aP STATISTICS BAR GRAPH PROJ_
advertisement

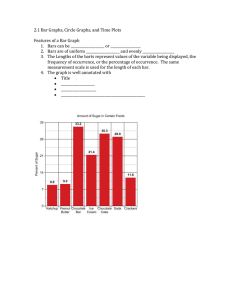
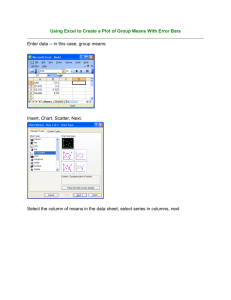
By: Dorian C. Hardin-Hebert Michel’le C. Simpson Kevinique M. Walker-Smith A graph in which horizontal or vertical bars represents data It’s used to visually display frequencies or percentages and can be used to compare data. Changing Scale- Whenever you use a change in scale in a graphic, warn the viewer by using a squiggle On the changed axis. Sometimes, if a single bar is usually long, the bar length is compressed with a squiggle in the bar itself. Pareto Chart- is a bar graph in which the bar height represents frequency of an event. In addition, the bars are arranged from left to right according to decreasing height. 1. Bars can be vertical or horizontal. 2. Bars are of uniform width and uniformly spaced. 3. The lengths of the bars represent values of the variable being displayed, the frequency of occurrence, or the percentage of occurrence. The same measurement scale is used for the length of each bar. 4. The graph is well annotated with title,, labels for each bar, and vertical scale or actual value for the length of each bar. 7 6 5 Mexican Chinese Italian Seafood 4 3 2 1 0 First Pick First Pick • We conducted a quick and easy survey to gather information from our class of 13 students and 1 teacher. • We picked four popular food groups and asked each person to pick a first favorite pick and a second favorite pick. • Then, transferred the information to the format of a bar graph!!! 7 6 5 4 Mexican Chinese Italian Seafood 3 2 1 0 First Pick Second Pick •How many more students prefer seafood and Chinese food as a first pick than a second pick. S+C=9 2 +7=9 S+C=8 6+2=8 9-8= 1 person •Understandable Statistics by Houghton Mifflin. •AP Statistics 6th Block Class