∆ 3 ⎤ P2 = 3k Al ⎢ − g ⎥ = 0.6 P − 1.2k Al g ⎣ 2 ⎦ P3 = k Al ∆ 3 = −0.05 P + 0.6k Al g Note: for P2 > 0 we need P > 2k Al g Otherwise the gap will not be closed