Heat of a Reaction Bond Dissociation Energy Reaction Energy + energy
advertisement
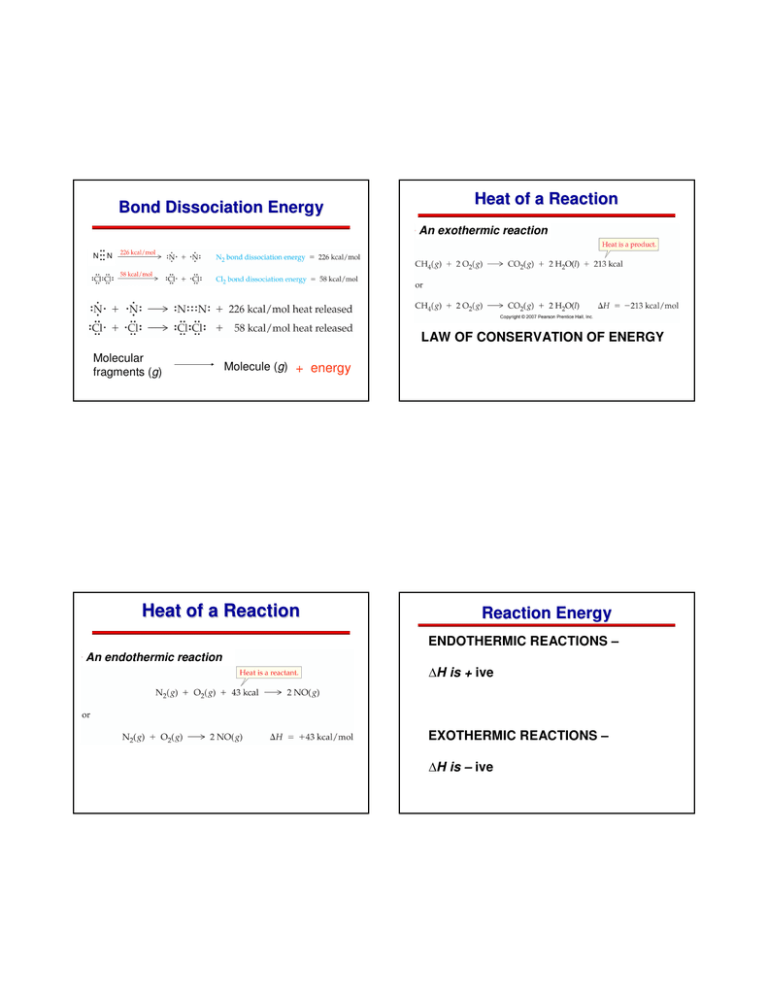
Bond Dissociation Energy Heat of a Reaction An exothermic reaction … … N N Bond energy LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Molecular fragments (g) Molecule (g) + energy Heat of a Reaction Reaction Energy ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS – An endothermic reaction ∆H is + ive EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS – ∆H is – ive So What is Going On? How to Calculate Heat of Reaction? A large bond dissociation energy corresponds to a strong covalent bond. Redistribution of ‘bonds’ means redistribution of energies How to Calculate Heat of Reaction? As you can see different covalent bonds have different amounts of energy needed to break apart. A large dissociation energy (see N triple N) is a strong bond. A low dissociation energy (see N-O) is a weak bond. How to Calculate Heat of Reaction? Enthalpy: A measure of the heat content of a substance at constant pressure you cannot measure the actual enthalpy of a substance you can measure an enthalpy CHANGE written as the symbol ∆H , “delta H ” Enthalpy change (∆H) = Enthalpy of products - Enthalpy of reactants Energy required = 610 kJ for 1 mol of C=C bonds + 436 kJ for 1 mol of H―H bond = 1046 kJ/mol Energy evolevd = 346 kJ for C―C bond + 2 mol Χ 413 kJ for C―H bonds = 1172 kJ/mol ∆H = 1046 kJ/mol – 1172 kJ/mol = -126 kJ/mol